En Yu
STEP3-VL-10B Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We present STEP3-VL-10B, a lightweight open-source foundation model designed to redefine the trade-off between compact efficiency and frontier-level multimodal intelligence. STEP3-VL-10B is realized through two strategic shifts: first, a unified, fully unfrozen pre-training strategy on 1.2T multimodal tokens that integrates a language-aligned Perception Encoder with a Qwen3-8B decoder to establish intrinsic vision-language synergy; and second, a scaled post-training pipeline featuring over 1k iterations of reinforcement learning. Crucially, we implement Parallel Coordinated Reasoning (PaCoRe) to scale test-time compute, allocating resources to scalable perceptual reasoning that explores and synthesizes diverse visual hypotheses. Consequently, despite its compact 10B footprint, STEP3-VL-10B rivals or surpasses models 10$\times$-20$\times$ larger (e.g., GLM-4.6V-106B, Qwen3-VL-235B) and top-tier proprietary flagships like Gemini 2.5 Pro and Seed-1.5-VL. Delivering best-in-class performance, it records 92.2% on MMBench and 80.11% on MMMU, while excelling in complex reasoning with 94.43% on AIME2025 and 75.95% on MathVision. We release the full model suite to provide the community with a powerful, efficient, and reproducible baseline.
Bandwidth-constrained Variational Message Encoding for Cooperative Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Graph-based multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) enables coordinated behavior under partial observability by modeling agents as nodes and communication links as edges. While recent methods excel at learning sparse coordination graphs-determining who communicates with whom-they do not address what information should be transmitted under hard bandwidth constraints. We study this bandwidth-limited regime and show that naive dimensionality reduction consistently degrades coordination performance. Hard bandwidth constraints force selective encoding, but deterministic projections lack mechanisms to control how compression occurs. We introduce Bandwidth-constrained Variational Message Encoding (BVME), a lightweight module that treats messages as samples from learned Gaussian posteriors regularized via KL divergence to an uninformative prior. BVME's variational framework provides principled, tunable control over compression strength through interpretable hyperparameters, directly constraining the representations used for decision-making. Across SMACv1, SMACv2, and MPE benchmarks, BVME achieves comparable or superior performance while using 67--83% fewer message dimensions, with gains most pronounced on sparse graphs where message quality critically impacts coordination. Ablations reveal U-shaped sensitivity to bandwidth, with BVME excelling at extreme ratios while adding minimal overhead.
Autonomous Concept Drift Threshold Determination
Nov 13, 2025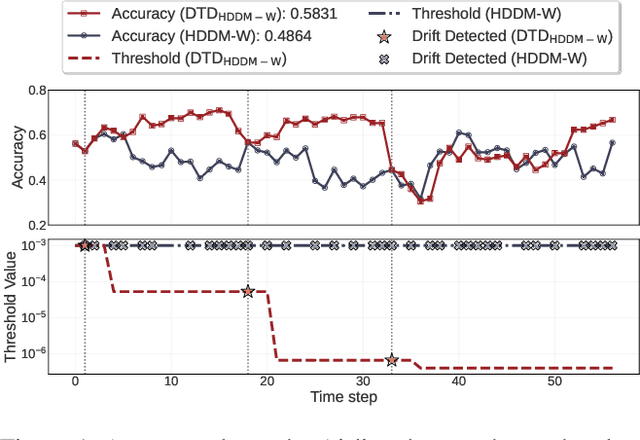
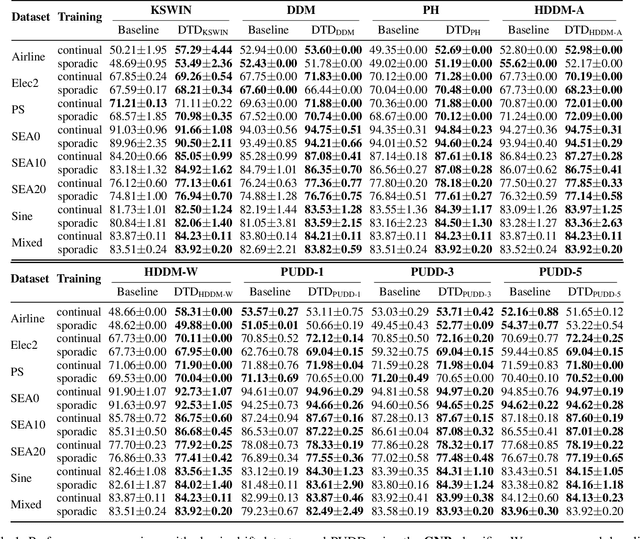
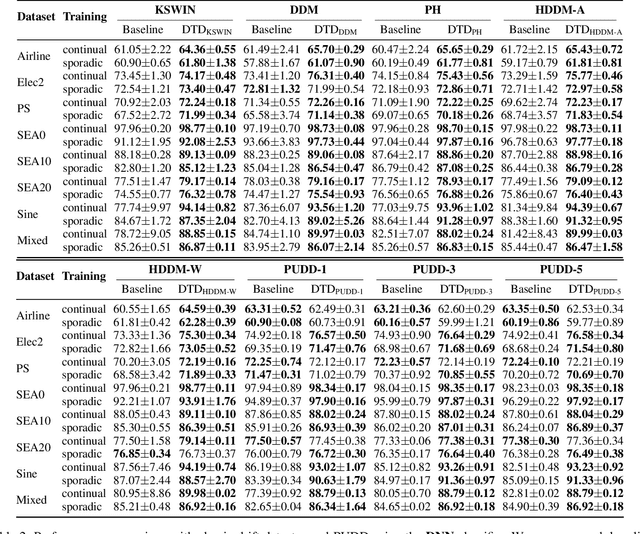
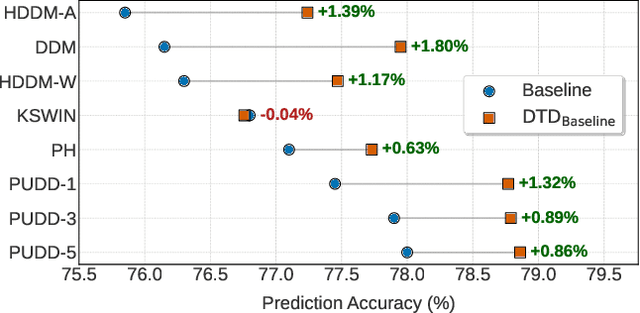
Abstract:Existing drift detection methods focus on designing sensitive test statistics. They treat the detection threshold as a fixed hyperparameter, set once to balance false alarms and late detections, and applied uniformly across all datasets and over time. However, maintaining model performance is the key objective from the perspective of machine learning, and we observe that model performance is highly sensitive to this threshold. This observation inspires us to investigate whether a dynamic threshold could be provably better. In this paper, we prove that a threshold that adapts over time can outperform any single fixed threshold. The main idea of the proof is that a dynamic strategy, constructed by combining the best threshold from each individual data segment, is guaranteed to outperform any single threshold that apply to all segments. Based on the theorem, we propose a Dynamic Threshold Determination algorithm. It enhances existing drift detection frameworks with a novel comparison phase to inform how the threshold should be adjusted. Extensive experiments on a wide range of synthetic and real-world datasets, including both image and tabular data, validate that our approach substantially enhances the performance of state-of-the-art drift detectors.
Generalized Incremental Learning under Concept Drift across Evolving Data Streams
Jun 06, 2025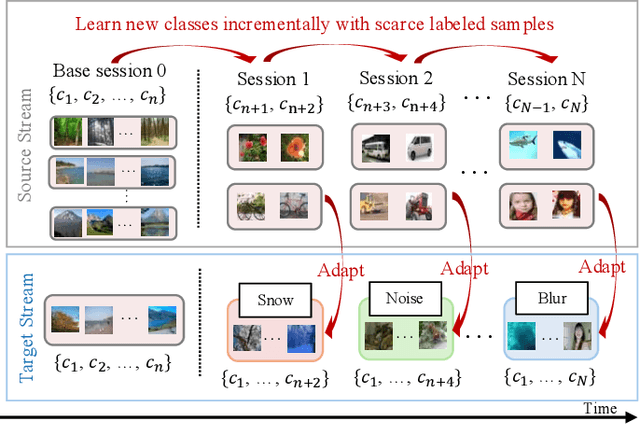
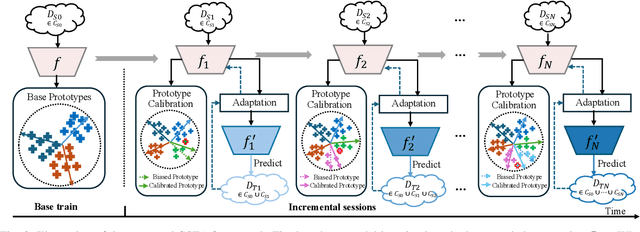
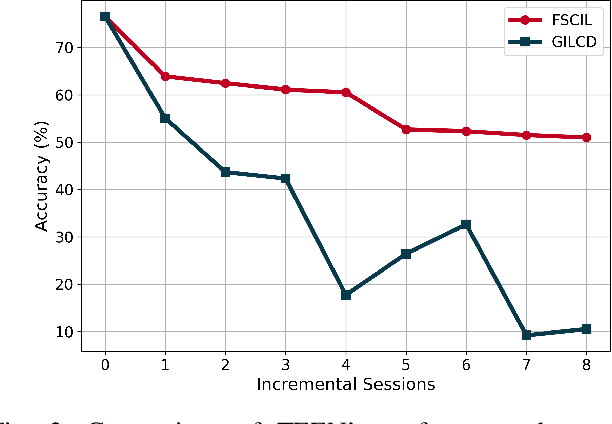
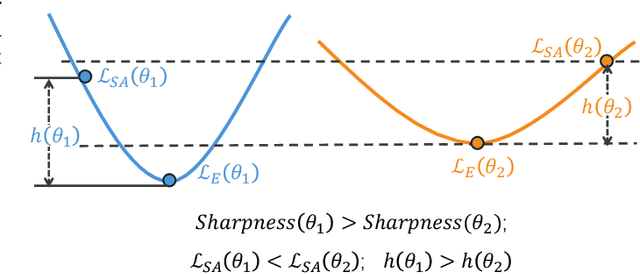
Abstract:Real-world data streams exhibit inherent non-stationarity characterized by concept drift, posing significant challenges for adaptive learning systems. While existing methods address isolated distribution shifts, they overlook the critical co-evolution of label spaces and distributions under limited supervision and persistent uncertainty. To address this, we formalize Generalized Incremental Learning under Concept Drift (GILCD), characterizing the joint evolution of distributions and label spaces in open-environment streaming contexts, and propose a novel framework called Calibrated Source-Free Adaptation (CSFA). First, CSFA introduces a training-free prototype calibration mechanism that dynamically fuses emerging prototypes with base representations, enabling stable new-class identification without optimization overhead. Second, we design a novel source-free adaptation algorithm, i.e., Reliable Surrogate Gap Sharpness-aware (RSGS) minimization. It integrates sharpness-aware perturbation loss optimization with surrogate gap minimization, while employing entropy-based uncertainty filtering to discard unreliable samples. This mechanism ensures robust distribution alignment and mitigates generalization degradation caused by uncertainties. Therefore, CSFA establishes a unified framework for stable adaptation to evolving semantics and distributions in open-world streaming scenarios. Extensive experiments validate the superior performance and effectiveness of CSFA compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
ReaMOT: A Benchmark and Framework for Reasoning-based Multi-Object Tracking
May 26, 2025Abstract:Referring Multi-object tracking (RMOT) is an important research field in computer vision. Its task form is to guide the models to track the objects that conform to the language instruction. However, the RMOT task commonly requires clear language instructions, such methods often fail to work when complex language instructions with reasoning characteristics appear. In this work, we propose a new task, called Reasoning-based Multi-Object Tracking (ReaMOT). ReaMOT is a more challenging task that requires accurate reasoning about objects that match the language instruction with reasoning characteristic and tracking the objects' trajectories. To advance the ReaMOT task and evaluate the reasoning capabilities of tracking models, we construct ReaMOT Challenge, a reasoning-based multi-object tracking benchmark built upon 12 datasets. Specifically, it comprises 1,156 language instructions with reasoning characteristic, 423,359 image-language pairs, and 869 diverse scenes, which is divided into three levels of reasoning difficulty. In addition, we propose a set of evaluation metrics tailored for the ReaMOT task. Furthermore, we propose ReaTrack, a training-free framework for reasoning-based multi-object tracking based on large vision-language models (LVLM) and SAM2, as a baseline for the ReaMOT task. Extensive experiments on the ReaMOT Challenge benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness of our ReaTrack framework.
Learning Robust Spectral Dynamics for Temporal Domain Generalization
May 19, 2025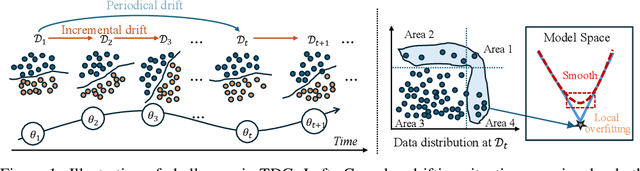
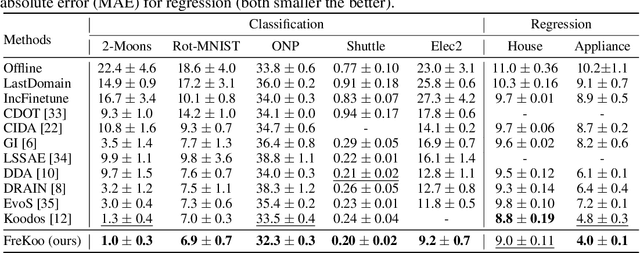
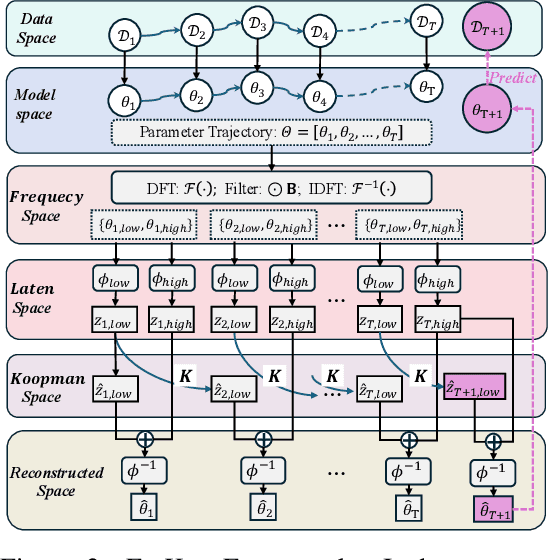

Abstract:Modern machine learning models struggle to maintain performance in dynamic environments where temporal distribution shifts, \emph{i.e., concept drift}, are prevalent. Temporal Domain Generalization (TDG) seeks to enable model generalization across evolving domains, yet existing approaches typically assume smooth incremental changes, struggling with complex real-world drifts involving long-term structure (incremental evolution/periodicity) and local uncertainties. To overcome these limitations, we introduce FreKoo, which tackles these challenges via a novel frequency-domain analysis of parameter trajectories. It leverages the Fourier transform to disentangle parameter evolution into distinct spectral bands. Specifically, low-frequency component with dominant dynamics are learned and extrapolated using the Koopman operator, robustly capturing diverse drift patterns including both incremental and periodicity. Simultaneously, potentially disruptive high-frequency variations are smoothed via targeted temporal regularization, preventing overfitting to transient noise and domain uncertainties. In addition, this dual spectral strategy is rigorously grounded through theoretical analysis, providing stability guarantees for the Koopman prediction, a principled Bayesian justification for the high-frequency regularization, and culminating in a multiscale generalization bound connecting spectral dynamics to improved generalization. Extensive experiments demonstrate FreKoo's significant superiority over SOTA TDG approaches, particularly excelling in real-world streaming scenarios with complex drifts and uncertainties.
Walking the Tightrope: Disentangling Beneficial and Detrimental Drifts in Non-Stationary Custom-Tuning
May 19, 2025Abstract:This paper uncovers a critical yet overlooked phenomenon in multi-modal large language models (MLLMs): detrimental concept drift within chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning during non-stationary reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT), where reasoning token distributions evolve unpredictably, thereby introducing significant biases in final predictions. To address this, we are pioneers in establishing the theoretical bridge between concept drift theory and RFT processes by formalizing CoT's autoregressive token streams as non-stationary distributions undergoing arbitrary temporal shifts. Leveraging this framework, we propose a novel counterfact-aware RFT that systematically decouples beneficial distribution adaptation from harmful concept drift through concept graph-empowered LLM experts generating counterfactual reasoning trajectories. Our solution, Counterfactual Preference Optimization (CPO), enables stable RFT in non-stationary environments, particularly within the medical domain, through custom-tuning of counterfactual-aware preference alignment. Extensive experiments demonstrate our superior performance of robustness, generalization and coordination within RFT. Besides, we also contributed a large-scale dataset CXR-CounterFact (CCF), comprising 320,416 meticulously curated counterfactual reasoning trajectories derived from MIMIC-CXR. Our code and data are public.
Perception-R1: Pioneering Perception Policy with Reinforcement Learning
Apr 10, 2025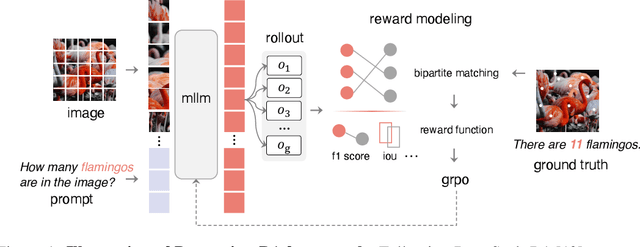
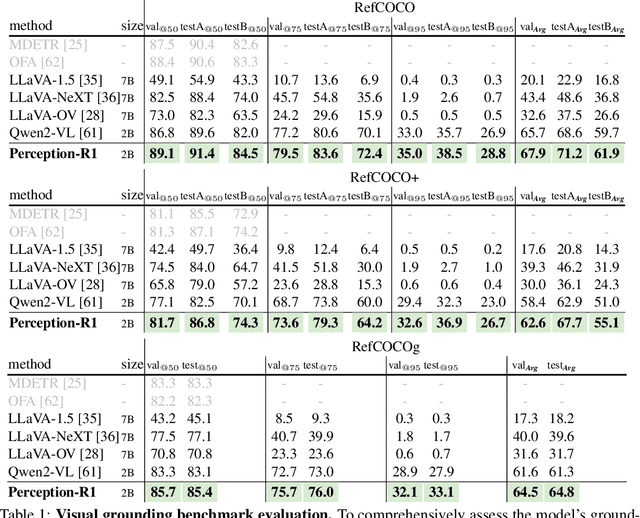
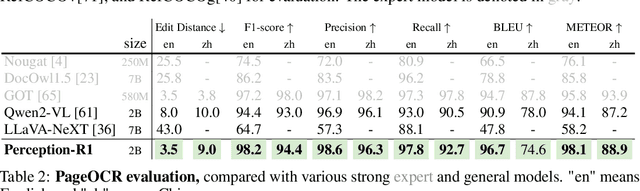
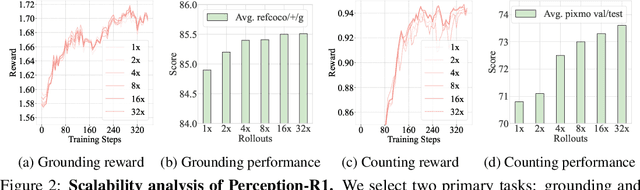
Abstract:Inspired by the success of DeepSeek-R1, we explore the potential of rule-based reinforcement learning (RL) in MLLM post-training for perception policy learning. While promising, our initial experiments reveal that incorporating a thinking process through RL does not consistently lead to performance gains across all visual perception tasks. This leads us to delve into the essential role of RL in the context of visual perception. In this work, we return to the fundamentals and explore the effects of RL on different perception tasks. We observe that the perceptual complexity is a major factor in determining the effectiveness of RL. We also observe that reward design plays a crucial role in further approching the upper limit of model perception. To leverage these findings, we propose Perception-R1, a scalable RL framework using GRPO during MLLM post-training. With a standard Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct, Perception-R1 achieves +4.2% on RefCOCO+, +17.9% on PixMo-Count, +4.2% on PageOCR, and notably, 31.9% AP on COCO2017 val for the first time, establishing a strong baseline for perception policy learning.
Perception in Reflection
Apr 09, 2025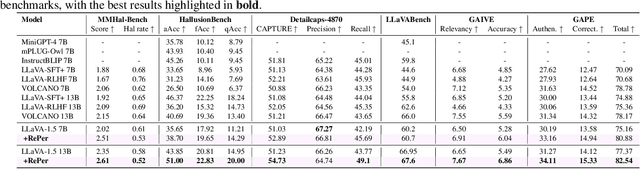
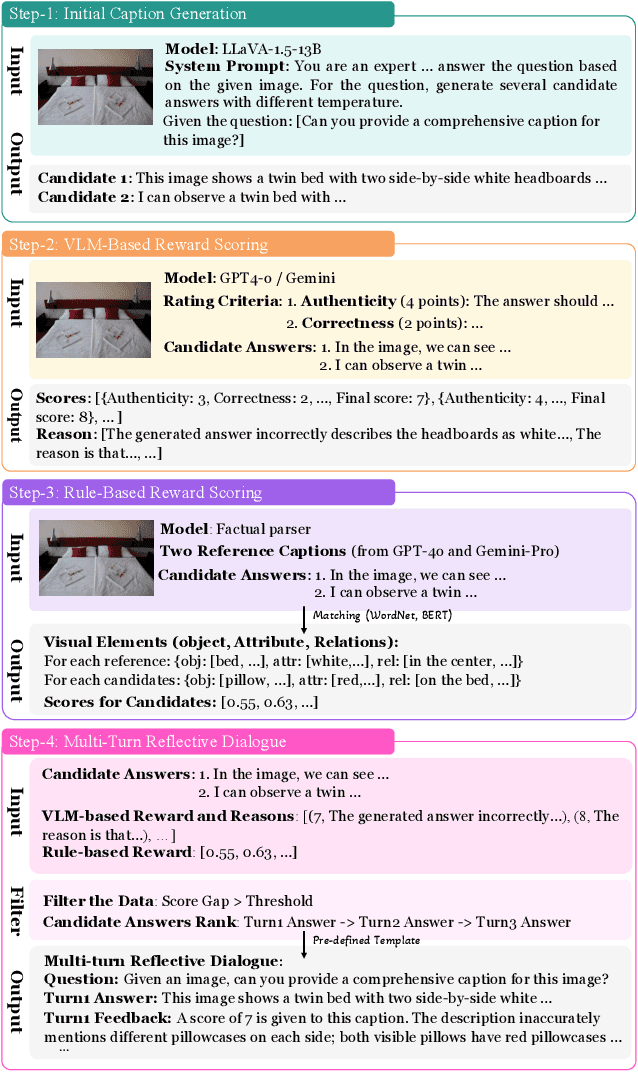
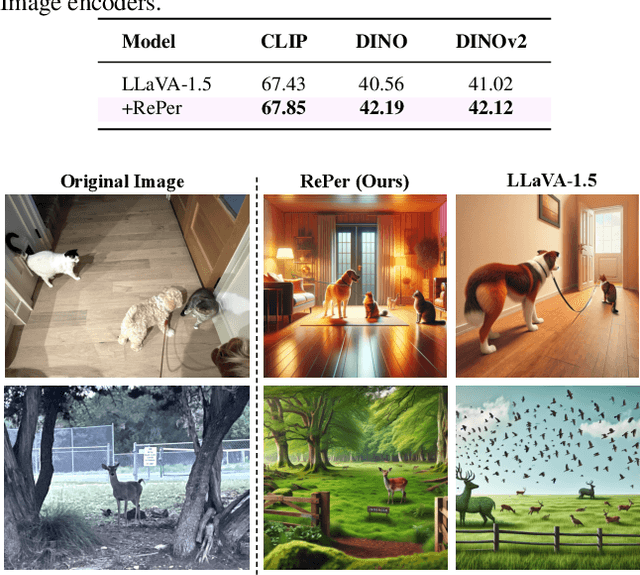

Abstract:We present a perception in reflection paradigm designed to transcend the limitations of current large vision-language models (LVLMs), which are expected yet often fail to achieve perfect perception initially. Specifically, we propose Reflective Perception (RePer), a dual-model reflection mechanism that systematically alternates between policy and critic models, enables iterative refinement of visual perception. This framework is powered by Reflective Perceptual Learning (RPL), which reinforces intrinsic reflective capabilities through a methodically constructed visual reflection dataset and reflective unlikelihood training. Comprehensive experimental evaluation demonstrates RePer's quantifiable improvements in image understanding, captioning precision, and hallucination reduction. Notably, RePer achieves strong alignment between model attention patterns and human visual focus, while RPL optimizes fine-grained and free-form preference alignment. These advancements establish perception in reflection as a robust paradigm for future multimodal agents, particularly in tasks requiring complex reasoning and multi-step manipulation.
OVTR: End-to-End Open-Vocabulary Multiple Object Tracking with Transformer
Mar 13, 2025



Abstract:Open-vocabulary multiple object tracking aims to generalize trackers to unseen categories during training, enabling their application across a variety of real-world scenarios. However, the existing open-vocabulary tracker is constrained by its framework structure, isolated frame-level perception, and insufficient modal interactions, which hinder its performance in open-vocabulary classification and tracking. In this paper, we propose OVTR (End-to-End Open-Vocabulary Multiple Object Tracking with TRansformer), the first end-to-end open-vocabulary tracker that models motion, appearance, and category simultaneously. To achieve stable classification and continuous tracking, we design the CIP (Category Information Propagation) strategy, which establishes multiple high-level category information priors for subsequent frames. Additionally, we introduce a dual-branch structure for generalization capability and deep multimodal interaction, and incorporate protective strategies in the decoder to enhance performance. Experimental results show that our method surpasses previous trackers on the open-vocabulary MOT benchmark while also achieving faster inference speeds and significantly reducing preprocessing requirements. Moreover, the experiment transferring the model to another dataset demonstrates its strong adaptability. Models and code are released at https://github.com/jinyanglii/OVTR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge