Yuang Peng
Step 3.5 Flash: Open Frontier-Level Intelligence with 11B Active Parameters
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:We introduce Step 3.5 Flash, a sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model that bridges frontier-level agentic intelligence and computational efficiency. We focus on what matters most when building agents: sharp reasoning and fast, reliable execution. Step 3.5 Flash pairs a 196B-parameter foundation with 11B active parameters for efficient inference. It is optimized with interleaved 3:1 sliding-window/full attention and Multi-Token Prediction (MTP-3) to reduce the latency and cost of multi-round agentic interactions. To reach frontier-level intelligence, we design a scalable reinforcement learning framework that combines verifiable signals with preference feedback, while remaining stable under large-scale off-policy training, enabling consistent self-improvement across mathematics, code, and tool use. Step 3.5 Flash demonstrates strong performance across agent, coding, and math tasks, achieving 85.4% on IMO-AnswerBench, 86.4% on LiveCodeBench-v6 (2024.08-2025.05), 88.2% on tau2-Bench, 69.0% on BrowseComp (with context management), and 51.0% on Terminal-Bench 2.0, comparable to frontier models such as GPT-5.2 xHigh and Gemini 3.0 Pro. By redefining the efficiency frontier, Step 3.5 Flash provides a high-density foundation for deploying sophisticated agents in real-world industrial environments.
STEP3-VL-10B Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We present STEP3-VL-10B, a lightweight open-source foundation model designed to redefine the trade-off between compact efficiency and frontier-level multimodal intelligence. STEP3-VL-10B is realized through two strategic shifts: first, a unified, fully unfrozen pre-training strategy on 1.2T multimodal tokens that integrates a language-aligned Perception Encoder with a Qwen3-8B decoder to establish intrinsic vision-language synergy; and second, a scaled post-training pipeline featuring over 1k iterations of reinforcement learning. Crucially, we implement Parallel Coordinated Reasoning (PaCoRe) to scale test-time compute, allocating resources to scalable perceptual reasoning that explores and synthesizes diverse visual hypotheses. Consequently, despite its compact 10B footprint, STEP3-VL-10B rivals or surpasses models 10$\times$-20$\times$ larger (e.g., GLM-4.6V-106B, Qwen3-VL-235B) and top-tier proprietary flagships like Gemini 2.5 Pro and Seed-1.5-VL. Delivering best-in-class performance, it records 92.2% on MMBench and 80.11% on MMMU, while excelling in complex reasoning with 94.43% on AIME2025 and 75.95% on MathVision. We release the full model suite to provide the community with a powerful, efficient, and reproducible baseline.
DGAE: Diffusion-Guided Autoencoder for Efficient Latent Representation Learning
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Autoencoders empower state-of-the-art image and video generative models by compressing pixels into a latent space through visual tokenization. Although recent advances have alleviated the performance degradation of autoencoders under high compression ratios, addressing the training instability caused by GAN remains an open challenge. While improving spatial compression, we also aim to minimize the latent space dimensionality, enabling more efficient and compact representations. To tackle these challenges, we focus on improving the decoder's expressiveness. Concretely, we propose DGAE, which employs a diffusion model to guide the decoder in recovering informative signals that are not fully decoded from the latent representation. With this design, DGAE effectively mitigates the performance degradation under high spatial compression rates. At the same time, DGAE achieves state-of-the-art performance with a 2x smaller latent space. When integrated with Diffusion Models, DGAE demonstrates competitive performance on image generation for ImageNet-1K and shows that this compact latent representation facilitates faster convergence of the diffusion model.
Step1X-Edit: A Practical Framework for General Image Editing
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:In recent years, image editing models have witnessed remarkable and rapid development. The recent unveiling of cutting-edge multimodal models such as GPT-4o and Gemini2 Flash has introduced highly promising image editing capabilities. These models demonstrate an impressive aptitude for fulfilling a vast majority of user-driven editing requirements, marking a significant advancement in the field of image manipulation. However, there is still a large gap between the open-source algorithm with these closed-source models. Thus, in this paper, we aim to release a state-of-the-art image editing model, called Step1X-Edit, which can provide comparable performance against the closed-source models like GPT-4o and Gemini2 Flash. More specifically, we adopt the Multimodal LLM to process the reference image and the user's editing instruction. A latent embedding has been extracted and integrated with a diffusion image decoder to obtain the target image. To train the model, we build a data generation pipeline to produce a high-quality dataset. For evaluation, we develop the GEdit-Bench, a novel benchmark rooted in real-world user instructions. Experimental results on GEdit-Bench demonstrate that Step1X-Edit outperforms existing open-source baselines by a substantial margin and approaches the performance of leading proprietary models, thereby making significant contributions to the field of image editing.
Perception-R1: Pioneering Perception Policy with Reinforcement Learning
Apr 10, 2025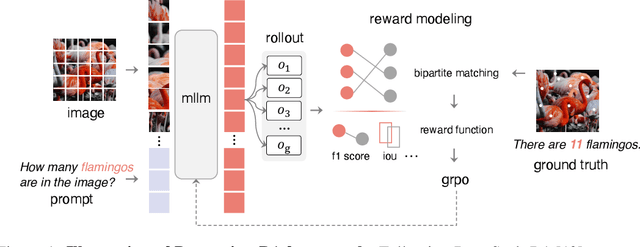
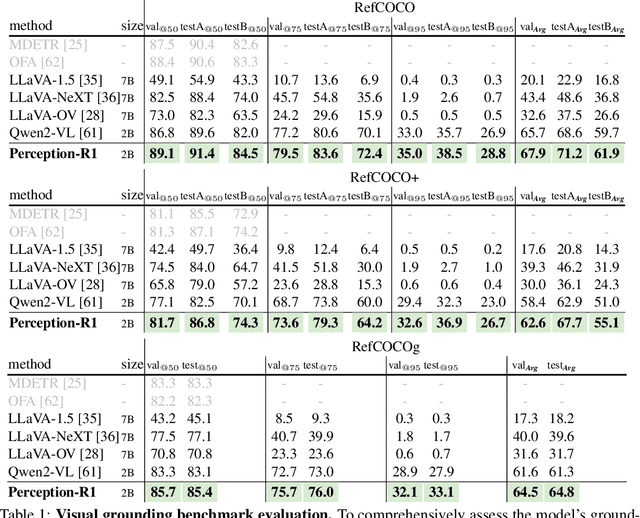
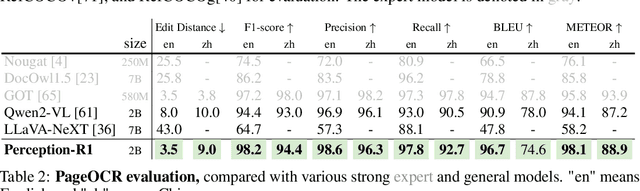
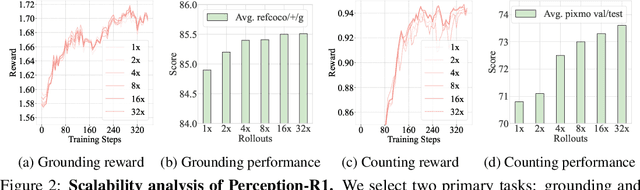
Abstract:Inspired by the success of DeepSeek-R1, we explore the potential of rule-based reinforcement learning (RL) in MLLM post-training for perception policy learning. While promising, our initial experiments reveal that incorporating a thinking process through RL does not consistently lead to performance gains across all visual perception tasks. This leads us to delve into the essential role of RL in the context of visual perception. In this work, we return to the fundamentals and explore the effects of RL on different perception tasks. We observe that the perceptual complexity is a major factor in determining the effectiveness of RL. We also observe that reward design plays a crucial role in further approching the upper limit of model perception. To leverage these findings, we propose Perception-R1, a scalable RL framework using GRPO during MLLM post-training. With a standard Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct, Perception-R1 achieves +4.2% on RefCOCO+, +17.9% on PixMo-Count, +4.2% on PageOCR, and notably, 31.9% AP on COCO2017 val for the first time, establishing a strong baseline for perception policy learning.
Perception in Reflection
Apr 09, 2025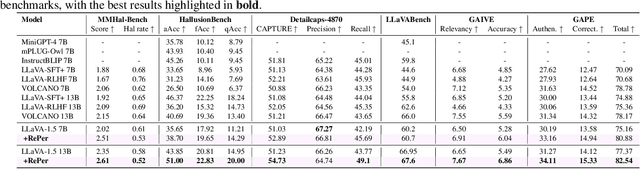
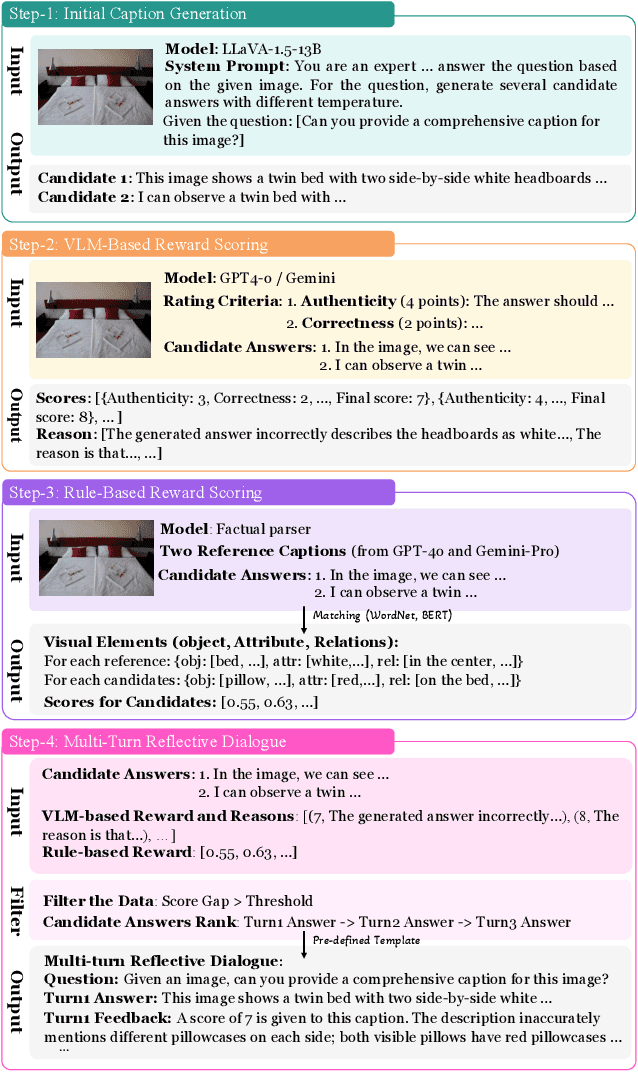
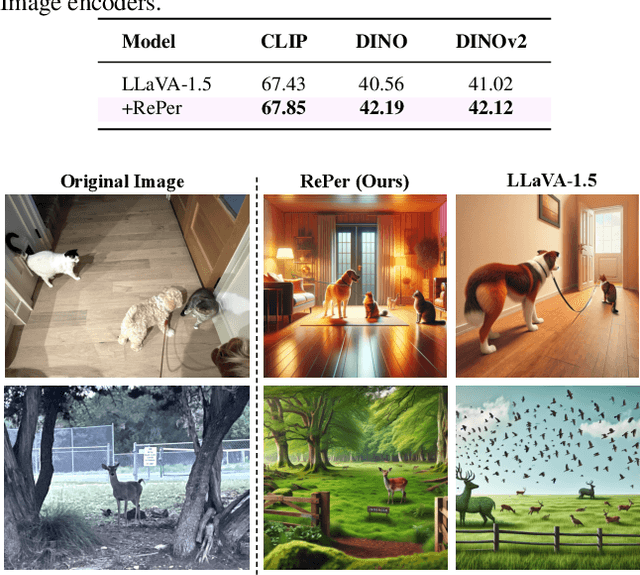

Abstract:We present a perception in reflection paradigm designed to transcend the limitations of current large vision-language models (LVLMs), which are expected yet often fail to achieve perfect perception initially. Specifically, we propose Reflective Perception (RePer), a dual-model reflection mechanism that systematically alternates between policy and critic models, enables iterative refinement of visual perception. This framework is powered by Reflective Perceptual Learning (RPL), which reinforces intrinsic reflective capabilities through a methodically constructed visual reflection dataset and reflective unlikelihood training. Comprehensive experimental evaluation demonstrates RePer's quantifiable improvements in image understanding, captioning precision, and hallucination reduction. Notably, RePer achieves strong alignment between model attention patterns and human visual focus, while RPL optimizes fine-grained and free-form preference alignment. These advancements establish perception in reflection as a robust paradigm for future multimodal agents, particularly in tasks requiring complex reasoning and multi-step manipulation.
Taming Teacher Forcing for Masked Autoregressive Video Generation
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:We introduce MAGI, a hybrid video generation framework that combines masked modeling for intra-frame generation with causal modeling for next-frame generation. Our key innovation, Complete Teacher Forcing (CTF), conditions masked frames on complete observation frames rather than masked ones (namely Masked Teacher Forcing, MTF), enabling a smooth transition from token-level (patch-level) to frame-level autoregressive generation. CTF significantly outperforms MTF, achieving a +23% improvement in FVD scores on first-frame conditioned video prediction. To address issues like exposure bias, we employ targeted training strategies, setting a new benchmark in autoregressive video generation. Experiments show that MAGI can generate long, coherent video sequences exceeding 100 frames, even when trained on as few as 16 frames, highlighting its potential for scalable, high-quality video generation.
General OCR Theory: Towards OCR-2.0 via a Unified End-to-end Model
Sep 03, 2024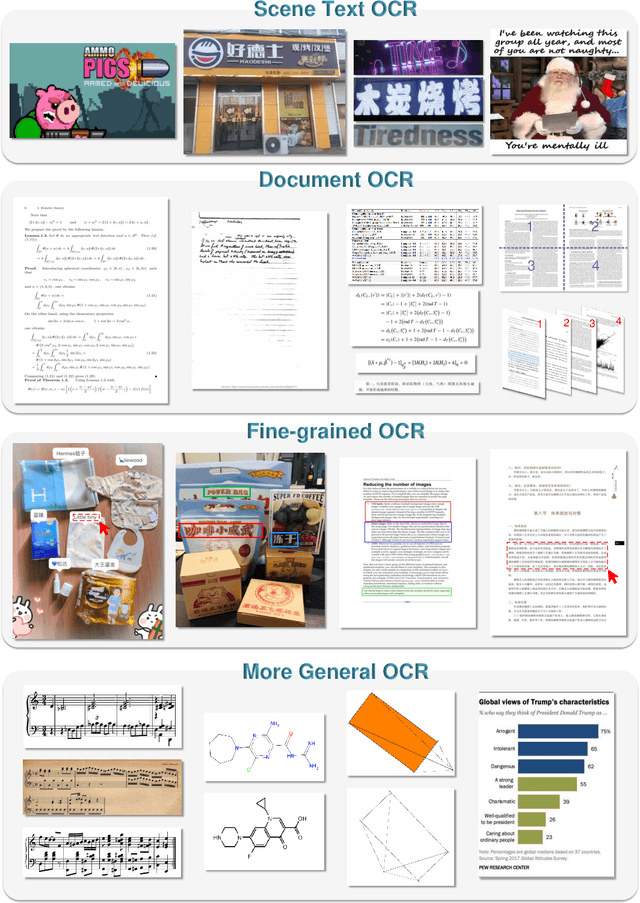
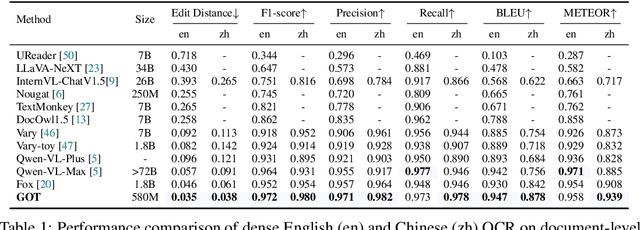
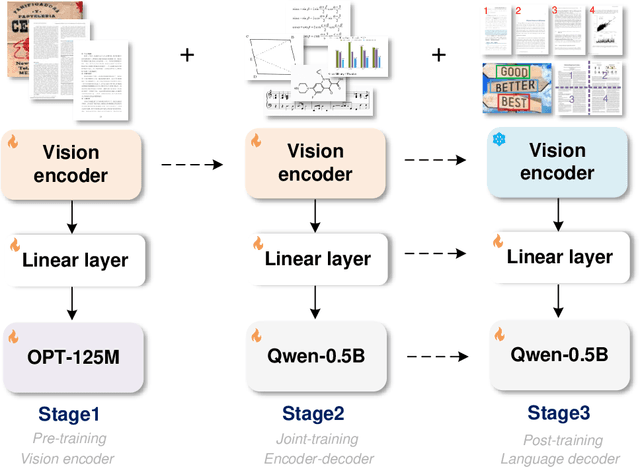

Abstract:Traditional OCR systems (OCR-1.0) are increasingly unable to meet people's usage due to the growing demand for intelligent processing of man-made optical characters. In this paper, we collectively refer to all artificial optical signals (e.g., plain texts, math/molecular formulas, tables, charts, sheet music, and even geometric shapes) as "characters" and propose the General OCR Theory along with an excellent model, namely GOT, to promote the arrival of OCR-2.0. The GOT, with 580M parameters, is a unified, elegant, and end-to-end model, consisting of a high-compression encoder and a long-contexts decoder. As an OCR-2.0 model, GOT can handle all the above "characters" under various OCR tasks. On the input side, the model supports commonly used scene- and document-style images in slice and whole-page styles. On the output side, GOT can generate plain or formatted results (markdown/tikz/smiles/kern) via an easy prompt. Besides, the model enjoys interactive OCR features, i.e., region-level recognition guided by coordinates or colors. Furthermore, we also adapt dynamic resolution and multi-page OCR technologies to GOT for better practicality. In experiments, we provide sufficient results to prove the superiority of our model.
DreamBench++: A Human-Aligned Benchmark for Personalized Image Generation
Jun 24, 2024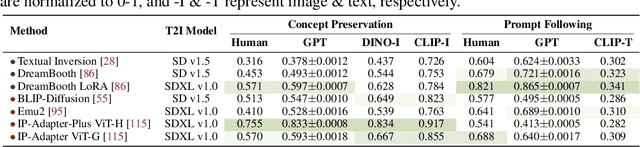



Abstract:Personalized image generation holds great promise in assisting humans in everyday work and life due to its impressive function in creatively generating personalized content. However, current evaluations either are automated but misalign with humans or require human evaluations that are time-consuming and expensive. In this work, we present DreamBench++, a human-aligned benchmark automated by advanced multimodal GPT models. Specifically, we systematically design the prompts to let GPT be both human-aligned and self-aligned, empowered with task reinforcement. Further, we construct a comprehensive dataset comprising diverse images and prompts. By benchmarking 7 modern generative models, we demonstrate that DreamBench++ results in significantly more human-aligned evaluation, helping boost the community with innovative findings.
DreamLLM: Synergistic Multimodal Comprehension and Creation
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:This paper presents DreamLLM, a learning framework that first achieves versatile Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) empowered with frequently overlooked synergy between multimodal comprehension and creation. DreamLLM operates on two fundamental principles. The first focuses on the generative modeling of both language and image posteriors by direct sampling in the raw multimodal space. This approach circumvents the limitations and information loss inherent to external feature extractors like CLIP, and a more thorough multimodal understanding is obtained. Second, DreamLLM fosters the generation of raw, interleaved documents, modeling both text and image contents, along with unstructured layouts. This allows DreamLLM to learn all conditional, marginal, and joint multimodal distributions effectively. As a result, DreamLLM is the first MLLM capable of generating free-form interleaved content. Comprehensive experiments highlight DreamLLM's superior performance as a zero-shot multimodal generalist, reaping from the enhanced learning synergy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge