Qin Lei
Latent Distribution Decoupling: A Probabilistic Framework for Uncertainty-Aware Multimodal Emotion Recognition
Feb 19, 2025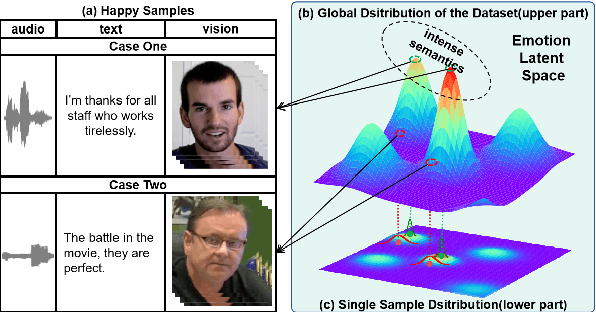
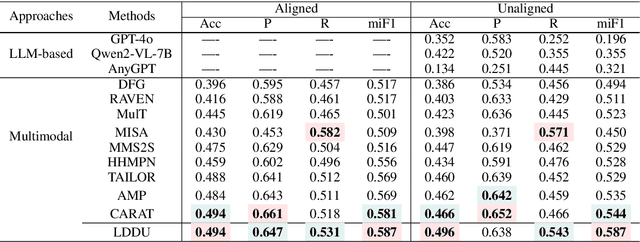
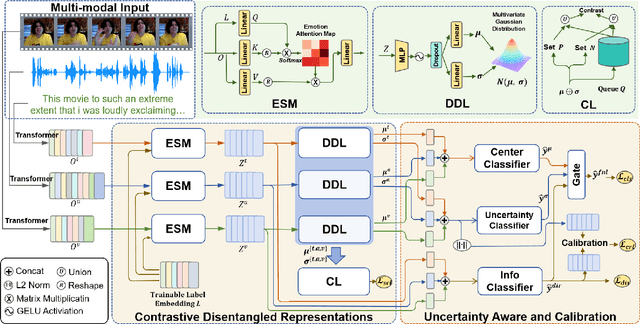
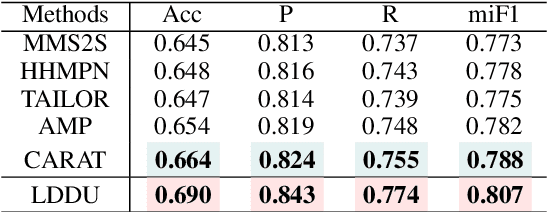
Abstract:Multimodal multi-label emotion recognition (MMER) aims to identify the concurrent presence of multiple emotions in multimodal data. Existing studies primarily focus on improving fusion strategies and modeling modality-to-label dependencies. However, they often overlook the impact of \textbf{aleatoric uncertainty}, which is the inherent noise in the multimodal data and hinders the effectiveness of modality fusion by introducing ambiguity into feature representations. To address this issue and effectively model aleatoric uncertainty, this paper proposes Latent emotional Distribution Decomposition with Uncertainty perception (LDDU) framework from a novel perspective of latent emotional space probabilistic modeling. Specifically, we introduce a contrastive disentangled distribution mechanism within the emotion space to model the multimodal data, allowing for the extraction of semantic features and uncertainty. Furthermore, we design an uncertainty-aware fusion multimodal method that accounts for the dispersed distribution of uncertainty and integrates distribution information. Experimental results show that LDDU achieves state-of-the-art performance on the CMU-MOSEI and M$^3$ED datasets, highlighting the importance of uncertainty modeling in MMER. Code is available at https://github.com/201983290498/lddu\_mmer.git.
Enriching Information and Preserving Semantic Consistency in Expanding Curvilinear Object Segmentation Datasets
Jul 11, 2024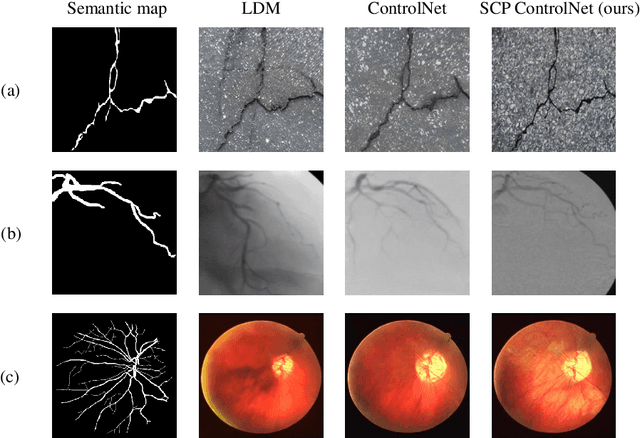
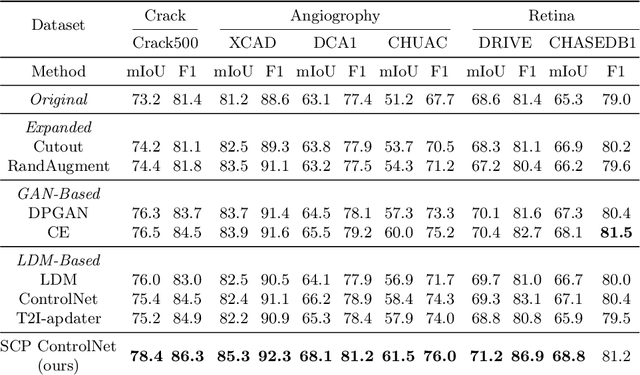

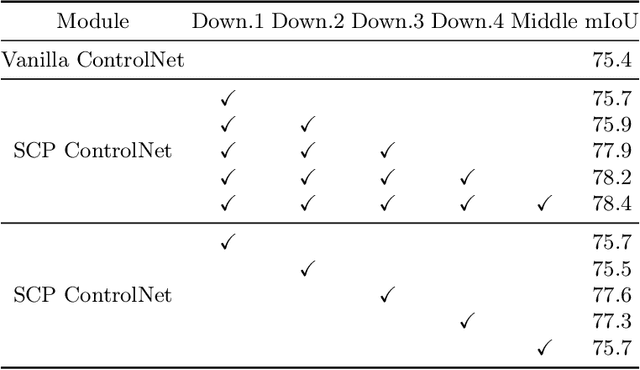
Abstract:Curvilinear object segmentation plays a crucial role across various applications, yet datasets in this domain often suffer from small scale due to the high costs associated with data acquisition and annotation. To address these challenges, this paper introduces a novel approach for expanding curvilinear object segmentation datasets, focusing on enhancing the informativeness of generated data and the consistency between semantic maps and generated images. Our method enriches synthetic data informativeness by generating curvilinear objects through their multiple textual features. By combining textual features from each sample in original dataset, we obtain synthetic images that beyond the original dataset's distribution. This initiative necessitated the creation of the Curvilinear Object Segmentation based on Text Generation (COSTG) dataset. Designed to surpass the limitations of conventional datasets, COSTG incorporates not only standard semantic maps but also some textual descriptions of curvilinear object features. To ensure consistency between synthetic semantic maps and images, we introduce the Semantic Consistency Preserving ControlNet (SCP ControlNet). This involves an adaptation of ControlNet with Spatially-Adaptive Normalization (SPADE), allowing it to preserve semantic information that would typically be washed away in normalization layers. This modification facilitates more accurate semantic image synthesis. Experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of our approach across three types of curvilinear objects (angiography, crack and retina) and six public datasets (CHUAC, XCAD, DCA1, DRIVE, CHASEDB1 and Crack500). The synthetic data generated by our method not only expand the dataset, but also effectively improves the performance of other curvilinear object segmentation models. Source code and dataset are available at \url{https://github.com/tanlei0/COSTG}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge