Haoji Zhang
ChatUMM: Robust Context Tracking for Conversational Interleaved Generation
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Unified multimodal models (UMMs) have achieved remarkable progress yet remain constrained by a single-turn interaction paradigm, effectively functioning as solvers for independent requests rather than assistants in continuous dialogue. To bridge this gap, we present ChatUMM. As a conversational unified model, it excels at robust context tracking to sustain interleaved multimodal generation. ChatUMM derives its capabilities from two key innovations: an interleaved multi-turn training strategy that models serialized text-image streams as a continuous conversational flow, and a systematic conversational data synthesis pipeline. This pipeline transforms a diverse set of standard single-turn datasets into fluid dialogues through three progressive stages: constructing basic stateful dialogues, enforcing long-range dependency resolution via ``distractor'' turns with history-dependent query rewriting, and synthesizing naturally interleaved multimodal responses. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that ChatUMM achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source unified models on visual understanding and instruction-guided editing benchmarks, while maintaining competitive fidelity in text-to-image generation. Notably, ChatUMM exhibits superior robustness in complex multi-turn scenarios, ensuring fluid, context-aware dialogues.
Adaptive Confidence Gating in Multi-Agent Collaboration for Efficient and Optimized Code Generation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have catalyzed breakthroughs in automated code generation, Small Language Models (SLMs) often encounter reasoning bottlenecks and failure loops when addressing complex logical requirements. To overcome these challenges, we propose DebateCoder, a multi-agent collaborative framework designed to improve the reasoning ability of SLMs (e.g., Pangu-1B) in resource-constrained environments. DebateCoder uses a structured role-playing protocol with three agents: User Agent (A_UA), Technical Agent (A_TA), and Quality Assurance Agent (A_QA). It also includes an Adaptive Confidence Gating mechanism with a 95% threshold to balance accuracy and inference efficiency. In addition, we introduce a multi-turn deliberation module and a reviewer-guided analytical debugging loop for orthogonal pre-generation debate and post-generation refinement. Experiments on HumanEval and MBPP show that DebateCoder achieves 70.12% Pass@1 on HumanEval, outperforming MapCoder while reducing API overhead by about 35%. These results indicate that collaborative protocols can mitigate limitations of small-parameter models and provide a scalable, efficient approach to high-quality automated software engineering.
DDAVS: Disentangled Audio Semantics and Delayed Bidirectional Alignment for Audio-Visual Segmentation
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Audio-Visual Segmentation (AVS) aims to localize sound-producing objects at the pixel level by jointly leveraging auditory and visual information. However, existing methods often suffer from multi-source entanglement and audio-visual misalignment, which lead to biases toward louder or larger objects while overlooking weaker, smaller, or co-occurring sources. To address these challenges, we propose DDAVS, a Disentangled Audio Semantics and Delayed Bidirectional Alignment framework. To mitigate multi-source entanglement, DDAVS employs learnable queries to extract audio semantics and anchor them within a structured semantic space derived from an audio prototype memory bank. This is further optimized through contrastive learning to enhance discriminability and robustness. To alleviate audio-visual misalignment, DDAVS introduces dual cross-attention with delayed modality interaction, improving the robustness of multimodal alignment. Extensive experiments on the AVS-Objects and VPO benchmarks demonstrate that DDAVS consistently outperforms existing approaches, exhibiting strong performance across single-source, multi-source, and multi-instance scenarios. These results validate the effectiveness and generalization ability of our framework under challenging real-world audio-visual segmentation conditions. Project page: https://trilarflagz.github.io/DDAVS-page/
UniVG-R1: Reasoning Guided Universal Visual Grounding with Reinforcement Learning
May 20, 2025Abstract:Traditional visual grounding methods primarily focus on single-image scenarios with simple textual references. However, extending these methods to real-world scenarios that involve implicit and complex instructions, particularly in conjunction with multiple images, poses significant challenges, which is mainly due to the lack of advanced reasoning ability across diverse multi-modal contexts. In this work, we aim to address the more practical universal grounding task, and propose UniVG-R1, a reasoning guided multimodal large language model (MLLM) for universal visual grounding, which enhances reasoning capabilities through reinforcement learning (RL) combined with cold-start data. Specifically, we first construct a high-quality Chain-of-Thought (CoT) grounding dataset, annotated with detailed reasoning chains, to guide the model towards correct reasoning paths via supervised fine-tuning. Subsequently, we perform rule-based reinforcement learning to encourage the model to identify correct reasoning chains, thereby incentivizing its reasoning capabilities. In addition, we identify a difficulty bias arising from the prevalence of easy samples as RL training progresses, and we propose a difficulty-aware weight adjustment strategy to further strengthen the performance. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of UniVG-R1, which achieves state-of-the-art performance on MIG-Bench with a 9.1% improvement over the previous method. Furthermore, our model exhibits strong generalizability, achieving an average improvement of 23.4% in zero-shot performance across four image and video reasoning grounding benchmarks. The project page can be accessed at https://amap-ml.github.io/UniVG-R1-page/.
Uni-AdaFocus: Spatial-temporal Dynamic Computation for Video Recognition
Dec 15, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive exploration of the phenomenon of data redundancy in video understanding, with the aim to improve computational efficiency. Our investigation commences with an examination of spatial redundancy, which refers to the observation that the most informative region in each video frame usually corresponds to a small image patch, whose shape, size and location shift smoothly across frames. Motivated by this phenomenon, we formulate the patch localization problem as a dynamic decision task, and introduce a spatially adaptive video recognition approach, termed AdaFocus. In specific, a lightweight encoder is first employed to quickly process the full video sequence, whose features are then utilized by a policy network to identify the most task-relevant regions. Subsequently, the selected patches are inferred by a high-capacity deep network for the final prediction. The full model can be trained in end-to-end conveniently. Furthermore, AdaFocus can be extended by further considering temporal and sample-wise redundancies, i.e., allocating the majority of computation to the most task-relevant frames, and minimizing the computation spent on relatively "easier" videos. Our resulting approach, Uni-AdaFocus, establishes a comprehensive framework that seamlessly integrates spatial, temporal, and sample-wise dynamic computation, while it preserves the merits of AdaFocus in terms of efficient end-to-end training and hardware friendliness. In addition, Uni-AdaFocus is general and flexible as it is compatible with off-the-shelf efficient backbones (e.g., TSM and X3D), which can be readily deployed as our feature extractor, yielding a significantly improved computational efficiency. Empirically, extensive experiments based on seven benchmark datasets and three application scenarios substantiate that Uni-AdaFocus is considerably more efficient than the competitive baselines.
Ponder & Press: Advancing Visual GUI Agent towards General Computer Control
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Most existing GUI agents typically depend on non-vision inputs like HTML source code or accessibility trees, limiting their flexibility across diverse software environments and platforms. Current multimodal large language models (MLLMs), which excel at using vision to ground real-world objects, offer a potential alternative. However, they often struggle with accurately localizing GUI elements -- a critical requirement for effective GUI automation -- due to the semantic gap between real-world objects and GUI elements. In this work, we introduce Ponder & Press, a divide-and-conquer framework for general computer control using only visual input. Our approach combines an general-purpose MLLM as an 'interpreter', responsible for translating high-level user instructions into detailed action descriptions, with a GUI-specific MLLM as a 'locator' that precisely locates GUI elements for action placement. By leveraging a purely visual input, our agent offers a versatile, human-like interaction paradigm applicable to a wide range of applications. Ponder & Press locator outperforms existing models by +22.5% on the ScreenSpot GUI grounding benchmark. Both offline and interactive agent benchmarks across various GUI environments -- including web pages, desktop software, and mobile UIs -- demonstrate that Ponder & Press framework achieves state-of-the-art performance, highlighting the potential of visual GUI agents. Refer to the project homepage https://invinciblewyq.github.io/ponder-press-page/
Self-Calibrated CLIP for Training-Free Open-Vocabulary Segmentation
Nov 24, 2024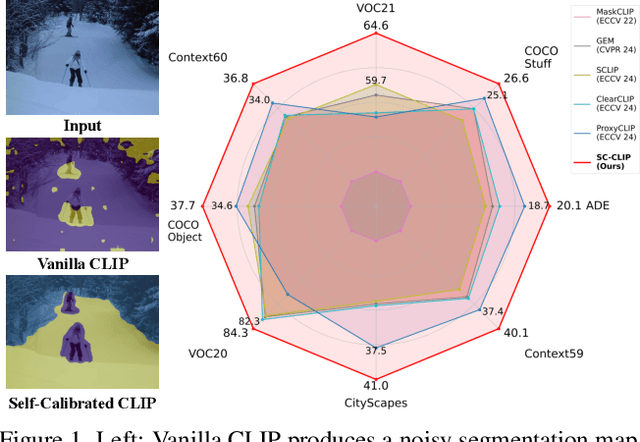
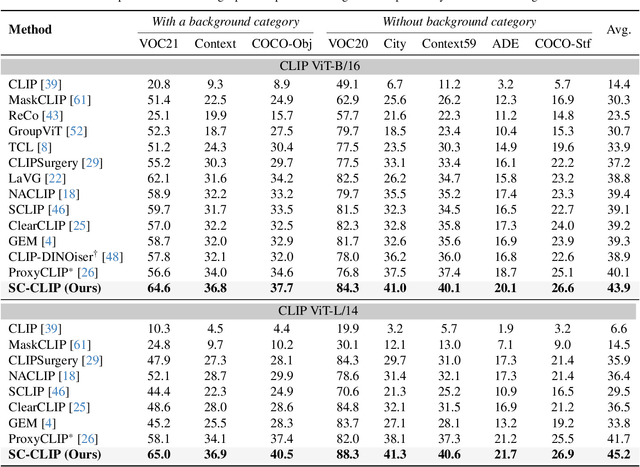
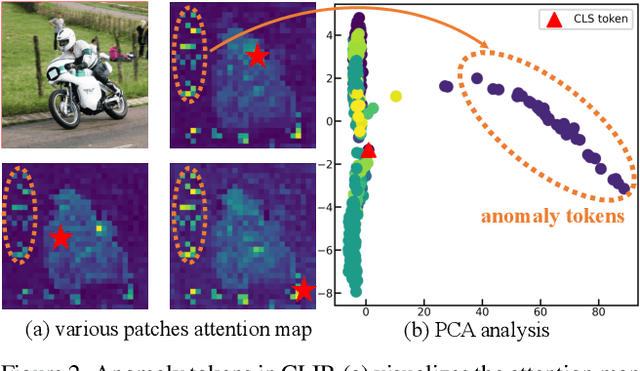
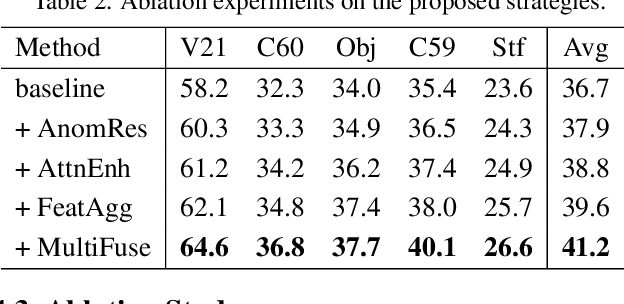
Abstract:Recent advancements in pre-trained vision-language models like CLIP, have enabled the task of open-vocabulary segmentation. CLIP demonstrates impressive zero-shot capabilities in various downstream tasks that require holistic image understanding. However, due to its image-level pre-training, CLIP struggles to capture local details, resulting in poor performance in segmentation tasks. Our analysis reveals that anomaly tokens emerge during the forward pass, drawing excessive attention from normal patch tokens, thereby diminishing spatial awareness. To address this issue, we propose Self-Calibrated CLIP (SC-CLIP), a training-free method that calibrates CLIP to produce finer-grained representations while preserving its original generalization ability, without introducing new parameters or relying on additional backbones. Specifically, we first identify and resolve the anomaly tokens to mitigate their negative impact. Next, we enhance feature discriminability and attention correlation by leveraging the semantic consistency found in CLIP's intermediate features. Furthermore, we employ multi-level feature fusion to enrich details. Collectively, these strategies enhance CLIP's feature representation with greater granularity and coherence. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of SC-CLIP, achieving state-of-the-art results across eight semantic segmentation datasets and surpassing previous methods by 9.5%. Notably, SC-CLIP boosts the performance of vanilla CLIP ViT-L/14 by 6.8 times. Our source code is available at https://github.com/SuleBai/SC-CLIP.
Hierarchical Memory for Long Video QA
Jun 30, 2024


Abstract:This paper describes our champion solution to the LOVEU Challenge @ CVPR'24, Track 1 (Long Video VQA). Processing long sequences of visual tokens is computationally expensive and memory-intensive, making long video question-answering a challenging task. The key is to compress visual tokens effectively, reducing memory footprint and decoding latency, while preserving the essential information for accurate question-answering. We adopt a hierarchical memory mechanism named STAR Memory, proposed in Flash-VStream, that is capable of processing long videos with limited GPU memory (VRAM). We further utilize the video and audio data of MovieChat-1K training set to fine-tune the pretrained weight released by Flash-VStream, achieving 1st place in the challenge. Code is available at project homepage https://invinciblewyq.github.io/vstream-page
Flash-VStream: Memory-Based Real-Time Understanding for Long Video Streams
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Benefiting from the advancements in large language models and cross-modal alignment, existing multi-modal video understanding methods have achieved prominent performance in offline scenario. However, online video streams, as one of the most common media forms in the real world, have seldom received attention. Compared to offline videos, the 'dynamic' nature of online video streams poses challenges for the direct application of existing models and introduces new problems, such as the storage of extremely long-term information, interaction between continuous visual content and 'asynchronous' user questions. Therefore, in this paper we present Flash-VStream, a video-language model that simulates the memory mechanism of human. Our model is able to process extremely long video streams in real-time and respond to user queries simultaneously. Compared to existing models, Flash-VStream achieves significant reductions in inference latency and VRAM consumption, which is intimately related to performing understanding of online streaming video. In addition, given that existing video understanding benchmarks predominantly concentrate on offline scenario, we propose VStream-QA, a novel question answering benchmark specifically designed for online video streaming understanding. Comparisons with popular existing methods on the proposed benchmark demonstrate the superiority of our method for such challenging setting. To verify the generalizability of our approach, we further evaluate it on existing video understanding benchmarks and achieves state-of-the-art performance in offline scenarios as well. All code, models, and datasets are available at the https://invinciblewyq.github.io/vstream-page/
PREIM3D: 3D Consistent Precise Image Attribute Editing from a Single Image
Apr 20, 2023
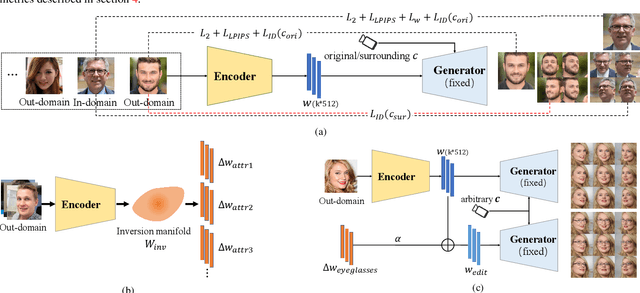
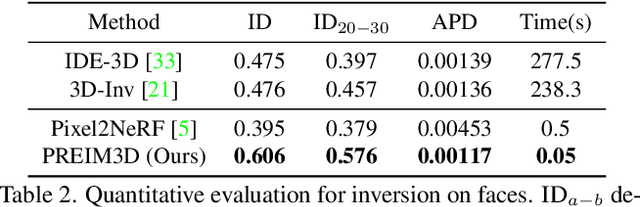
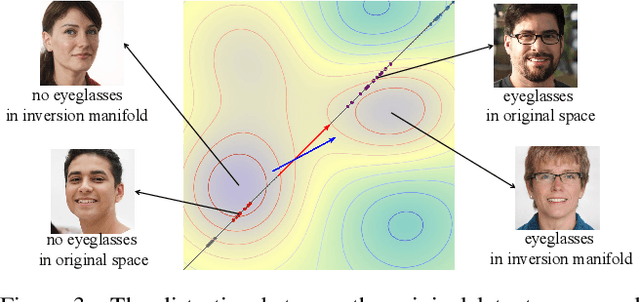
Abstract:We study the 3D-aware image attribute editing problem in this paper, which has wide applications in practice. Recent methods solved the problem by training a shared encoder to map images into a 3D generator's latent space or by per-image latent code optimization and then edited images in the latent space. Despite their promising results near the input view, they still suffer from the 3D inconsistency of produced images at large camera poses and imprecise image attribute editing, like affecting unspecified attributes during editing. For more efficient image inversion, we train a shared encoder for all images. To alleviate 3D inconsistency at large camera poses, we propose two novel methods, an alternating training scheme and a multi-view identity loss, to maintain 3D consistency and subject identity. As for imprecise image editing, we attribute the problem to the gap between the latent space of real images and that of generated images. We compare the latent space and inversion manifold of GAN models and demonstrate that editing in the inversion manifold can achieve better results in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations. Extensive experiments show that our method produces more 3D consistent images and achieves more precise image editing than previous work. Source code and pretrained models can be found on our project page: https://mybabyyh.github.io/Preim3D/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge