Zhi Cai
Beijing University of Technology
Towards Unbiased Source-Free Object Detection via Vision Foundation Models
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Source-Free Object Detection (SFOD) has garnered much attention in recent years by eliminating the need of source-domain data in cross-domain tasks, but existing SFOD methods suffer from the Source Bias problem, i.e. the adapted model remains skewed towards the source domain, leading to poor generalization and error accumulation during self-training. To overcome this challenge, we propose Debiased Source-free Object Detection (DSOD), a novel VFM-assisted SFOD framework that can effectively mitigate source bias with the help of powerful VFMs. Specifically, we propose Unified Feature Injection (UFI) module that integrates VFM features into the CNN backbone through Simple-Scale Extension (SSE) and Domain-aware Adaptive Weighting (DAAW). Then, we propose Semantic-aware Feature Regularization (SAFR) that constrains feature learning to prevent overfitting to source domain characteristics. Furthermore, we propose a VFM-free variant, termed DSOD-distill for computation-restricted scenarios through a novel Dual-Teacher distillation scheme. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that DSOD outperforms state-of-the-art SFOD methods, achieving 48.1% AP on Normal-to-Foggy weather adaptation, 39.3% AP on Cross-scene adaptation, and 61.4% AP on Synthetic-to-Real adaptation.
CoSDH: Communication-Efficient Collaborative Perception via Supply-Demand Awareness and Intermediate-Late Hybridization
Mar 05, 2025



Abstract:Multi-agent collaborative perception enhances perceptual capabilities by utilizing information from multiple agents and is considered a fundamental solution to the problem of weak single-vehicle perception in autonomous driving. However, existing collaborative perception methods face a dilemma between communication efficiency and perception accuracy. To address this issue, we propose a novel communication-efficient collaborative perception framework based on supply-demand awareness and intermediate-late hybridization, dubbed as \mymethodname. By modeling the supply-demand relationship between agents, the framework refines the selection of collaboration regions, reducing unnecessary communication cost while maintaining accuracy. In addition, we innovatively introduce the intermediate-late hybrid collaboration mode, where late-stage collaboration compensates for the performance degradation in collaborative perception under low communication bandwidth. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets, including both simulated and real-world scenarios, demonstrate that \mymethodname~ achieves state-of-the-art detection accuracy and optimal bandwidth trade-offs, delivering superior detection precision under real communication bandwidths, thus proving its effectiveness and practical applicability. The code will be released at https://github.com/Xu2729/CoSDH.
Centerness-based Instance-aware Knowledge Distillation with Task-wise Mutual Lifting for Object Detection on Drone Imagery
Nov 05, 2024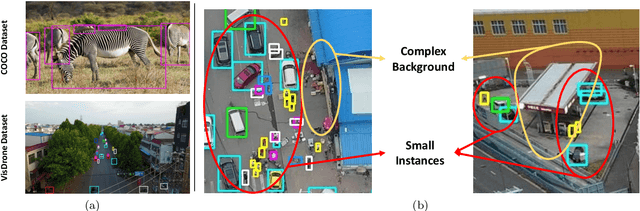
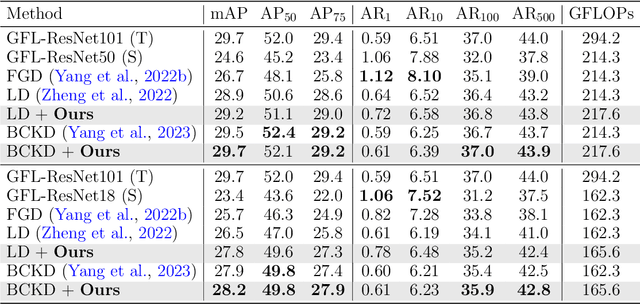
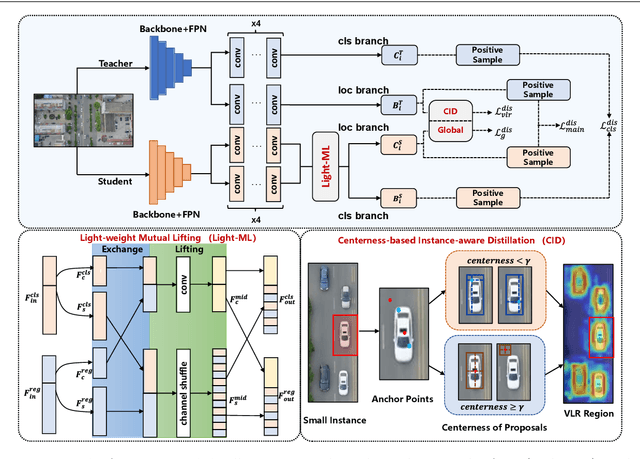
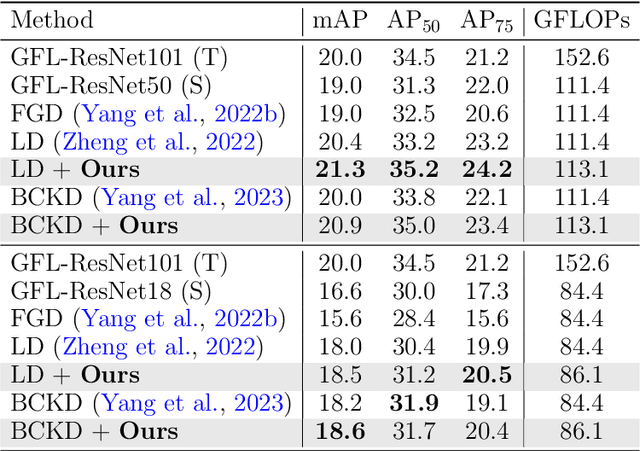
Abstract:Developing accurate and efficient detectors for drone imagery is challenging due to the inherent complexity of aerial scenes. While some existing methods aim to achieve high accuracy by utilizing larger models, their computational cost is prohibitive for drones. Recently, Knowledge Distillation (KD) has shown promising potential for maintaining satisfactory accuracy while significantly compressing models in general object detection. Considering the advantages of KD, this paper presents the first attempt to adapt it to object detection on drone imagery and addresses two intrinsic issues: (1) low foreground-background ratio and (2) small instances and complex backgrounds, which lead to inadequate training, resulting insufficient distillation. Therefore, we propose a task-wise Lightweight Mutual Lifting (Light-ML) module with a Centerness-based Instance-aware Distillation (CID) strategy. The Light-ML module mutually harmonizes the classification and localization branches by channel shuffling and convolution, integrating teacher supervision across different tasks during back-propagation, thus facilitating training the student model. The CID strategy extracts valuable regions surrounding instances through the centerness of proposals, enhancing distillation efficacy. Experiments on the VisDrone, UAVDT, and COCO benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed approach promotes the accuracies of existing state-of-the-art KD methods with comparable computational requirements. Codes will be available upon acceptance.
Crowd-SAM: SAM as a Smart Annotator for Object Detection in Crowded Scenes
Jul 16, 2024

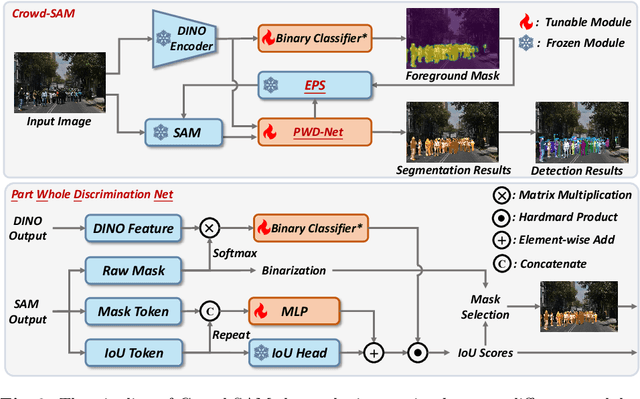

Abstract:In computer vision, object detection is an important task that finds its application in many scenarios. However, obtaining extensive labels can be challenging, especially in crowded scenes. Recently, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has been proposed as a powerful zero-shot segmenter, offering a novel approach to instance segmentation tasks. However, the accuracy and efficiency of SAM and its variants are often compromised when handling objects in crowded and occluded scenes. In this paper, we introduce Crowd-SAM, a SAM-based framework designed to enhance SAM's performance in crowded and occluded scenes with the cost of few learnable parameters and minimal labeled images. We introduce an efficient prompt sampler (EPS) and a part-whole discrimination network (PWD-Net), enhancing mask selection and accuracy in crowded scenes. Despite its simplicity, Crowd-SAM rivals state-of-the-art (SOTA) fully-supervised object detection methods on several benchmarks including CrowdHuman and CityPersons. Our code is available at https://github.com/FelixCaae/CrowdSAM.
Research on Foundation Model for Spatial Data Intelligence: China's 2024 White Paper on Strategic Development of Spatial Data Intelligence
May 30, 2024Abstract:This report focuses on spatial data intelligent large models, delving into the principles, methods, and cutting-edge applications of these models. It provides an in-depth discussion on the definition, development history, current status, and trends of spatial data intelligent large models, as well as the challenges they face. The report systematically elucidates the key technologies of spatial data intelligent large models and their applications in urban environments, aerospace remote sensing, geography, transportation, and other scenarios. Additionally, it summarizes the latest application cases of spatial data intelligent large models in themes such as urban development, multimodal systems, remote sensing, smart transportation, and resource environments. Finally, the report concludes with an overview and outlook on the development prospects of spatial data intelligent large models.
Align-DETR: Improving DETR with Simple IoU-aware BCE loss
Apr 15, 2023



Abstract:DETR has set up a simple end-to-end pipeline for object detection by formulating this task as a set prediction problem, showing promising potential. However, despite the significant progress in improving DETR, this paper identifies a problem of misalignment in the output distribution, which prevents the best-regressed samples from being assigned with high confidence, hindering the model's accuracy. We propose a metric, recall of best-regressed samples, to quantitively evaluate the misalignment problem. Observing its importance, we propose a novel Align-DETR that incorporates a localization precision-aware classification loss in optimization. The proposed loss, IA-BCE, guides the training of DETR to build a strong correlation between classification score and localization precision. We also adopt the mixed-matching strategy, to facilitate DETR-based detectors with faster training convergence while keeping an end-to-end scheme. Moreover, to overcome the dramatic decrease in sample quality induced by the sparsity of queries, we introduce a prime sample weighting mechanism to suppress the interference of unimportant samples. Extensive experiments are conducted with very competitive results reported. In particular, it delivers a 46 (+3.8)% AP on the DAB-DETR baseline with the ResNet-50 backbone and reaches a new SOTA performance of 50.2% AP in the 1x setting on the COCO validation set when employing the strong baseline DINO. Our code is available at https://github.com/FelixCaae/AlignDETR.
A Lightweight Music Texture Transfer System
Sep 27, 2018



Abstract:Deep learning researches on the transformation problems for image and text have raised great attention. However, present methods for music feature transfer using neural networks are far from practical application. In this paper, we initiate a novel system for transferring the texture of music, and release it as an open source project. Its core algorithm is composed of a converter which represents sounds as texture spectra, a corresponding reconstructor and a feed-forward transfer network. We evaluate this system from multiple perspectives, and experimental results reveal that it achieves convincing results in both sound effects and computational performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge