Zheng Ge
STEP3-VL-10B Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We present STEP3-VL-10B, a lightweight open-source foundation model designed to redefine the trade-off between compact efficiency and frontier-level multimodal intelligence. STEP3-VL-10B is realized through two strategic shifts: first, a unified, fully unfrozen pre-training strategy on 1.2T multimodal tokens that integrates a language-aligned Perception Encoder with a Qwen3-8B decoder to establish intrinsic vision-language synergy; and second, a scaled post-training pipeline featuring over 1k iterations of reinforcement learning. Crucially, we implement Parallel Coordinated Reasoning (PaCoRe) to scale test-time compute, allocating resources to scalable perceptual reasoning that explores and synthesizes diverse visual hypotheses. Consequently, despite its compact 10B footprint, STEP3-VL-10B rivals or surpasses models 10$\times$-20$\times$ larger (e.g., GLM-4.6V-106B, Qwen3-VL-235B) and top-tier proprietary flagships like Gemini 2.5 Pro and Seed-1.5-VL. Delivering best-in-class performance, it records 92.2% on MMBench and 80.11% on MMMU, while excelling in complex reasoning with 94.43% on AIME2025 and 75.95% on MathVision. We release the full model suite to provide the community with a powerful, efficient, and reproducible baseline.
PaCoRe: Learning to Scale Test-Time Compute with Parallel Coordinated Reasoning
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:We introduce Parallel Coordinated Reasoning (PaCoRe), a training-and-inference framework designed to overcome a central limitation of contemporary language models: their inability to scale test-time compute (TTC) far beyond sequential reasoning under a fixed context window. PaCoRe departs from the traditional sequential paradigm by driving TTC through massive parallel exploration coordinated via a message-passing architecture in multiple rounds. Each round launches many parallel reasoning trajectories, compacts their findings into context-bounded messages, and synthesizes these messages to guide the next round and ultimately produce the final answer. Trained end-to-end with large-scale, outcome-based reinforcement learning, the model masters the synthesis abilities required by PaCoRe and scales to multi-million-token effective TTC without exceeding context limits. The approach yields strong improvements across diverse domains, and notably pushes reasoning beyond frontier systems in mathematics: an 8B model reaches 94.5% on HMMT 2025, surpassing GPT-5's 93.2% by scaling effective TTC to roughly two million tokens. We open-source model checkpoints, training data, and the full inference pipeline to accelerate follow-up work.
Step-GUI Technical Report
Dec 19, 2025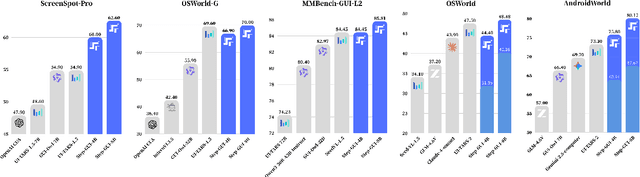
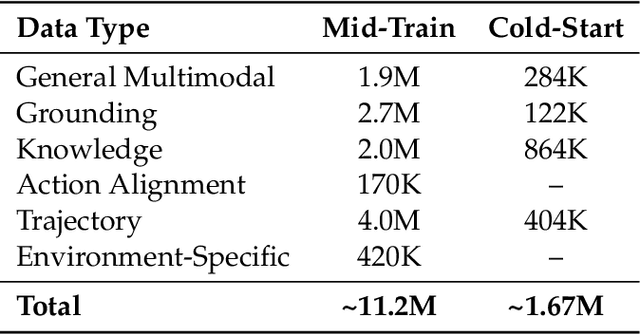
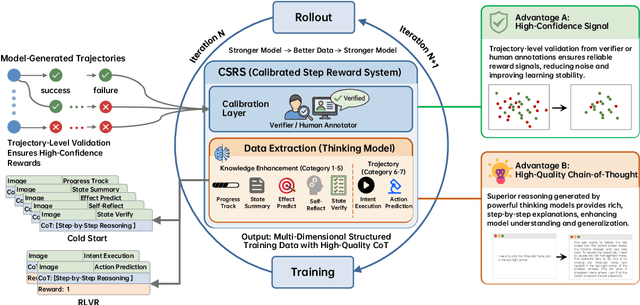

Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models unlock unprecedented opportunities for GUI automation. However, a fundamental challenge remains: how to efficiently acquire high-quality training data while maintaining annotation reliability? We introduce a self-evolving training pipeline powered by the Calibrated Step Reward System, which converts model-generated trajectories into reliable training signals through trajectory-level calibration, achieving >90% annotation accuracy with 10-100x lower cost. Leveraging this pipeline, we introduce Step-GUI, a family of models (4B/8B) that achieves state-of-the-art GUI performance (8B: 80.2% AndroidWorld, 48.5% OSWorld, 62.6% ScreenShot-Pro) while maintaining robust general capabilities. As GUI agent capabilities improve, practical deployment demands standardized interfaces across heterogeneous devices while protecting user privacy. To this end, we propose GUI-MCP, the first Model Context Protocol for GUI automation with hierarchical architecture that combines low-level atomic operations and high-level task delegation to local specialist models, enabling high-privacy execution where sensitive data stays on-device. Finally, to assess whether agents can handle authentic everyday usage, we introduce AndroidDaily, a benchmark grounded in real-world mobile usage patterns with 3146 static actions and 235 end-to-end tasks across high-frequency daily scenarios (8B: static 89.91%, end-to-end 52.50%). Our work advances the development of practical GUI agents and demonstrates strong potential for real-world deployment in everyday digital interactions.
DGAE: Diffusion-Guided Autoencoder for Efficient Latent Representation Learning
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Autoencoders empower state-of-the-art image and video generative models by compressing pixels into a latent space through visual tokenization. Although recent advances have alleviated the performance degradation of autoencoders under high compression ratios, addressing the training instability caused by GAN remains an open challenge. While improving spatial compression, we also aim to minimize the latent space dimensionality, enabling more efficient and compact representations. To tackle these challenges, we focus on improving the decoder's expressiveness. Concretely, we propose DGAE, which employs a diffusion model to guide the decoder in recovering informative signals that are not fully decoded from the latent representation. With this design, DGAE effectively mitigates the performance degradation under high spatial compression rates. At the same time, DGAE achieves state-of-the-art performance with a 2x smaller latent space. When integrated with Diffusion Models, DGAE demonstrates competitive performance on image generation for ImageNet-1K and shows that this compact latent representation facilitates faster convergence of the diffusion model.
Step-Audio-AQAA: a Fully End-to-End Expressive Large Audio Language Model
Jun 10, 2025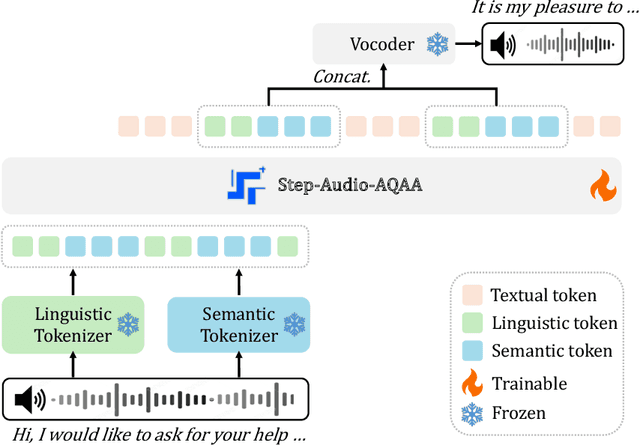
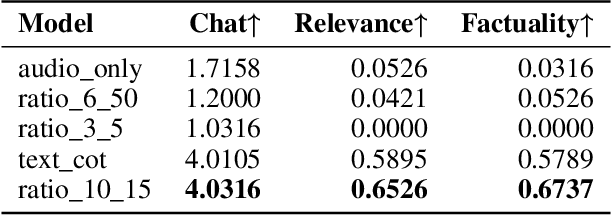
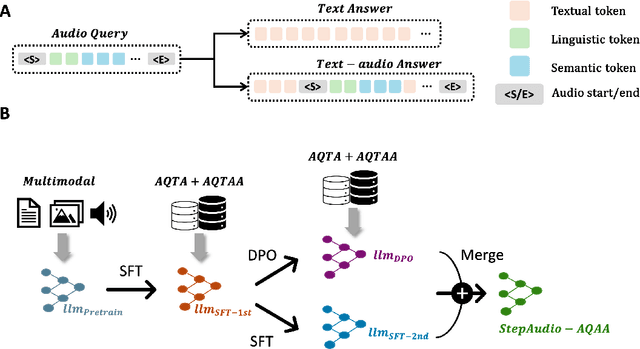
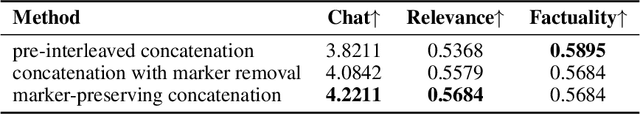
Abstract:Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) have significantly advanced intelligent human-computer interaction, yet their reliance on text-based outputs limits their ability to generate natural speech responses directly, hindering seamless audio interactions. To address this, we introduce Step-Audio-AQAA, a fully end-to-end LALM designed for Audio Query-Audio Answer (AQAA) tasks. The model integrates a dual-codebook audio tokenizer for linguistic and semantic feature extraction, a 130-billion-parameter backbone LLM and a neural vocoder for high-fidelity speech synthesis. Our post-training approach employs interleaved token-output of text and audio to enhance semantic coherence and combines Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with model merge to improve performance. Evaluations on the StepEval-Audio-360 benchmark demonstrate that Step-Audio-AQAA excels especially in speech control, outperforming the state-of-art LALMs in key areas. This work contributes a promising solution for end-to-end LALMs and highlights the critical role of token-based vocoder in enhancing overall performance for AQAA tasks.
Step1X-Edit: A Practical Framework for General Image Editing
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:In recent years, image editing models have witnessed remarkable and rapid development. The recent unveiling of cutting-edge multimodal models such as GPT-4o and Gemini2 Flash has introduced highly promising image editing capabilities. These models demonstrate an impressive aptitude for fulfilling a vast majority of user-driven editing requirements, marking a significant advancement in the field of image manipulation. However, there is still a large gap between the open-source algorithm with these closed-source models. Thus, in this paper, we aim to release a state-of-the-art image editing model, called Step1X-Edit, which can provide comparable performance against the closed-source models like GPT-4o and Gemini2 Flash. More specifically, we adopt the Multimodal LLM to process the reference image and the user's editing instruction. A latent embedding has been extracted and integrated with a diffusion image decoder to obtain the target image. To train the model, we build a data generation pipeline to produce a high-quality dataset. For evaluation, we develop the GEdit-Bench, a novel benchmark rooted in real-world user instructions. Experimental results on GEdit-Bench demonstrate that Step1X-Edit outperforms existing open-source baselines by a substantial margin and approaches the performance of leading proprietary models, thereby making significant contributions to the field of image editing.
Perception-R1: Pioneering Perception Policy with Reinforcement Learning
Apr 10, 2025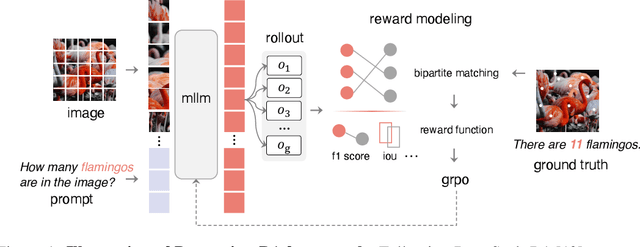
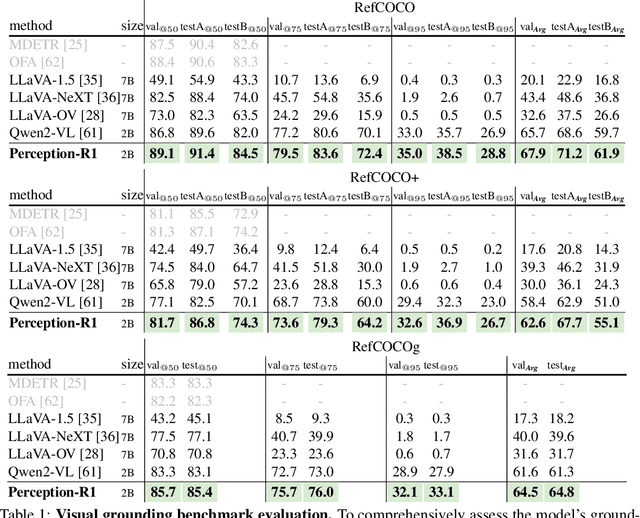
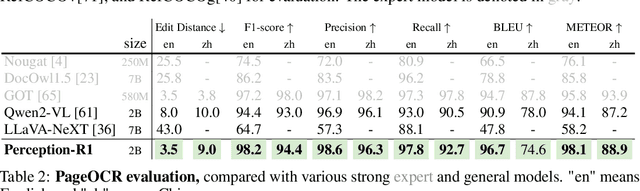
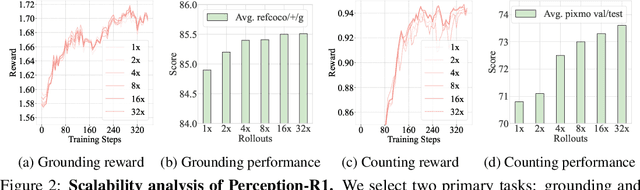
Abstract:Inspired by the success of DeepSeek-R1, we explore the potential of rule-based reinforcement learning (RL) in MLLM post-training for perception policy learning. While promising, our initial experiments reveal that incorporating a thinking process through RL does not consistently lead to performance gains across all visual perception tasks. This leads us to delve into the essential role of RL in the context of visual perception. In this work, we return to the fundamentals and explore the effects of RL on different perception tasks. We observe that the perceptual complexity is a major factor in determining the effectiveness of RL. We also observe that reward design plays a crucial role in further approching the upper limit of model perception. To leverage these findings, we propose Perception-R1, a scalable RL framework using GRPO during MLLM post-training. With a standard Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct, Perception-R1 achieves +4.2% on RefCOCO+, +17.9% on PixMo-Count, +4.2% on PageOCR, and notably, 31.9% AP on COCO2017 val for the first time, establishing a strong baseline for perception policy learning.
Perception in Reflection
Apr 09, 2025
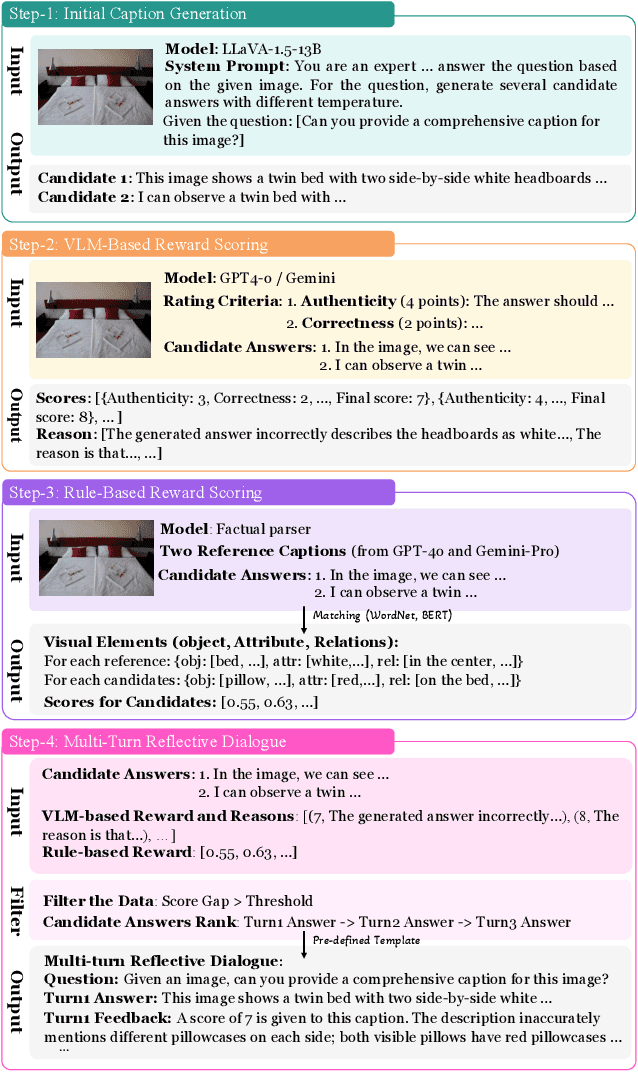
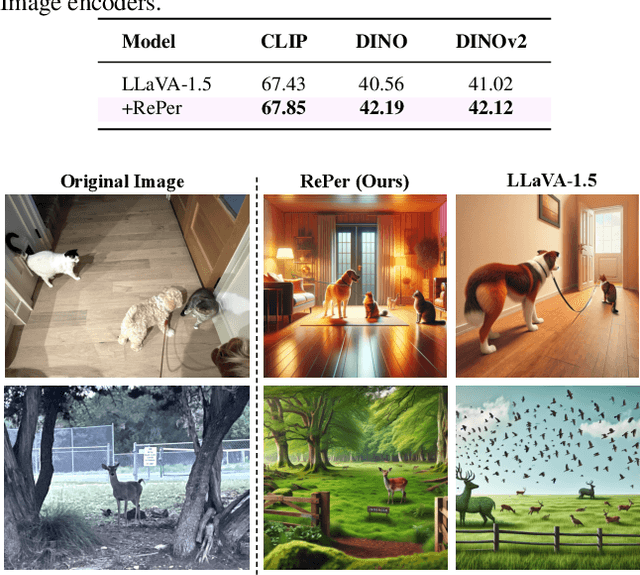

Abstract:We present a perception in reflection paradigm designed to transcend the limitations of current large vision-language models (LVLMs), which are expected yet often fail to achieve perfect perception initially. Specifically, we propose Reflective Perception (RePer), a dual-model reflection mechanism that systematically alternates between policy and critic models, enables iterative refinement of visual perception. This framework is powered by Reflective Perceptual Learning (RPL), which reinforces intrinsic reflective capabilities through a methodically constructed visual reflection dataset and reflective unlikelihood training. Comprehensive experimental evaluation demonstrates RePer's quantifiable improvements in image understanding, captioning precision, and hallucination reduction. Notably, RePer achieves strong alignment between model attention patterns and human visual focus, while RPL optimizes fine-grained and free-form preference alignment. These advancements establish perception in reflection as a robust paradigm for future multimodal agents, particularly in tasks requiring complex reasoning and multi-step manipulation.
M-DocSum: Do LVLMs Genuinely Comprehend Interleaved Image-Text in Document Summarization?
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:We investigate a critical yet under-explored question in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs): Do LVLMs genuinely comprehend interleaved image-text in the document? Existing document understanding benchmarks often assess LVLMs using question-answer formats, which are information-sparse and difficult to guarantee the coverage of long-range dependencies. To address this issue, we introduce a novel and challenging Multimodal Document Summarization Benchmark (M-DocSum-Bench), which comprises 500 high-quality arXiv papers, along with interleaved multimodal summaries aligned with human preferences. M-DocSum-Bench is a reference-based generation task and necessitates the generation of interleaved image-text summaries using provided reference images, thereby simultaneously evaluating capabilities in understanding, reasoning, localization, and summarization within complex multimodal document scenarios. To facilitate this benchmark, we develop an automated framework to construct summaries and propose a fine-grained evaluation method called M-DocEval. Moreover, we further develop a robust summarization baseline, i.e., M-DocSum-7B, by progressive two-stage training with diverse instruction and preference data. The extensive results on our M-DocSum-Bench reveal that the leading LVLMs struggle to maintain coherence and accurately integrate information within long and interleaved contexts, often exhibiting confusion between similar images and a lack of robustness. Notably, M-DocSum-7B achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to larger and closed-source models (including GPT-4o, Gemini Pro, Claude-3.5-Sonnet and Qwen2.5-VL-72B, etc.), demonstrating the potential of LVLMs for improved interleaved image-text understanding. The code, data, and models are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/M-DocSum-Bench.
Step-Video-TI2V Technical Report: A State-of-the-Art Text-Driven Image-to-Video Generation Model
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:We present Step-Video-TI2V, a state-of-the-art text-driven image-to-video generation model with 30B parameters, capable of generating videos up to 102 frames based on both text and image inputs. We build Step-Video-TI2V-Eval as a new benchmark for the text-driven image-to-video task and compare Step-Video-TI2V with open-source and commercial TI2V engines using this dataset. Experimental results demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of Step-Video-TI2V in the image-to-video generation task. Both Step-Video-TI2V and Step-Video-TI2V-Eval are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Video-TI2V.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge