Yike Wang
MentorCollab: Selective Large-to-Small Inference-Time Guidance for Efficient Reasoning
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) achieve strong performance by producing long chains of thought, but their inference costs are high and often generate redundant reasoning. Small language models (SLMs) are far more efficient, yet struggle on multi-step reasoning tasks. A natural idea is to let a large model guide a small one at inference time as a mentor, yet existing collaboration methods often promote imitation, resulting in verbose reasoning without consistent error correction. We propose MentorCollab, an inference-time collaboration method in which an LRM selectively and sparsely guides an SLM, rather than taking over generation. At randomly sampled token positions, we probe for divergences between the two models and use a lightweight verifier to decide whether the SLM should follow a short lookahead segment from its mentor or continue on its own. Across 15 SLM--LRM pairs and 3 domains (math reasoning, general knowledge, and commonsense reasoning), our method improves performance in 12 settings, with average gains of 3.0% and up to 8.0%, while adopting only having 18.4% tokens generated by the expensive mentor model on average. We find that short segments and selective probing are sufficient for effective collaboration. Our results show that selective inference-time guidance restores large-model reasoning ability without substantial inference overhead.
MoCo: A One-Stop Shop for Model Collaboration Research
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Advancing beyond single monolithic language models (LMs), recent research increasingly recognizes the importance of model collaboration, where multiple LMs collaborate, compose, and complement each other. Existing research on this topic has mostly been disparate and disconnected, from different research communities, and lacks rigorous comparison. To consolidate existing research and establish model collaboration as a school of thought, we present MoCo: a one-stop Python library of executing, benchmarking, and comparing model collaboration algorithms at scale. MoCo features 26 model collaboration methods, spanning diverse levels of cross-model information exchange such as routing, text, logit, and model parameters. MoCo integrates 25 evaluation datasets spanning reasoning, QA, code, safety, and more, while users could flexibly bring their own data. Extensive experiments with MoCo demonstrate that most collaboration strategies outperform models without collaboration in 61.0% of (model, data) settings on average, with the most effective methods outperforming by up to 25.8%. We further analyze the scaling of model collaboration strategies, the training/inference efficiency of diverse methods, highlight that the collaborative system solves problems where single LMs struggle, and discuss future work in model collaboration, all made possible by MoCo. We envision MoCo as a valuable toolkit to facilitate and turbocharge the quest for an open, modular, decentralized, and collaborative AI future.
QoS-Aware Integrated Sensing, Communication, and Control with Movable Antenna
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Integrated sensing, communication, and control (ISCC) has emerged as a key enabler for low-altitude wireless networks with enhanced adaptability through resource allocation co-design and intelligent environment awareness. However, dynamic interference and channel attenuation constrain the potential of the ISCC system. To address this challenge, we propose a novel movable antenna-empowered ISCC system. An achievable data rate maximization problem is formulated while guaranteeing the sensing and control quality-of-service (QoS) by optimizing the positions of the antennas and the beamforming strategy for communication, sensing, and control co-design. An efficient alternating optimization (AO)-based algorithm is proposed to solve the highly coupled non-convex problem. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed AO-based algorithm achieves substantial gains in the achievable data rate and the control QoS compared with benchmark schemes.
ScienceMeter: Tracking Scientific Knowledge Updates in Language Models
May 30, 2025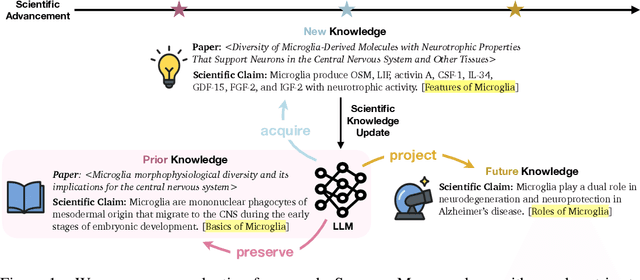
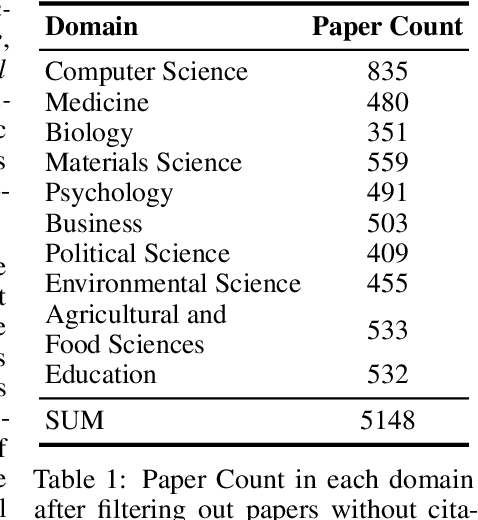
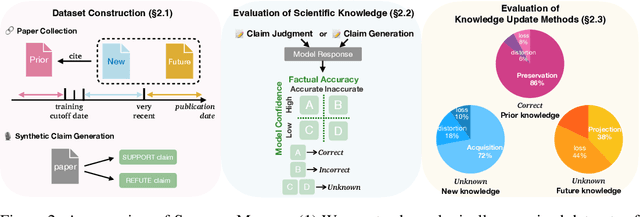
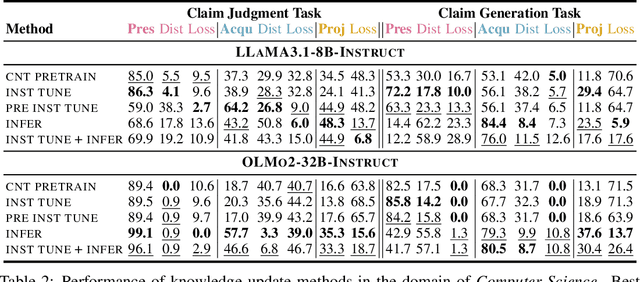
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used to support scientific research, but their knowledge of scientific advancements can quickly become outdated. We introduce ScienceMeter, a new framework for evaluating scientific knowledge update methods over scientific knowledge spanning the past, present, and future. ScienceMeter defines three metrics: knowledge preservation, the extent to which models' understanding of previously learned papers are preserved; knowledge acquisition, how well scientific claims from newly introduced papers are acquired; and knowledge projection, the ability of the updated model to anticipate or generalize to related scientific claims that may emerge in the future. Using ScienceMeter, we examine the scientific knowledge of LLMs on claim judgment and generation tasks across a curated dataset of 15,444 scientific papers and 30,888 scientific claims from ten domains including medicine, biology, materials science, and computer science. We evaluate five representative knowledge update approaches including training- and inference-time methods. With extensive experiments, we find that the best-performing knowledge update methods can preserve only 85.9% of existing knowledge, acquire 71.7% of new knowledge, and project 37.7% of future knowledge. Inference-based methods work for larger models, whereas smaller models require training to achieve comparable performance. Cross-domain analysis reveals that performance on these objectives is correlated. Even when applying on specialized scientific LLMs, existing knowledge update methods fail to achieve these objectives collectively, underscoring that developing robust scientific knowledge update mechanisms is both crucial and challenging.
Heterogeneous Swarms: Jointly Optimizing Model Roles and Weights for Multi-LLM Systems
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:We propose Heterogeneous Swarms, an algorithm to design multi-LLM systems by jointly optimizing model roles and weights. We represent multi-LLM systems as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) of LLMs with topological message passing for collaborative generation. Given a pool of LLM experts and a utility function, Heterogeneous Swarms employs two iterative steps: role-step and weight-step. For role-step, we interpret model roles as learning a DAG that specifies the flow of inputs and outputs between LLMs. Starting from a swarm of random continuous adjacency matrices, we decode them into discrete DAGs, call the LLMs in topological order, evaluate on the utility function (e.g. accuracy on a task), and optimize the adjacency matrices with particle swarm optimization based on the utility score. For weight-step, we assess the contribution of individual LLMs in the multi-LLM systems and optimize model weights with swarm intelligence. We propose JFK-score to quantify the individual contribution of each LLM in the best-found DAG of the role-step, then optimize model weights with particle swarm optimization based on the JFK-score. Experiments demonstrate that Heterogeneous Swarms outperforms 15 role- and/or weight-based baselines by 18.5% on average across 12 tasks. Further analysis reveals that Heterogeneous Swarms discovers multi-LLM systems with heterogeneous model roles and substantial collaborative gains, and benefits from the diversity of language models.
When One LLM Drools, Multi-LLM Collaboration Rules
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:This position paper argues that in many realistic (i.e., complex, contextualized, subjective) scenarios, one LLM is not enough to produce a reliable output. We challenge the status quo of relying solely on a single general-purpose LLM and argue for multi-LLM collaboration to better represent the extensive diversity of data, skills, and people. We first posit that a single LLM underrepresents real-world data distributions, heterogeneous skills, and pluralistic populations, and that such representation gaps cannot be trivially patched by further training a single LLM. We then organize existing multi-LLM collaboration methods into a hierarchy, based on the level of access and information exchange, ranging from API-level, text-level, logit-level, to weight-level collaboration. Based on these methods, we highlight how multi-LLM collaboration addresses challenges that a single LLM struggles with, such as reliability, democratization, and pluralism. Finally, we identify the limitations of existing multi-LLM methods and motivate future work. We envision multi-LLM collaboration as an essential path toward compositional intelligence and collaborative AI development.
Model Swarms: Collaborative Search to Adapt LLM Experts via Swarm Intelligence
Oct 15, 2024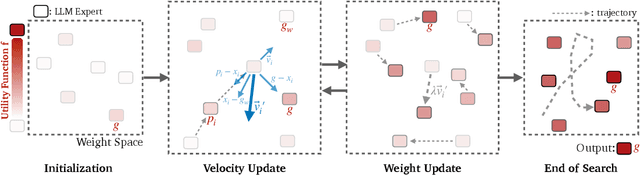
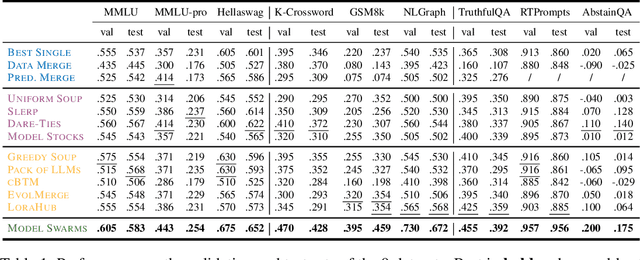
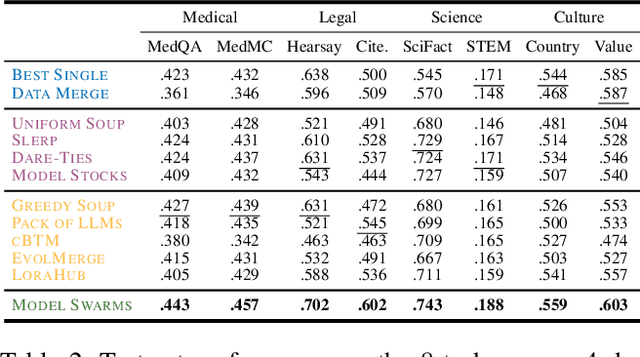
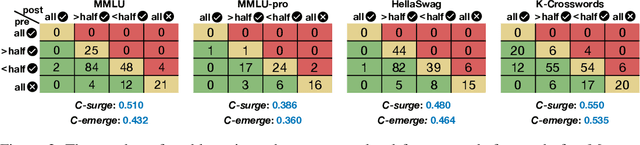
Abstract:We propose Model Swarms, a collaborative search algorithm to adapt LLMs via swarm intelligence, the collective behavior guiding individual systems. Specifically, Model Swarms starts with a pool of LLM experts and a utility function. Guided by the best-found checkpoints across models, diverse LLM experts collaboratively move in the weight space and optimize a utility function representing model adaptation objectives. Compared to existing model composition approaches, Model Swarms offers tuning-free model adaptation, works in low-data regimes with as few as 200 examples, and does not require assumptions about specific experts in the swarm or how they should be composed. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Model Swarms could flexibly adapt LLM experts to a single task, multi-task domains, reward models, as well as diverse human interests, improving over 12 model composition baselines by up to 21.0% across tasks and contexts. Further analysis reveals that LLM experts discover previously unseen capabilities in initial checkpoints and that Model Swarms enable the weak-to-strong transition of experts through the collaborative search process.
Teaching LLMs to Abstain across Languages via Multilingual Feedback
Jun 22, 2024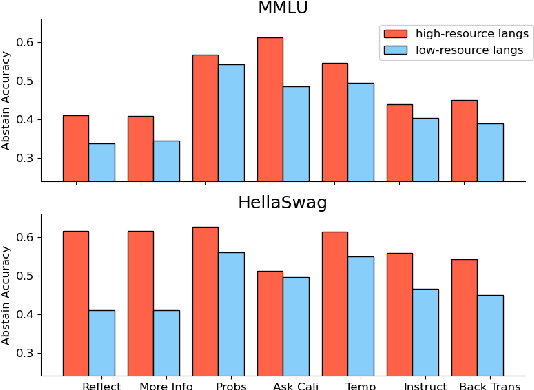
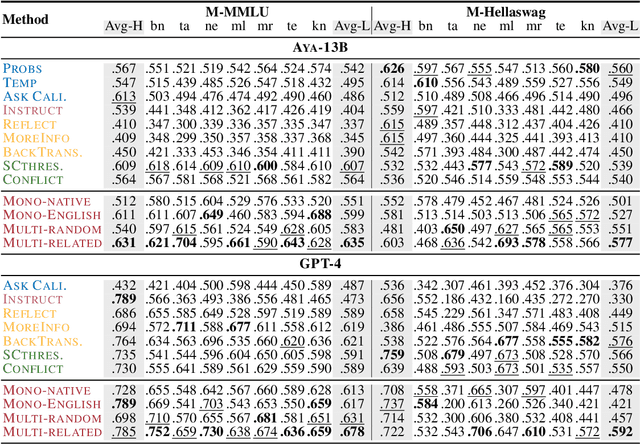
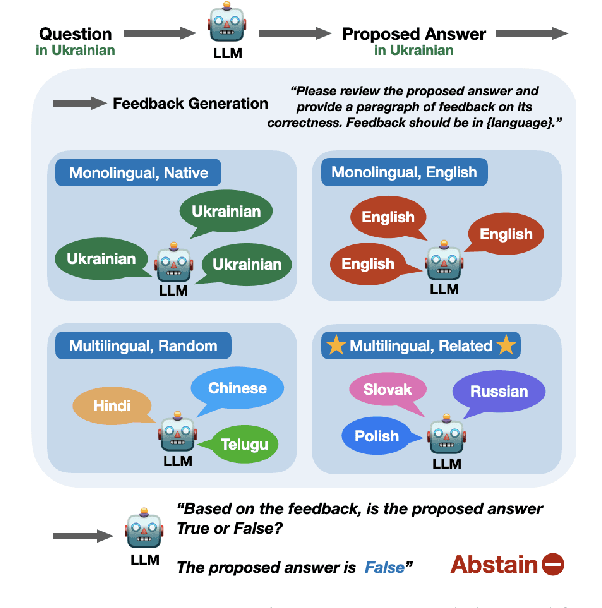
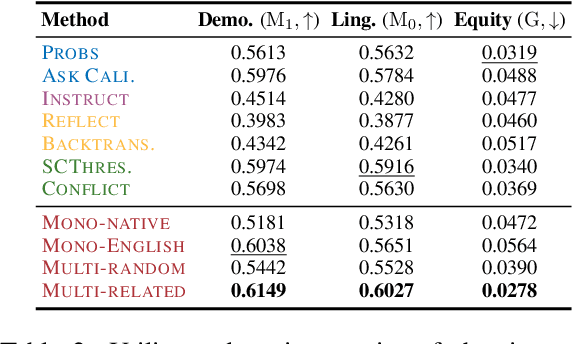
Abstract:Multilingual LLMs often have knowledge disparities across languages, with larger gaps in under-resourced languages. Teaching LLMs to abstain in the face of knowledge gaps is thus a promising strategy to mitigate hallucinations in multilingual settings. However, previous studies on LLM abstention primarily focus on English; we find that directly applying existing solutions beyond English results in up to 20.5% performance gaps between high and low-resource languages, potentially due to LLMs' drop in calibration and reasoning beyond a few resource-rich languages. To this end, we propose strategies to enhance LLM abstention by learning from multilingual feedback, where LLMs self-reflect on proposed answers in one language by generating multiple feedback items in related languages: we show that this helps identifying the knowledge gaps across diverse languages, cultures, and communities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our multilingual feedback approach outperforms various strong baselines, achieving up to 9.2% improvement for low-resource languages across three black-box and open models on three datasets, featuring open-book, closed-book, and commonsense QA. Further analysis reveals that multilingual feedback is both an effective and a more equitable abstain strategy to serve diverse language speakers, and cultural factors have great impact on language selection and LLM abstention behavior, highlighting future directions for multilingual and multi-cultural reliable language modeling.
Don't Hallucinate, Abstain: Identifying LLM Knowledge Gaps via Multi-LLM Collaboration
Feb 01, 2024



Abstract:Despite efforts to expand the knowledge of large language models (LLMs), knowledge gaps -- missing or outdated information in LLMs -- might always persist given the evolving nature of knowledge. In this work, we study approaches to identify LLM knowledge gaps and abstain from answering questions when knowledge gaps are present. We first adapt existing approaches to model calibration or adaptation through fine-tuning/prompting and analyze their ability to abstain from generating low-confidence outputs. Motivated by their failures in self-reflection and over-reliance on held-out sets, we propose two novel approaches that are based on model collaboration, i.e., LLMs probing other LLMs for knowledge gaps, either cooperatively or competitively. Extensive experiments with three LLMs on four QA tasks featuring diverse knowledge domains demonstrate that both cooperative and competitive approaches to unveiling LLM knowledge gaps achieve up to 19.3% improvements on abstain accuracy against the strongest baseline. Further analysis reveals that our proposed mechanisms could help identify failure cases in retrieval augmentation and pinpoint knowledge gaps in multi-hop reasoning.
Resolving Knowledge Conflicts in Large Language Models
Oct 02, 2023
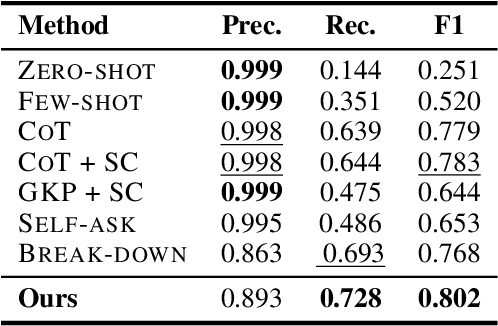
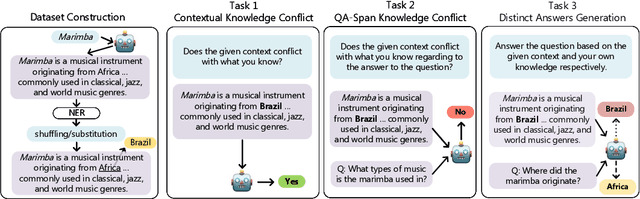
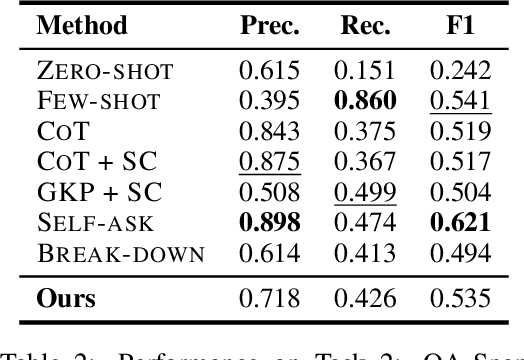
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often encounter knowledge conflicts, scenarios where discrepancy arises between the internal parametric knowledge of LLMs and non-parametric information provided in the prompt context. In this work we ask what are the desiderata for LLMs when a knowledge conflict arises and whether existing LLMs fulfill them. We posit that LLMs should 1) identify knowledge conflicts, 2) pinpoint conflicting information segments, and 3) provide distinct answers or viewpoints in conflicting scenarios. To this end, we introduce KNOWLEDGE CONFLICT, an evaluation framework for simulating contextual knowledge conflicts and quantitatively evaluating to what extent LLMs achieve these goals. KNOWLEDGE CONFLICT includes diverse and complex situations of knowledge conflict, knowledge from diverse entities and domains, two synthetic conflict creation methods, and settings with progressively increasing difficulty to reflect realistic knowledge conflicts. Extensive experiments with the KNOWLEDGE CONFLICT framework reveal that while LLMs perform well in identifying the existence of knowledge conflicts, they struggle to determine the specific conflicting knowledge and produce a response with distinct answers amidst conflicting information. To address these challenges, we propose new instruction-based approaches that augment LLMs to better achieve the three goals. Further analysis shows that abilities to tackle knowledge conflicts are greatly impacted by factors such as knowledge domain and prompt text, while generating robust responses to knowledge conflict scenarios remains an open research question.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge