Hamid Palangi
ScholarPeer: A Context-Aware Multi-Agent Framework for Automated Peer Review
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Automated peer review has evolved from simple text classification to structured feedback generation. However, current state-of-the-art systems still struggle with "surface-level" critiques: they excel at summarizing content but often fail to accurately assess novelty and significance or identify deep methodological flaws because they evaluate papers in a vacuum, lacking the external context a human expert possesses. In this paper, we introduce ScholarPeer, a search-enabled multi-agent framework designed to emulate the cognitive processes of a senior researcher. ScholarPeer employs a dual-stream process of context acquisition and active verification. It dynamically constructs a domain narrative using a historian agent, identifies missing comparisons via a baseline scout, and verifies claims through a multi-aspect Q&A engine, grounding the critique in live web-scale literature. We evaluate ScholarPeer on DeepReview-13K and the results demonstrate that ScholarPeer achieves significant win-rates against state-of-the-art approaches in side-by-side evaluations and reduces the gap to human-level diversity.
InfSplign: Inference-Time Spatial Alignment of Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Dec 19, 2025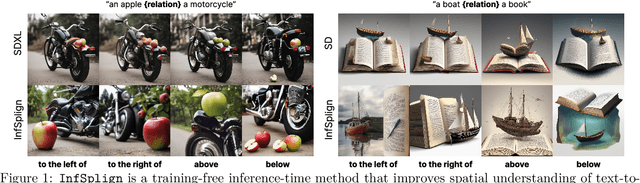
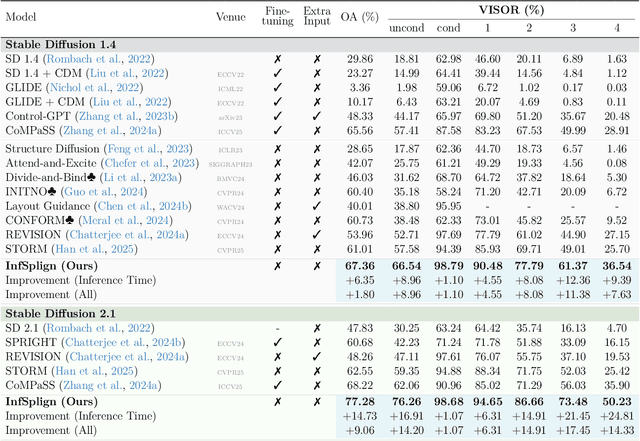
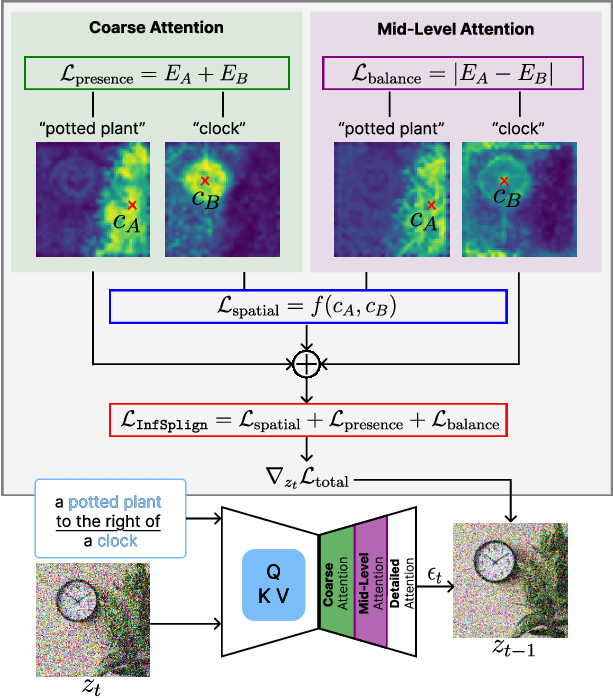
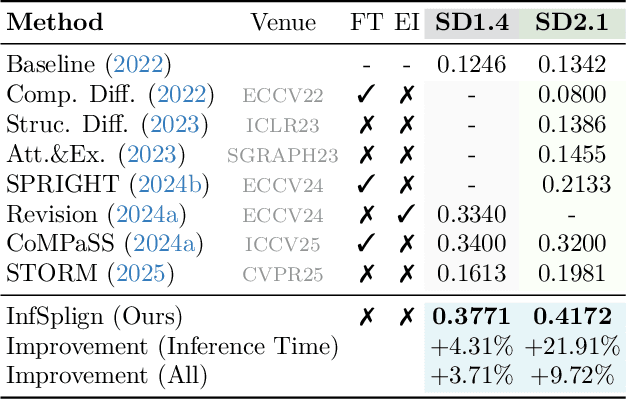
Abstract:Text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models generate high-quality images but often fail to capture the spatial relations specified in text prompts. This limitation can be traced to two factors: lack of fine-grained spatial supervision in training data and inability of text embeddings to encode spatial semantics. We introduce InfSplign, a training-free inference-time method that improves spatial alignment by adjusting the noise through a compound loss in every denoising step. Proposed loss leverages different levels of cross-attention maps extracted from the backbone decoder to enforce accurate object placement and a balanced object presence during sampling. The method is lightweight, plug-and-play, and compatible with any diffusion backbone. Our comprehensive evaluations on VISOR and T2I-CompBench show that InfSplign establishes a new state-of-the-art (to the best of our knowledge), achieving substantial performance gains over the strongest existing inference-time baselines and even outperforming the fine-tuning-based methods. Codebase is available at GitHub.
Synapse: Adaptive Arbitration of Complementary Expertise in Time Series Foundational Models
Nov 07, 2025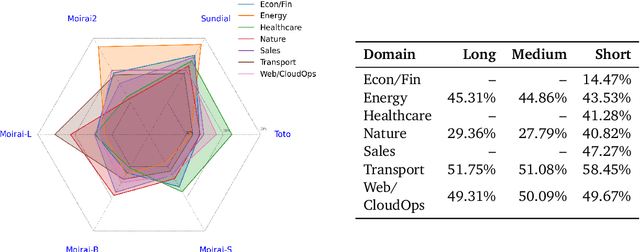
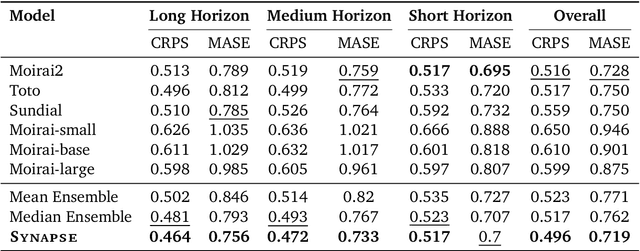
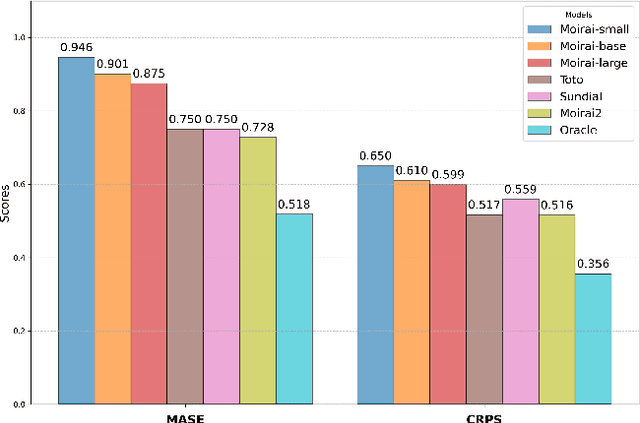
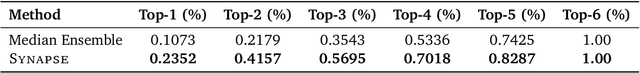
Abstract:Pre-trained Time Series Foundational Models (TSFMs) represent a significant advance, capable of forecasting diverse time series with complex characteristics, including varied seasonalities, trends, and long-range dependencies. Despite their primary goal of universal time series forecasting, their efficacy is far from uniform; divergent training protocols and data sources cause individual TSFMs to exhibit highly variable performance across different forecasting tasks, domains, and horizons. Leveraging this complementary expertise by arbitrating existing TSFM outputs presents a compelling strategy, yet this remains a largely unexplored area of research. In this paper, we conduct a thorough examination of how different TSFMs exhibit specialized performance profiles across various forecasting settings, and how we can effectively leverage this behavior in arbitration between different time series models. We specifically analyze how factors such as model selection and forecast horizon distribution can influence the efficacy of arbitration strategies. Based on this analysis, we propose Synapse, a novel arbitration framework for TSFMs. Synapse is designed to dynamically leverage a pool of TSFMs, assign and adjust predictive weights based on their relative, context-dependent performance, and construct a robust forecast distribution by adaptively sampling from the output quantiles of constituent models. Experimental results demonstrate that Synapse consistently outperforms other popular ensembling techniques as well as individual TSFMs, demonstrating Synapse's efficacy in time series forecasting.
Watch and Learn: Learning to Use Computers from Online Videos
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Computer use agents (CUAs) need to plan task workflows grounded in diverse, ever-changing applications and environments, but learning is hindered by the scarcity of large-scale, high-quality training data in the target application. Existing datasets are domain-specific, static, and costly to annotate, while current synthetic data generation methods often yield simplistic or misaligned task demonstrations. To address these limitations, we introduce Watch & Learn (W&L), a framework that converts human demonstration videos readily available on the Internet into executable UI trajectories at scale. Instead of directly generating trajectories or relying on ad hoc reasoning heuristics, we cast the problem as an inverse dynamics objective: predicting the user's action from consecutive screen states. This formulation reduces manual engineering, is easier to learn, and generalizes more robustly across applications. Concretely, we develop an inverse dynamics labeling pipeline with task-aware video retrieval, generate over 53k high-quality trajectories from raw web videos, and demonstrate that these trajectories improve CUAs both as in-context demonstrations and as supervised training data. On the challenging OSWorld benchmark, UI trajectories extracted with W&L consistently enhance both general-purpose and state-of-the-art frameworks in-context, and deliver stronger gains for open-source models under supervised training. These results highlight web-scale human demonstration videos as a practical and scalable foundation for advancing CUAs towards real-world deployment.
PLAN-TUNING: Post-Training Language Models to Learn Step-by-Step Planning for Complex Problem Solving
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Recently, decomposing complex problems into simple subtasks--a crucial part of human-like natural planning--to solve the given problem has significantly boosted the performance of large language models (LLMs). However, leveraging such planning structures during post-training to boost the performance of smaller open-source LLMs remains underexplored. Motivated by this, we introduce PLAN-TUNING, a unified post-training framework that (i) distills synthetic task decompositions (termed "planning trajectories") from large-scale LLMs and (ii) fine-tunes smaller models via supervised and reinforcement-learning objectives designed to mimic these planning processes to improve complex reasoning. On GSM8k and the MATH benchmarks, plan-tuned models outperform strong baselines by an average $\sim7\%$. Furthermore, plan-tuned models show better generalization capabilities on out-of-domain datasets, with average $\sim10\%$ and $\sim12\%$ performance improvements on OlympiadBench and AIME 2024, respectively. Our detailed analysis demonstrates how planning trajectories improves complex reasoning capabilities, showing that PLAN-TUNING is an effective strategy for improving task-specific performance of smaller LLMs.
RADAR: Benchmarking Language Models on Imperfect Tabular Data
Jun 09, 2025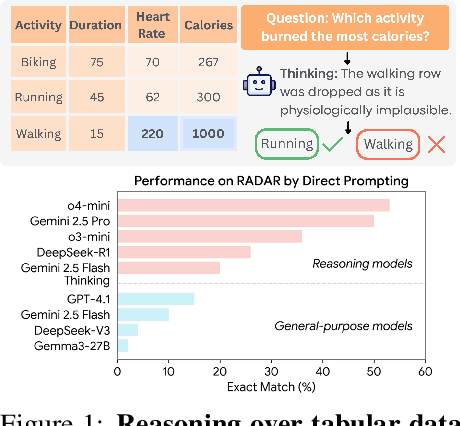
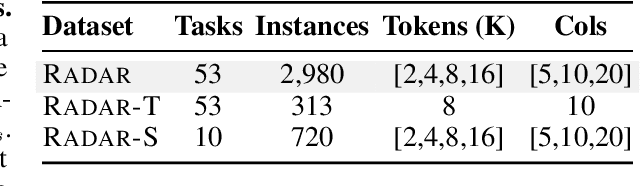
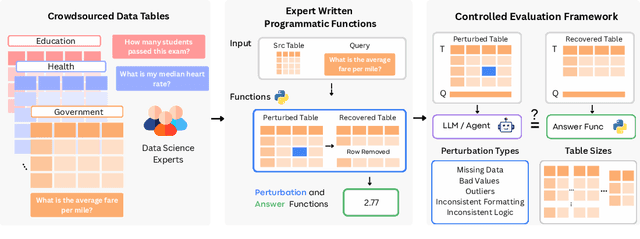
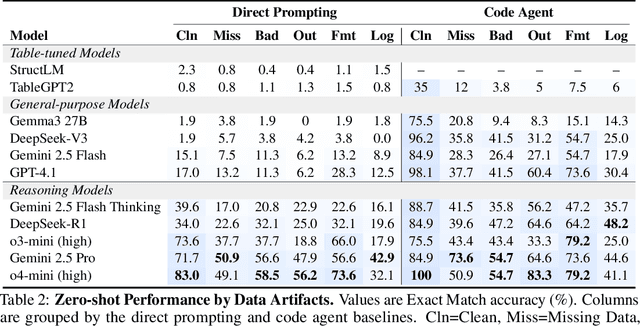
Abstract:Language models (LMs) are increasingly being deployed to perform autonomous data analyses. However, their data awareness -- the ability to recognize, reason over, and appropriately handle data artifacts such as missing values, outliers, and logical inconsistencies -- remains underexplored. These artifacts are especially common in real-world tabular data and, if mishandled, can significantly compromise the validity of analytical conclusions. To address this gap, we present RADAR, a benchmark for systematically evaluating data-aware reasoning on tabular data. We develop a framework to simulate data artifacts via programmatic perturbations to enable targeted evaluation of model behavior. RADAR comprises 2980 table query pairs, grounded in real-world data spanning 9 domains and 5 data artifact types. In addition to evaluating artifact handling, RADAR systematically varies table size to study how reasoning performance holds when increasing table size. Our evaluation reveals that, despite decent performance on tables without data artifacts, frontier models degrade significantly when data artifacts are introduced, exposing critical gaps in their capacity for robust, data-aware analysis. Designed to be flexible and extensible, RADAR supports diverse perturbation types and controllable table sizes, offering a valuable resource for advancing tabular reasoning.
X-Teaming: Multi-Turn Jailbreaks and Defenses with Adaptive Multi-Agents
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Multi-turn interactions with language models (LMs) pose critical safety risks, as harmful intent can be strategically spread across exchanges. Yet, the vast majority of prior work has focused on single-turn safety, while adaptability and diversity remain among the key challenges of multi-turn red-teaming. To address these challenges, we present X-Teaming, a scalable framework that systematically explores how seemingly harmless interactions escalate into harmful outcomes and generates corresponding attack scenarios. X-Teaming employs collaborative agents for planning, attack optimization, and verification, achieving state-of-the-art multi-turn jailbreak effectiveness and diversity with success rates up to 98.1% across representative leading open-weight and closed-source models. In particular, X-Teaming achieves a 96.2% attack success rate against the latest Claude 3.7 Sonnet model, which has been considered nearly immune to single-turn attacks. Building on X-Teaming, we introduce XGuard-Train, an open-source multi-turn safety training dataset that is 20x larger than the previous best resource, comprising 30K interactive jailbreaks, designed to enable robust multi-turn safety alignment for LMs. Our work offers essential tools and insights for mitigating sophisticated conversational attacks, advancing the multi-turn safety of LMs.
Review, Refine, Repeat: Understanding Iterative Decoding of AI Agents with Dynamic Evaluation and Selection
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:While AI agents have shown remarkable performance at various tasks, they still struggle with complex multi-modal applications, structured generation and strategic planning. Improvements via standard fine-tuning is often impractical, as solving agentic tasks usually relies on black box API access without control over model parameters. Inference-time methods such as Best-of-N (BON) sampling offer a simple yet effective alternative to improve performance. However, BON lacks iterative feedback integration mechanism. Hence, we propose Iterative Agent Decoding (IAD) which combines iterative refinement with dynamic candidate evaluation and selection guided by a verifier. IAD differs in how feedback is designed and integrated, specifically optimized to extract maximal signal from reward scores. We conduct a detailed comparison of baselines across key metrics on Sketch2Code, Text2SQL, and Webshop where IAD consistently outperforms baselines, achieving 3--6% absolute gains on Sketch2Code and Text2SQL (with and without LLM judges) and 8--10% gains on Webshop across multiple metrics. To better understand the source of IAD's gains, we perform controlled experiments to disentangle the effect of adaptive feedback from stochastic sampling, and find that IAD's improvements are primarily driven by verifier-guided refinement, not merely sampling diversity. We also show that both IAD and BON exhibit inference-time scaling with increased compute when guided by an optimal verifier. Our analysis highlights the critical role of verifier quality in effective inference-time optimization and examines the impact of noisy and sparse rewards on scaling behavior. Together, these findings offer key insights into the trade-offs and principles of effective inference-time optimization.
ShieldGemma 2: Robust and Tractable Image Content Moderation
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:We introduce ShieldGemma 2, a 4B parameter image content moderation model built on Gemma 3. This model provides robust safety risk predictions across the following key harm categories: Sexually Explicit, Violence \& Gore, and Dangerous Content for synthetic images (e.g. output of any image generation model) and natural images (e.g. any image input to a Vision-Language Model). We evaluated on both internal and external benchmarks to demonstrate state-of-the-art performance compared to LlavaGuard \citep{helff2024llavaguard}, GPT-4o mini \citep{hurst2024gpt}, and the base Gemma 3 model \citep{gemma_2025} based on our policies. Additionally, we present a novel adversarial data generation pipeline which enables a controlled, diverse, and robust image generation. ShieldGemma 2 provides an open image moderation tool to advance multimodal safety and responsible AI development.
In Prospect and Retrospect: Reflective Memory Management for Long-term Personalized Dialogue Agents
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have made significant progress in open-ended dialogue, yet their inability to retain and retrieve relevant information from long-term interactions limits their effectiveness in applications requiring sustained personalization. External memory mechanisms have been proposed to address this limitation, enabling LLMs to maintain conversational continuity. However, existing approaches struggle with two key challenges. First, rigid memory granularity fails to capture the natural semantic structure of conversations, leading to fragmented and incomplete representations. Second, fixed retrieval mechanisms cannot adapt to diverse dialogue contexts and user interaction patterns. In this work, we propose Reflective Memory Management (RMM), a novel mechanism for long-term dialogue agents, integrating forward- and backward-looking reflections: (1) Prospective Reflection, which dynamically summarizes interactions across granularities-utterances, turns, and sessions-into a personalized memory bank for effective future retrieval, and (2) Retrospective Reflection, which iteratively refines the retrieval in an online reinforcement learning (RL) manner based on LLMs' cited evidence. Experiments show that RMM demonstrates consistent improvement across various metrics and benchmarks. For example, RMM shows more than 10% accuracy improvement over the baseline without memory management on the LongMemEval dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge