Youyi Zheng
3DTeethSAM: Taming SAM2 for 3D Teeth Segmentation
Dec 12, 2025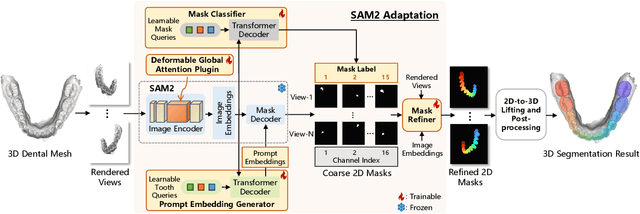
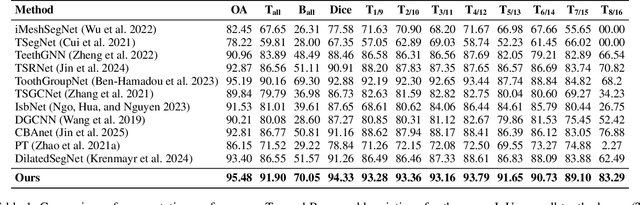
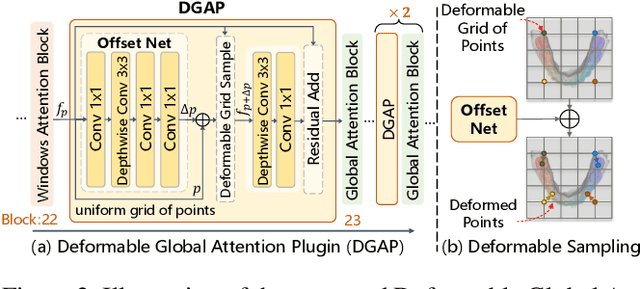
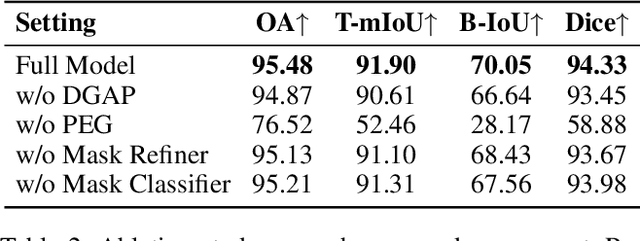
Abstract:3D teeth segmentation, involving the localization of tooth instances and their semantic categorization in 3D dental models, is a critical yet challenging task in digital dentistry due to the complexity of real-world dentition. In this paper, we propose 3DTeethSAM, an adaptation of the Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) for 3D teeth segmentation. SAM2 is a pretrained foundation model for image and video segmentation, demonstrating a strong backbone in various downstream scenarios. To adapt SAM2 for 3D teeth data, we render images of 3D teeth models from predefined views, apply SAM2 for 2D segmentation, and reconstruct 3D results using 2D-3D projections. Since SAM2's performance depends on input prompts and its initial outputs often have deficiencies, and given its class-agnostic nature, we introduce three light-weight learnable modules: (1) a prompt embedding generator to derive prompt embeddings from image embeddings for accurate mask decoding, (2) a mask refiner to enhance SAM2's initial segmentation results, and (3) a mask classifier to categorize the generated masks. Additionally, we incorporate Deformable Global Attention Plugins (DGAP) into SAM2's image encoder. The DGAP enhances both the segmentation accuracy and the speed of the training process. Our method has been validated on the 3DTeethSeg benchmark, achieving an IoU of 91.90% on high-resolution 3D teeth meshes, establishing a new state-of-the-art in the field.
Detecting Dental Landmarks from Intraoral 3D Scans: the 3DTeethLand challenge
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Teeth landmark detection is a critical task in modern clinical orthodontics. Their precise identification enables advanced diagnostics, facilitates personalized treatment strategies, and supports more effective monitoring of treatment progress in clinical dentistry. However, several significant challenges may arise due to the intricate geometry of individual teeth and the substantial variations observed across different individuals. To address these complexities, the development of advanced techniques, especially through the application of deep learning, is essential for the precise and reliable detection of 3D tooth landmarks. In this context, the 3DTeethLand challenge was held in collaboration with the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) in 2024, calling for algorithms focused on teeth landmark detection from intraoral 3D scans. This challenge introduced the first publicly available dataset for 3D teeth landmark detection, offering a valuable resource to assess the state-of-the-art methods in this task and encourage the community to provide methodological contributions towards the resolution of their problem with significant clinical implications.
Motion-example-controlled Co-speech Gesture Generation Leveraging Large Language Models
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:The automatic generation of controllable co-speech gestures has recently gained growing attention. While existing systems typically achieve gesture control through predefined categorical labels or implicit pseudo-labels derived from motion examples, these approaches often compromise the rich details present in the original motion examples. We present MECo, a framework for motion-example-controlled co-speech gesture generation by leveraging large language models (LLMs). Our method capitalizes on LLMs' comprehension capabilities through fine-tuning to simultaneously interpret speech audio and motion examples, enabling the synthesis of gestures that preserve example-specific characteristics while maintaining speech congruence. Departing from conventional pseudo-labeling paradigms, we position motion examples as explicit query contexts within the prompt structure to guide gesture generation. Experimental results demonstrate state-of-the-art performance across three metrics: Fr\'echet Gesture Distance (FGD), motion diversity, and example-gesture similarity. Furthermore, our framework enables granular control of individual body parts and accommodates diverse input modalities including motion clips, static poses, human video sequences, and textual descriptions. Our code, pre-trained models, and videos are available at https://robinwitch.github.io/MECo-Page.
DiffLocks: Generating 3D Hair from a Single Image using Diffusion Models
May 09, 2025



Abstract:We address the task of generating 3D hair geometry from a single image, which is challenging due to the diversity of hairstyles and the lack of paired image-to-3D hair data. Previous methods are primarily trained on synthetic data and cope with the limited amount of such data by using low-dimensional intermediate representations, such as guide strands and scalp-level embeddings, that require post-processing to decode, upsample, and add realism. These approaches fail to reconstruct detailed hair, struggle with curly hair, or are limited to handling only a few hairstyles. To overcome these limitations, we propose DiffLocks, a novel framework that enables detailed reconstruction of a wide variety of hairstyles directly from a single image. First, we address the lack of 3D hair data by automating the creation of the largest synthetic hair dataset to date, containing 40K hairstyles. Second, we leverage the synthetic hair dataset to learn an image-conditioned diffusion-transfomer model that generates accurate 3D strands from a single frontal image. By using a pretrained image backbone, our method generalizes to in-the-wild images despite being trained only on synthetic data. Our diffusion model predicts a scalp texture map in which any point in the map contains the latent code for an individual hair strand. These codes are directly decoded to 3D strands without post-processing techniques. Representing individual strands, instead of guide strands, enables the transformer to model the detailed spatial structure of complex hairstyles. With this, DiffLocks can recover highly curled hair, like afro hairstyles, from a single image for the first time. Data and code is available at https://radualexandru.github.io/difflocks/
RGBAvatar: Reduced Gaussian Blendshapes for Online Modeling of Head Avatars
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:We present Reduced Gaussian Blendshapes Avatar (RGBAvatar), a method for reconstructing photorealistic, animatable head avatars at speeds sufficient for on-the-fly reconstruction. Unlike prior approaches that utilize linear bases from 3D morphable models (3DMM) to model Gaussian blendshapes, our method maps tracked 3DMM parameters into reduced blendshape weights with an MLP, leading to a compact set of blendshape bases. The learned compact base composition effectively captures essential facial details for specific individuals, and does not rely on the fixed base composition weights of 3DMM, leading to enhanced reconstruction quality and higher efficiency. To further expedite the reconstruction process, we develop a novel color initialization estimation method and a batch-parallel Gaussian rasterization process, achieving state-of-the-art quality with training throughput of about 630 images per second. Moreover, we propose a local-global sampling strategy that enables direct on-the-fly reconstruction, immediately reconstructing the model as video streams in real time while achieving quality comparable to offline settings. Our source code is available at https://github.com/gapszju/RGBAvatar.
SG-NeRF: Neural Surface Reconstruction with Scene Graph Optimization
Jul 17, 2024Abstract:3D surface reconstruction from images is essential for numerous applications. Recently, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) have emerged as a promising framework for 3D modeling. However, NeRFs require accurate camera poses as input, and existing methods struggle to handle significantly noisy pose estimates (i.e., outliers), which are commonly encountered in real-world scenarios. To tackle this challenge, we present a novel approach that optimizes radiance fields with scene graphs to mitigate the influence of outlier poses. Our method incorporates an adaptive inlier-outlier confidence estimation scheme based on scene graphs, emphasizing images of high compatibility with the neighborhood and consistency in the rendering quality. We also introduce an effective intersection-over-union (IoU) loss to optimize the camera pose and surface geometry, together with a coarse-to-fine strategy to facilitate the training. Furthermore, we propose a new dataset containing typical outlier poses for a detailed evaluation. Experimental results on various datasets consistently demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method over existing approaches, showcasing its robustness in handling outliers and producing high-quality 3D reconstructions. Our code and data are available at: \url{https://github.com/Iris-cyy/SG-NeRF}.
InfoNorm: Mutual Information Shaping of Normals for Sparse-View Reconstruction
Jul 17, 2024



Abstract:3D surface reconstruction from multi-view images is essential for scene understanding and interaction. However, complex indoor scenes pose challenges such as ambiguity due to limited observations. Recent implicit surface representations, such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) and signed distance functions (SDFs), employ various geometric priors to resolve the lack of observed information. Nevertheless, their performance heavily depends on the quality of the pre-trained geometry estimation models. To ease such dependence, we propose regularizing the geometric modeling by explicitly encouraging the mutual information among surface normals of highly correlated scene points. In this way, the geometry learning process is modulated by the second-order correlations from noisy (first-order) geometric priors, thus eliminating the bias due to poor generalization. Additionally, we introduce a simple yet effective scheme that utilizes semantic and geometric features to identify correlated points, enhancing their mutual information accordingly. The proposed technique can serve as a plugin for SDF-based neural surface representations. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed in improving the surface reconstruction quality of major states of the arts. Our code is available at: \url{https://github.com/Muliphein/InfoNorm}.
MonoHair: High-Fidelity Hair Modeling from a Monocular Video
Mar 27, 2024



Abstract:Undoubtedly, high-fidelity 3D hair is crucial for achieving realism, artistic expression, and immersion in computer graphics. While existing 3D hair modeling methods have achieved impressive performance, the challenge of achieving high-quality hair reconstruction persists: they either require strict capture conditions, making practical applications difficult, or heavily rely on learned prior data, obscuring fine-grained details in images. To address these challenges, we propose MonoHair,a generic framework to achieve high-fidelity hair reconstruction from a monocular video, without specific requirements for environments. Our approach bifurcates the hair modeling process into two main stages: precise exterior reconstruction and interior structure inference. The exterior is meticulously crafted using our Patch-based Multi-View Optimization (PMVO). This method strategically collects and integrates hair information from multiple views, independent of prior data, to produce a high-fidelity exterior 3D line map. This map not only captures intricate details but also facilitates the inference of the hair's inner structure. For the interior, we employ a data-driven, multi-view 3D hair reconstruction method. This method utilizes 2D structural renderings derived from the reconstructed exterior, mirroring the synthetic 2D inputs used during training. This alignment effectively bridges the domain gap between our training data and real-world data, thereby enhancing the accuracy and reliability of our interior structure inference. Lastly, we generate a strand model and resolve the directional ambiguity by our hair growth algorithm. Our experiments demonstrate that our method exhibits robustness across diverse hairstyles and achieves state-of-the-art performance. For more results, please refer to our project page https://keyuwu-cs.github.io/MonoHair/.
AniDress: Animatable Loose-Dressed Avatar from Sparse Views Using Garment Rigging Model
Jan 27, 2024Abstract:Recent communities have seen significant progress in building photo-realistic animatable avatars from sparse multi-view videos. However, current workflows struggle to render realistic garment dynamics for loose-fitting characters as they predominantly rely on naked body models for human modeling while leaving the garment part un-modeled. This is mainly due to that the deformations yielded by loose garments are highly non-rigid, and capturing such deformations often requires dense views as supervision. In this paper, we introduce AniDress, a novel method for generating animatable human avatars in loose clothes using very sparse multi-view videos (4-8 in our setting). To allow the capturing and appearance learning of loose garments in such a situation, we employ a virtual bone-based garment rigging model obtained from physics-based simulation data. Such a model allows us to capture and render complex garment dynamics through a set of low-dimensional bone transformations. Technically, we develop a novel method for estimating temporal coherent garment dynamics from a sparse multi-view video. To build a realistic rendering for unseen garment status using coarse estimations, a pose-driven deformable neural radiance field conditioned on both body and garment motions is introduced, providing explicit control of both parts. At test time, the new garment poses can be captured from unseen situations, derived from a physics-based or neural network-based simulator to drive unseen garment dynamics. To evaluate our approach, we create a multi-view dataset that captures loose-dressed performers with diverse motions. Experiments show that our method is able to render natural garment dynamics that deviate highly from the body and generalize well to both unseen views and poses, surpassing the performance of existing methods. The code and data will be publicly available.
VDN-NeRF: Resolving Shape-Radiance Ambiguity via View-Dependence Normalization
Mar 31, 2023



Abstract:We propose VDN-NeRF, a method to train neural radiance fields (NeRFs) for better geometry under non-Lambertian surface and dynamic lighting conditions that cause significant variation in the radiance of a point when viewed from different angles. Instead of explicitly modeling the underlying factors that result in the view-dependent phenomenon, which could be complex yet not inclusive, we develop a simple and effective technique that normalizes the view-dependence by distilling invariant information already encoded in the learned NeRFs. We then jointly train NeRFs for view synthesis with view-dependence normalization to attain quality geometry. Our experiments show that even though shape-radiance ambiguity is inevitable, the proposed normalization can minimize its effect on geometry, which essentially aligns the optimal capacity needed for explaining view-dependent variations. Our method applies to various baselines and significantly improves geometry without changing the volume rendering pipeline, even if the data is captured under a moving light source. Code is available at: https://github.com/BoifZ/VDN-NeRF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge