Shixiong Zhang
LoRA-Whisper: Parameter-Efficient and Extensible Multilingual ASR
Jun 07, 2024



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed significant progress in multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR), driven by the emergence of end-to-end (E2E) models and the scaling of multilingual datasets. Despite that, two main challenges persist in multilingual ASR: language interference and the incorporation of new languages without degrading the performance of the existing ones. This paper proposes LoRA-Whisper, which incorporates LoRA matrix into Whisper for multilingual ASR, effectively mitigating language interference. Furthermore, by leveraging LoRA and the similarities between languages, we can achieve better performance on new languages while upholding consistent performance on original ones. Experiments on a real-world task across eight languages demonstrate that our proposed LoRA-Whisper yields a relative gain of 18.5% and 23.0% over the baseline system for multilingual ASR and language expansion respectively.
SECap: Speech Emotion Captioning with Large Language Model
Dec 23, 2023



Abstract:Speech emotions are crucial in human communication and are extensively used in fields like speech synthesis and natural language understanding. Most prior studies, such as speech emotion recognition, have categorized speech emotions into a fixed set of classes. Yet, emotions expressed in human speech are often complex, and categorizing them into predefined groups can be insufficient to adequately represent speech emotions. On the contrary, describing speech emotions directly by means of natural language may be a more effective approach. Regrettably, there are not many studies available that have focused on this direction. Therefore, this paper proposes a speech emotion captioning framework named SECap, aiming at effectively describing speech emotions using natural language. Owing to the impressive capabilities of large language models in language comprehension and text generation, SECap employs LLaMA as the text decoder to allow the production of coherent speech emotion captions. In addition, SECap leverages HuBERT as the audio encoder to extract general speech features and Q-Former as the Bridge-Net to provide LLaMA with emotion-related speech features. To accomplish this, Q-Former utilizes mutual information learning to disentangle emotion-related speech features and speech contents, while implementing contrastive learning to extract more emotion-related speech features. The results of objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate that: 1) the SECap framework outperforms the HTSAT-BART baseline in all objective evaluations; 2) SECap can generate high-quality speech emotion captions that attain performance on par with human annotators in subjective mean opinion score tests.
Survey on Controlable Image Synthesis with Deep Learning
Jul 18, 2023Abstract:Image synthesis has attracted emerging research interests in academic and industry communities. Deep learning technologies especially the generative models greatly inspired controllable image synthesis approaches and applications, which aim to generate particular visual contents with latent prompts. In order to further investigate low-level controllable image synthesis problem which is crucial for fine image rendering and editing tasks, we present a survey of some recent works on 3D controllable image synthesis using deep learning. We first introduce the datasets and evaluation indicators for 3D controllable image synthesis. Then, we review the state-of-the-art research for geometrically controllable image synthesis in two aspects: 1) Viewpoint/pose-controllable image synthesis; 2) Structure/shape-controllable image synthesis. Furthermore, the photometrically controllable image synthesis approaches are also reviewed for 3D re-lighting researches. While the emphasis is on 3D controllable image synthesis algorithms, the related applications, products and resources are also briefly summarized for practitioners.
MetricNet: Towards Improved Modeling For Non-Intrusive Speech Quality Assessment
Apr 02, 2021

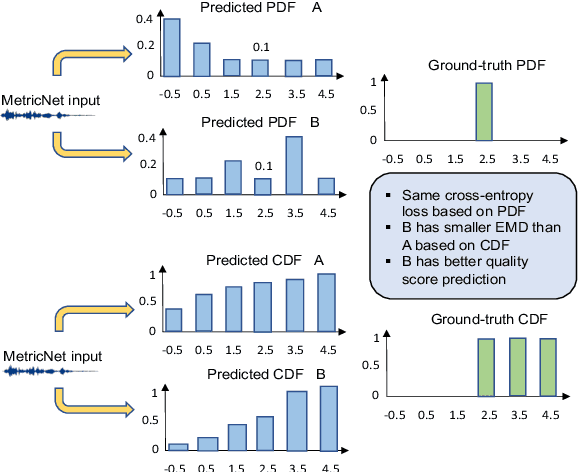
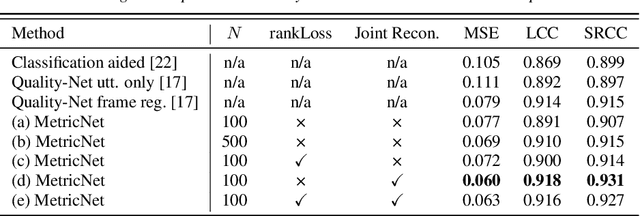
Abstract:The objective speech quality assessment is usually conducted by comparing received speech signal with its clean reference, while human beings are capable of evaluating the speech quality without any reference, such as in the mean opinion score (MOS) tests. Non-intrusive speech quality assessment has attracted much attention recently due to the lack of access to clean reference signals for objective evaluations in real scenarios. In this paper, we propose a novel non-intrusive speech quality measurement model, MetricNet, which leverages label distribution learning and joint speech reconstruction learning to achieve significantly improved performance compared to the existing non-intrusive speech quality measurement models. We demonstrate that the proposed approach yields promisingly high correlation to the intrusive objective evaluation of speech quality on clean, noisy and processed speech data.
Review of Single-cell RNA-seq Data Clustering for Cell Type Identification and Characterization
Jan 03, 2020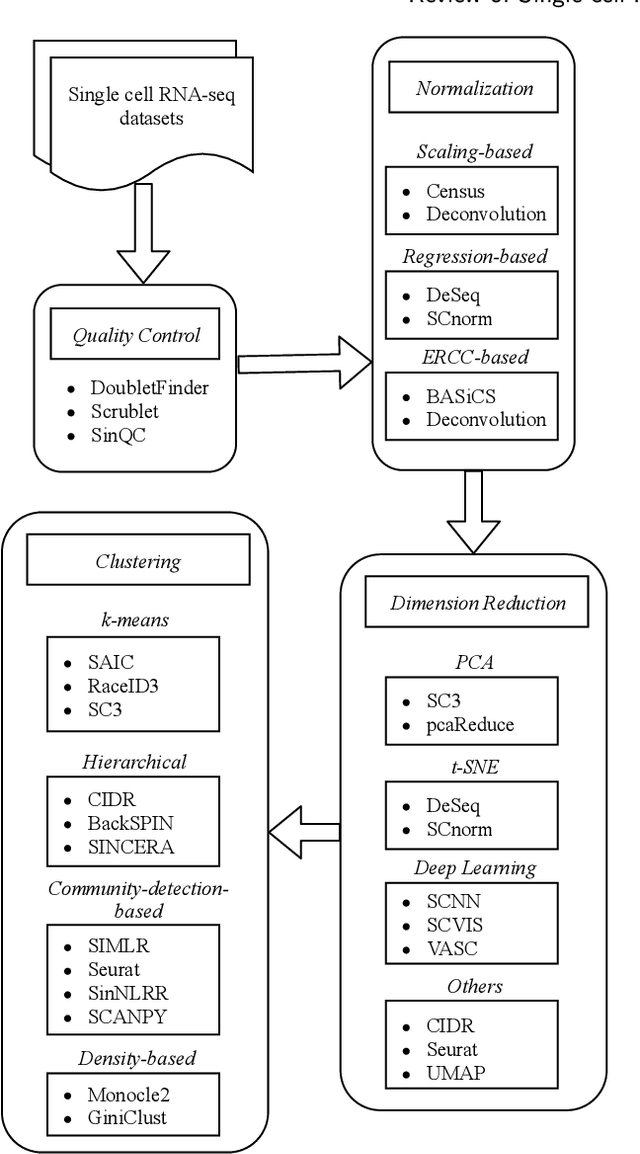
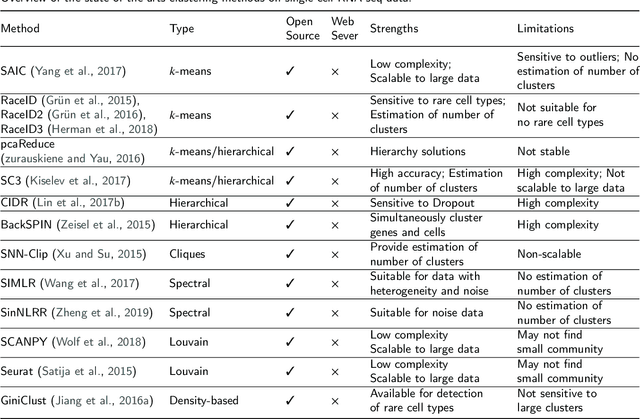
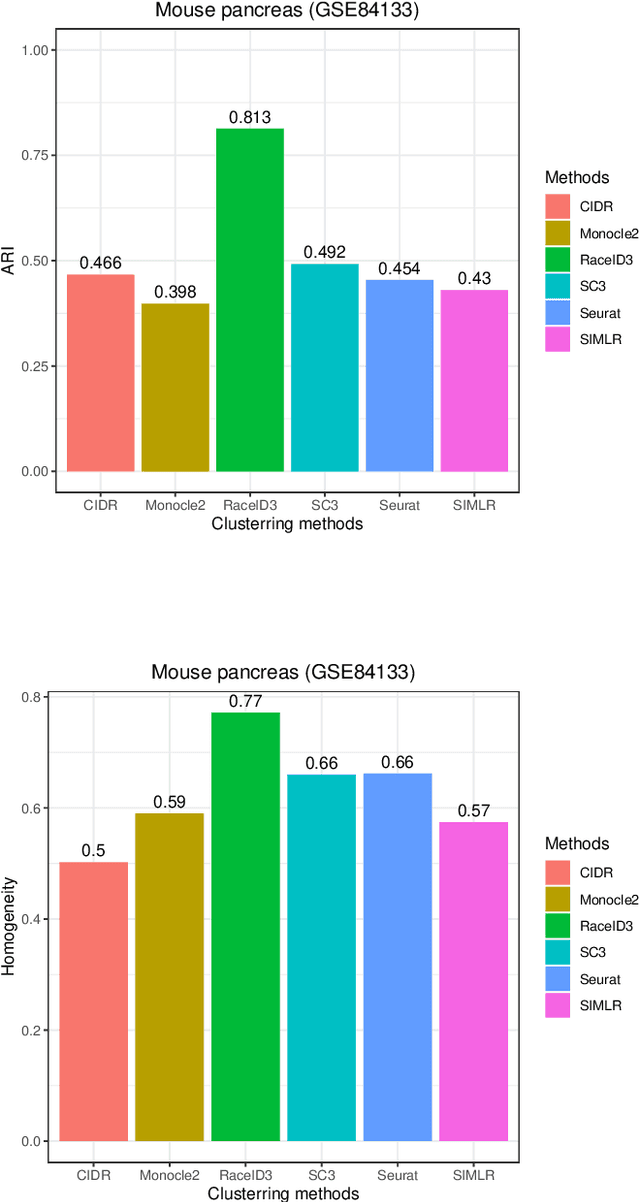
Abstract:In recent years, the advances in single-cell RNA-seq techniques have enabled us to perform large-scale transcriptomic profiling at single-cell resolution in a high-throughput manner. Unsupervised learning such as data clustering has become the central component to identify and characterize novel cell types and gene expression patterns. In this study, we review the existing single-cell RNA-seq data clustering methods with critical insights into the related advantages and limitations. In addition, we also review the upstream single-cell RNA-seq data processing techniques such as quality control, normalization, and dimension reduction. We conduct performance comparison experiments to evaluate several popular single-cell RNA-seq clustering approaches on two single-cell transcriptomic datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge