Ziang Qin
Pre-Training Meta-Rule Selection Policy for Visual Generative Abductive Learning
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Visual generative abductive learning studies jointly training symbol-grounded neural visual generator and inducing logic rules from data, such that after learning, the visual generation process is guided by the induced logic rules. A major challenge for this task is to reduce the time cost of logic abduction during learning, an essential step when the logic symbol set is large and the logic rule to induce is complicated. To address this challenge, we propose a pre-training method for obtaining meta-rule selection policy for the recently proposed visual generative learning approach AbdGen [Peng et al., 2023], aiming at significantly reducing the candidate meta-rule set and pruning the search space. The selection model is built based on the embedding representation of both symbol grounding of cases and meta-rules, which can be effectively integrated with both neural model and logic reasoning system. The pre-training process is done on pure symbol data, not involving symbol grounding learning of raw visual inputs, making the entire learning process low-cost. An additional interesting observation is that the selection policy can rectify symbol grounding errors unseen during pre-training, which is resulted from the memorization ability of attention mechanism and the relative stability of symbolic patterns. Experimental results show that our method is able to effectively address the meta-rule selection problem for visual abduction, boosting the efficiency of visual generative abductive learning. Code is available at https://github.com/future-item/metarule-select.
Enhancing Visual Reasoning with Autonomous Imagination in Multimodal Large Language Models
Nov 27, 2024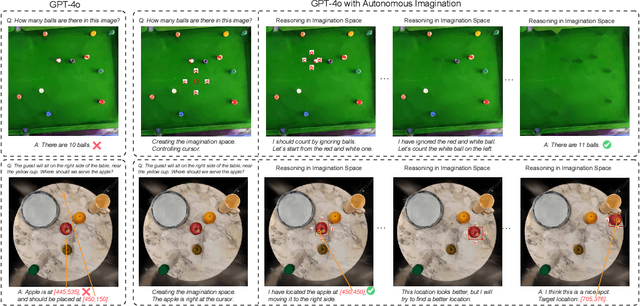
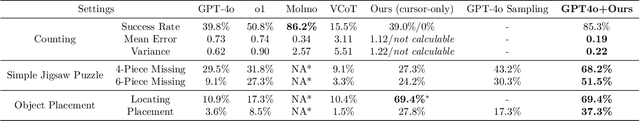
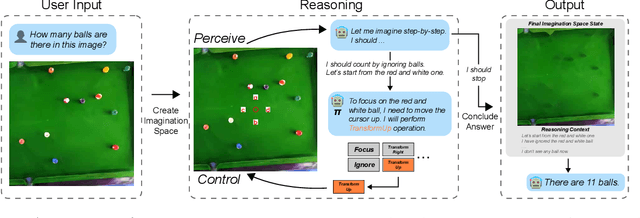
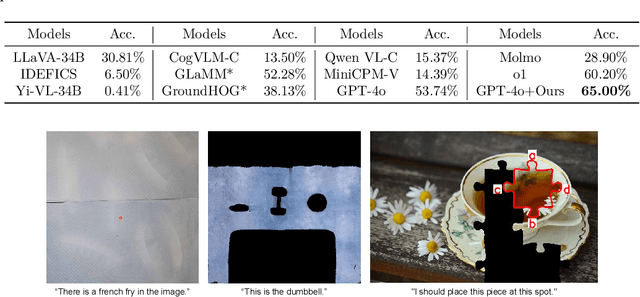
Abstract:There have been recent efforts to extend the Chain-of-Thought (CoT) paradigm to Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by finding visual clues in the input scene, advancing the visual reasoning ability of MLLMs. However, current approaches are specially designed for the tasks where clue finding plays a major role in the whole reasoning process, leading to the difficulty in handling complex visual scenes where clue finding does not actually simplify the whole reasoning task. To deal with this challenge, we propose a new visual reasoning paradigm enabling MLLMs to autonomously modify the input scene to new ones based on its reasoning status, such that CoT is reformulated as conducting simple closed-loop decision-making and reasoning steps under a sequence of imagined visual scenes, leading to natural and general CoT construction. To implement this paradigm, we introduce a novel plug-and-play imagination space, where MLLMs conduct visual modifications through operations like focus, ignore, and transform based on their native reasoning ability without specific training. We validate our approach through a benchmark spanning dense counting, simple jigsaw puzzle solving, and object placement, challenging the reasoning ability beyond clue finding. The results verify that while existing techniques fall short, our approach enables MLLMs to effectively reason step by step through autonomous imagination. Project page: https://future-item.github.io/autoimagine-site.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge