Yumeng Li
PLACID: Identity-Preserving Multi-Object Compositing via Video Diffusion with Synthetic Trajectories
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in generative AI have dramatically improved photorealistic image synthesis, yet they fall short for studio-level multi-object compositing. This task demands simultaneous (i) near-perfect preservation of each item's identity, (ii) precise background and color fidelity, (iii) layout and design elements control, and (iv) complete, appealing displays showcasing all objects. However, current state-of-the-art models often alter object details, omit or duplicate objects, and produce layouts with incorrect relative sizing or inconsistent item presentations. To bridge this gap, we introduce PLACID, a framework that transforms a collection of object images into an appealing multi-object composite. Our approach makes two main contributions. First, we leverage a pretrained image-to-video (I2V) diffusion model with text control to preserve objects consistency, identities, and background details by exploiting temporal priors from videos. Second, we propose a novel data curation strategy that generates synthetic sequences where randomly placed objects smoothly move to their target positions. This synthetic data aligns with the video model's temporal priors during training. At inference, objects initialized at random positions consistently converge into coherent layouts guided by text, with the final frame serving as the composite image. Extensive quantitative evaluations and user studies demonstrate that PLACID surpasses state-of-the-art methods in multi-object compositing, achieving superior identity, background, and color preservation, with less omitted objects and visually appealing results.
Motion-example-controlled Co-speech Gesture Generation Leveraging Large Language Models
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:The automatic generation of controllable co-speech gestures has recently gained growing attention. While existing systems typically achieve gesture control through predefined categorical labels or implicit pseudo-labels derived from motion examples, these approaches often compromise the rich details present in the original motion examples. We present MECo, a framework for motion-example-controlled co-speech gesture generation by leveraging large language models (LLMs). Our method capitalizes on LLMs' comprehension capabilities through fine-tuning to simultaneously interpret speech audio and motion examples, enabling the synthesis of gestures that preserve example-specific characteristics while maintaining speech congruence. Departing from conventional pseudo-labeling paradigms, we position motion examples as explicit query contexts within the prompt structure to guide gesture generation. Experimental results demonstrate state-of-the-art performance across three metrics: Fr\'echet Gesture Distance (FGD), motion diversity, and example-gesture similarity. Furthermore, our framework enables granular control of individual body parts and accommodates diverse input modalities including motion clips, static poses, human video sequences, and textual descriptions. Our code, pre-trained models, and videos are available at https://robinwitch.github.io/MECo-Page.
RGBAvatar: Reduced Gaussian Blendshapes for Online Modeling of Head Avatars
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:We present Reduced Gaussian Blendshapes Avatar (RGBAvatar), a method for reconstructing photorealistic, animatable head avatars at speeds sufficient for on-the-fly reconstruction. Unlike prior approaches that utilize linear bases from 3D morphable models (3DMM) to model Gaussian blendshapes, our method maps tracked 3DMM parameters into reduced blendshape weights with an MLP, leading to a compact set of blendshape bases. The learned compact base composition effectively captures essential facial details for specific individuals, and does not rely on the fixed base composition weights of 3DMM, leading to enhanced reconstruction quality and higher efficiency. To further expedite the reconstruction process, we develop a novel color initialization estimation method and a batch-parallel Gaussian rasterization process, achieving state-of-the-art quality with training throughput of about 630 images per second. Moreover, we propose a local-global sampling strategy that enables direct on-the-fly reconstruction, immediately reconstructing the model as video streams in real time while achieving quality comparable to offline settings. Our source code is available at https://github.com/gapszju/RGBAvatar.
Dual Mutual Learning Network with Global-local Awareness for RGB-D Salient Object Detection
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:RGB-D salient object detection (SOD), aiming to highlight prominent regions of a given scene by jointly modeling RGB and depth information, is one of the challenging pixel-level prediction tasks. Recently, the dual-attention mechanism has been devoted to this area due to its ability to strengthen the detection process. However, most existing methods directly fuse attentional cross-modality features under a manual-mandatory fusion paradigm without considering the inherent discrepancy between the RGB and depth, which may lead to a reduction in performance. Moreover, the long-range dependencies derived from global and local information make it difficult to leverage a unified efficient fusion strategy. Hence, in this paper, we propose the GL-DMNet, a novel dual mutual learning network with global-local awareness. Specifically, we present a position mutual fusion module and a channel mutual fusion module to exploit the interdependencies among different modalities in spatial and channel dimensions. Besides, we adopt an efficient decoder based on cascade transformer-infused reconstruction to integrate multi-level fusion features jointly. Extensive experiments on six benchmark datasets demonstrate that our proposed GL-DMNet performs better than 24 RGB-D SOD methods, achieving an average improvement of ~3% across four evaluation metrics compared to the second-best model (S3Net). Codes and results are available at https://github.com/kingkung2016/GL-DMNet.
Slow Perception: Let's Perceive Geometric Figures Step-by-step
Dec 30, 2024



Abstract:Recently, "visual o1" began to enter people's vision, with expectations that this slow-thinking design can solve visual reasoning tasks, especially geometric math problems. However, the reality is that current LVLMs (Large Vision Language Models) can hardly even accurately copy a geometric figure, let alone truly understand the complex inherent logic and spatial relationships within geometric shapes. We believe accurate copying (strong perception) is the first step to visual o1. Accordingly, we introduce the concept of "slow perception" (SP), which guides the model to gradually perceive basic point-line combinations, as our humans, reconstruct complex geometric structures progressively. There are two-fold stages in SP: a) perception decomposition. Perception is not instantaneous. In this stage, complex geometric figures are broken down into basic simple units to unify geometry representation. b) perception flow, which acknowledges that accurately tracing a line is not an easy task. This stage aims to avoid "long visual jumps" in regressing line segments by using a proposed "perceptual ruler" to trace each line stroke-by-stroke. Surprisingly, such a human-like perception manner enjoys an inference time scaling law -- the slower, the better. Researchers strive to speed up the model's perception in the past, but we slow it down again, allowing the model to read the image step-by-step and carefully.
Enhancing Visual Reasoning with Autonomous Imagination in Multimodal Large Language Models
Nov 27, 2024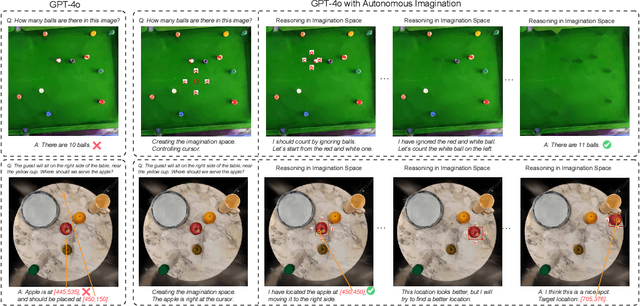
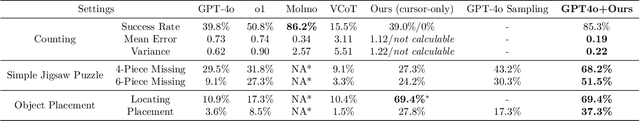
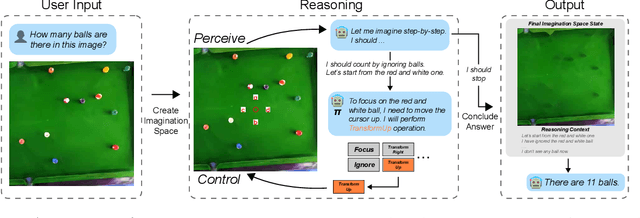
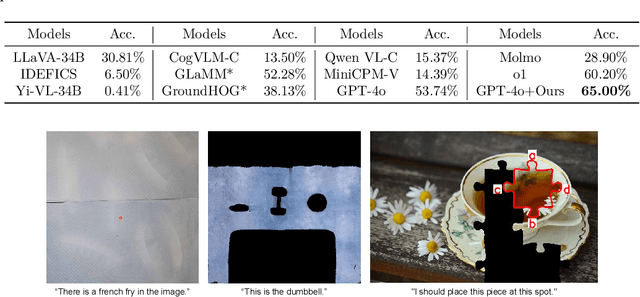
Abstract:There have been recent efforts to extend the Chain-of-Thought (CoT) paradigm to Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by finding visual clues in the input scene, advancing the visual reasoning ability of MLLMs. However, current approaches are specially designed for the tasks where clue finding plays a major role in the whole reasoning process, leading to the difficulty in handling complex visual scenes where clue finding does not actually simplify the whole reasoning task. To deal with this challenge, we propose a new visual reasoning paradigm enabling MLLMs to autonomously modify the input scene to new ones based on its reasoning status, such that CoT is reformulated as conducting simple closed-loop decision-making and reasoning steps under a sequence of imagined visual scenes, leading to natural and general CoT construction. To implement this paradigm, we introduce a novel plug-and-play imagination space, where MLLMs conduct visual modifications through operations like focus, ignore, and transform based on their native reasoning ability without specific training. We validate our approach through a benchmark spanning dense counting, simple jigsaw puzzle solving, and object placement, challenging the reasoning ability beyond clue finding. The results verify that while existing techniques fall short, our approach enables MLLMs to effectively reason step by step through autonomous imagination. Project page: https://future-item.github.io/autoimagine-site.
Physics-informed Machine Learning for Battery Pack Thermal Management
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:With the popularity of electric vehicles, the demand for lithium-ion batteries is increasing. Temperature significantly influences the performance and safety of batteries. Battery thermal management systems can effectively control the temperature of batteries; therefore, the performance and safety can be ensured. However, the development process of battery thermal management systems is time-consuming and costly due to the extensive training dataset needed by data-driven models requiring enormous computational costs for finite element analysis. Therefore, a new approach to constructing surrogate models is needed in the era of AI. Physics-informed machine learning enforces the physical laws in surrogate models, making it the perfect candidate for estimating battery pack temperature distribution. In this study, we first developed a 21700 battery pack indirect liquid cooling system with cold plates on the top and bottom with thermal paste surrounding the battery cells. Then, the simplified finite element model was built based on experiment results. Due to the high coolant flow rate, the cold plates can be considered as constant temperature boundaries, while battery cells are the heat sources. The physics-informed convolutional neural network served as a surrogate model to estimate the temperature distribution of the battery pack. The loss function was constructed considering the heat conduction equation based on the finite difference method. The physics-informed loss function helped the convergence of the training process with less data. As a result, the physics-informed convolutional neural network showed more than 15 percents improvement in accuracy compared to the data-driven method with the same training data.
Enabling Synergistic Full-Body Control in Prompt-Based Co-Speech Motion Generation
Oct 01, 2024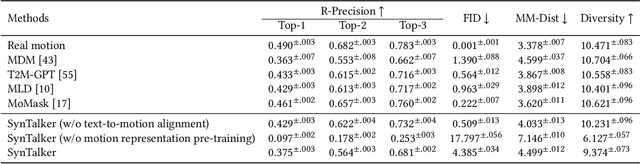
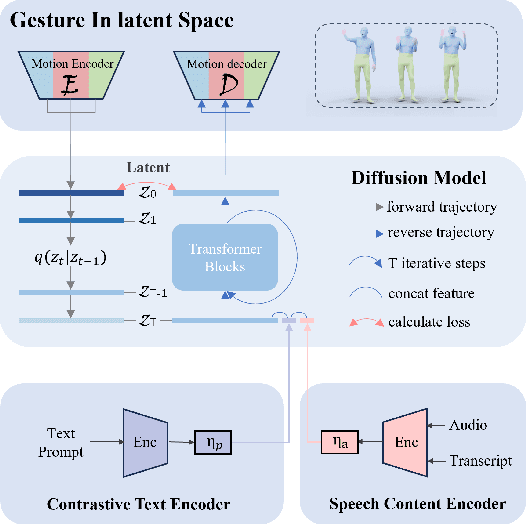
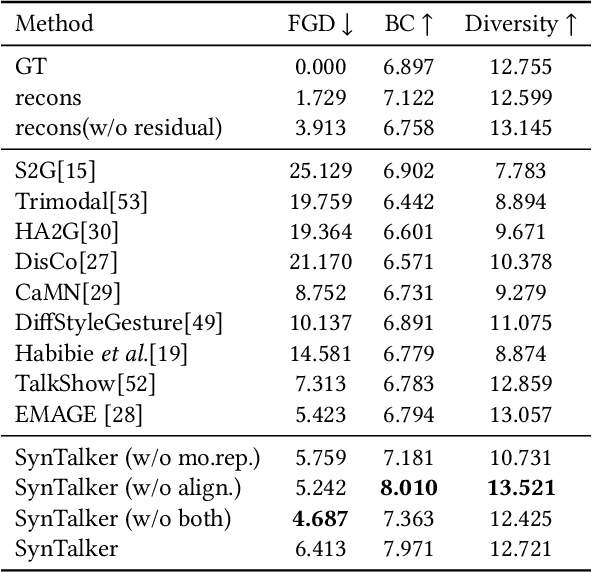
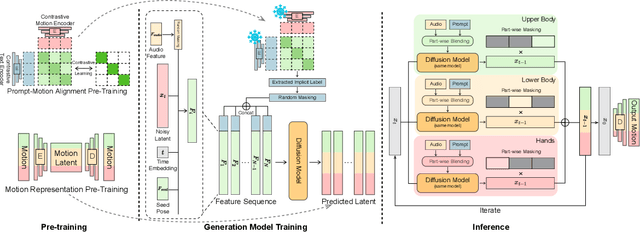
Abstract:Current co-speech motion generation approaches usually focus on upper body gestures following speech contents only, while lacking supporting the elaborate control of synergistic full-body motion based on text prompts, such as talking while walking. The major challenges lie in 1) the existing speech-to-motion datasets only involve highly limited full-body motions, making a wide range of common human activities out of training distribution; 2) these datasets also lack annotated user prompts. To address these challenges, we propose SynTalker, which utilizes the off-the-shelf text-to-motion dataset as an auxiliary for supplementing the missing full-body motion and prompts. The core technical contributions are two-fold. One is the multi-stage training process which obtains an aligned embedding space of motion, speech, and prompts despite the significant distributional mismatch in motion between speech-to-motion and text-to-motion datasets. Another is the diffusion-based conditional inference process, which utilizes the separate-then-combine strategy to realize fine-grained control of local body parts. Extensive experiments are conducted to verify that our approach supports precise and flexible control of synergistic full-body motion generation based on both speeches and user prompts, which is beyond the ability of existing approaches.
Domain-Aware Fine-Tuning of Foundation Models
Jul 03, 2024Abstract:Foundation models (FMs) have revolutionized computer vision, enabling effective learning across different domains. However, their performance under domain shift is yet underexplored. This paper investigates the zero-shot domain adaptation potential of FMs by comparing different backbone architectures and introducing novel domain-aware components that leverage domain related textual embeddings. We propose domain adaptive normalization, termed as Domino, which explicitly leverages domain embeddings during fine-tuning, thus making the model domain aware. Ultimately, Domino enables more robust computer vision models that can adapt effectively to various unseen domains.
Label-free Neural Semantic Image Synthesis
Jul 01, 2024



Abstract:Recent work has shown great progress in integrating spatial conditioning to control large, pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models. Despite these advances, existing methods describe the spatial image content using hand-crafted conditioning inputs, which are either semantically ambiguous (e.g., edges) or require expensive manual annotations (e.g., semantic segmentation). To address these limitations, we propose a new label-free way of conditioning diffusion models to enable fine-grained spatial control. We introduce the concept of neural semantic image synthesis, which uses neural layouts extracted from pre-trained foundation models as conditioning. Neural layouts are advantageous as they provide rich descriptions of the desired image, containing both semantics and detailed geometry of the scene. We experimentally show that images synthesized via neural semantic image synthesis achieve similar or superior pixel-level alignment of semantic classes compared to those created using expensive semantic label maps. At the same time, they capture better semantics, instance separation, and object orientation than other label-free conditioning options, such as edges or depth. Moreover, we show that images generated by neural layout conditioning can effectively augment real data for training various perception tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge