Yuta Saito
A General Framework for Off-Policy Learning with Partially-Observed Reward
Jun 17, 2025
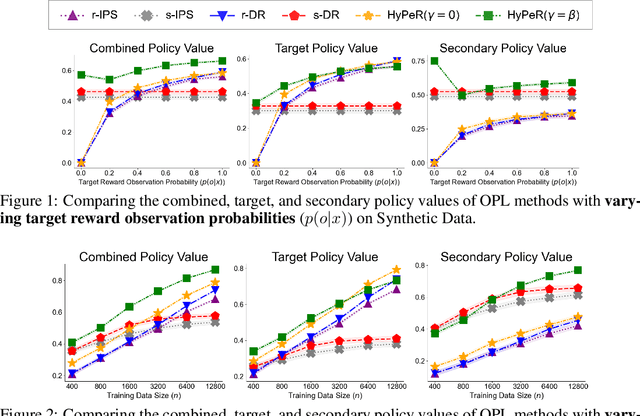
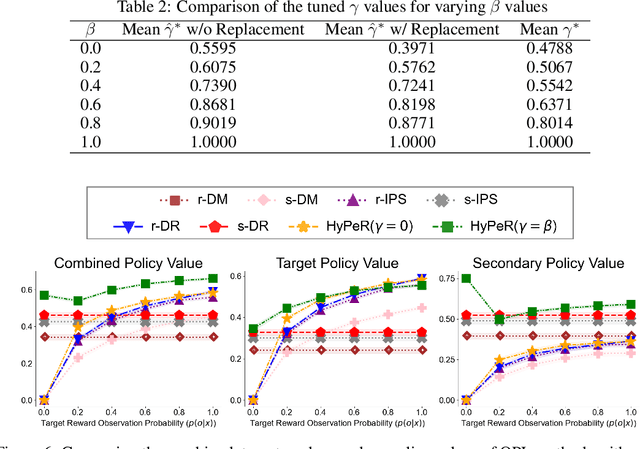
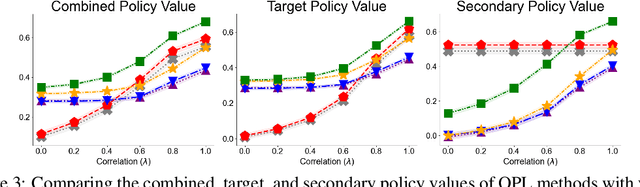
Abstract:Off-policy learning (OPL) in contextual bandits aims to learn a decision-making policy that maximizes the target rewards by using only historical interaction data collected under previously developed policies. Unfortunately, when rewards are only partially observed, the effectiveness of OPL degrades severely. Well-known examples of such partial rewards include explicit ratings in content recommendations, conversion signals on e-commerce platforms that are partial due to delay, and the issue of censoring in medical problems. One possible solution to deal with such partial rewards is to use secondary rewards, such as dwelling time, clicks, and medical indicators, which are more densely observed. However, relying solely on such secondary rewards can also lead to poor policy learning since they may not align with the target reward. Thus, this work studies a new and general problem of OPL where the goal is to learn a policy that maximizes the expected target reward by leveraging densely observed secondary rewards as supplemental data. We then propose a new method called Hybrid Policy Optimization for Partially-Observed Reward (HyPeR), which effectively uses the secondary rewards in addition to the partially-observed target reward to achieve effective OPL despite the challenging scenario. We also discuss a case where we aim to optimize not only the expected target reward but also the expected secondary rewards to some extent; counter-intuitively, we will show that leveraging the two objectives is in fact advantageous also for the optimization of only the target reward. Along with statistical analysis of our proposed methods, empirical evaluations on both synthetic and real-world data show that HyPeR outperforms existing methods in various scenarios.
* 10 pages, 5 figures. Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025
Prompt Optimization with Logged Bandit Data
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:We study how to use naturally available user feedback, such as clicks, to optimize large language model (LLM) pipelines for generating personalized sentences using prompts. Naive approaches, which estimate the policy gradient in the prompt space, suffer either from variance caused by the large action space of prompts or bias caused by inaccurate reward predictions. To circumvent these challenges, we propose a novel kernel-based off-policy gradient method, which estimates the policy gradient by leveraging similarity among generated sentences, substantially reducing variance while suppressing the bias. Empirical results on our newly established suite of benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in generating personalized descriptions for movie recommendations, particularly when the number of candidate prompts is large.
A Best-of-Both Approach to Improve Match Predictions and Reciprocal Recommendations for Job Search
Sep 18, 2024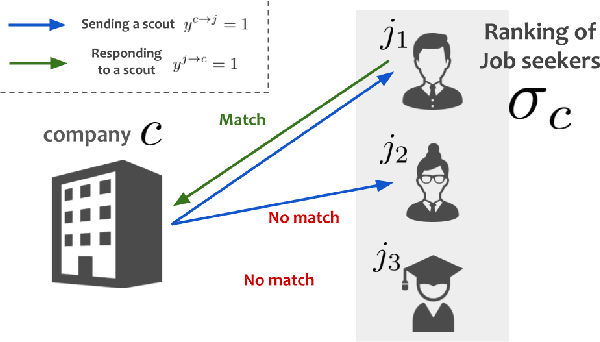
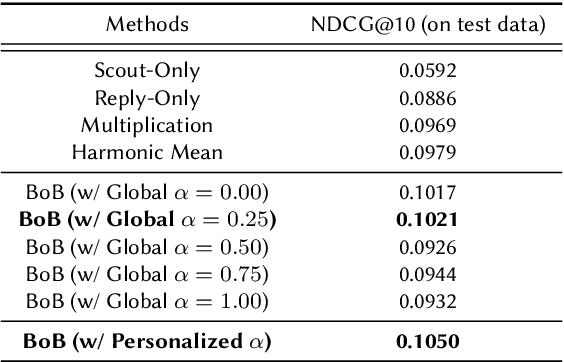
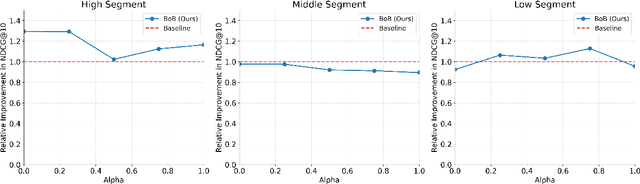
Abstract:Matching users with mutual preferences is a critical aspect of services driven by reciprocal recommendations, such as job search. To produce recommendations in such scenarios, one can predict match probabilities and construct rankings based on these predictions. However, this direct match prediction approach often underperforms due to the extreme sparsity of match labels. Therefore, most existing methods predict preferences separately for each direction (e.g., job seeker to employer and employer to job seeker) and then aggregate the predictions to generate overall matching scores and produce recommendations. However, this typical approach often leads to practical issues, such as biased error propagation between the two models. This paper introduces and demonstrates a novel and practical solution to improve reciprocal recommendations in production by leveraging pseudo-match scores. Specifically, our approach generates dense and more directly relevant pseudo-match scores by combining the true match labels, which are accurate but sparse, with relatively inaccurate but dense match predictions. We then train a meta-model to output the final match predictions by minimizing the prediction loss against the pseudo-match scores. Our method can be seen as a best-of-both (BoB) approach, as it combines the high-level ideas of both direct match prediction and the two separate models approach. It also allows for user-specific weights to construct personalized pseudo-match scores, achieving even better matching performance through appropriate tuning of the weights. Offline experiments on real-world job search data demonstrate the superior performance of our BoB method, particularly with personalized pseudo-match scores, compared to existing approaches in terms of finding potential matches.
Effective Off-Policy Evaluation and Learning in Contextual Combinatorial Bandits
Aug 20, 2024
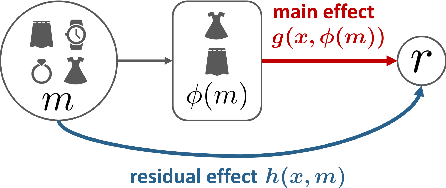
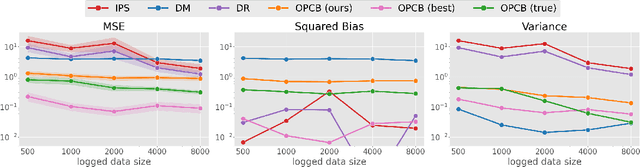
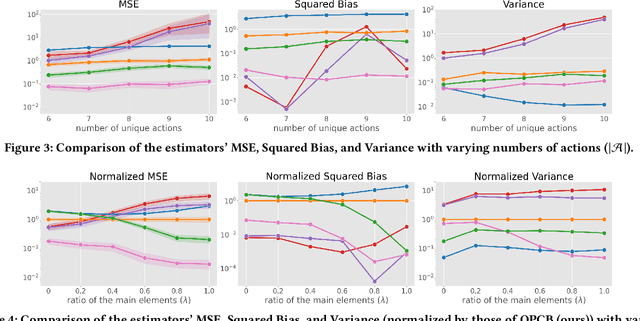
Abstract:We explore off-policy evaluation and learning (OPE/L) in contextual combinatorial bandits (CCB), where a policy selects a subset in the action space. For example, it might choose a set of furniture pieces (a bed and a drawer) from available items (bed, drawer, chair, etc.) for interior design sales. This setting is widespread in fields such as recommender systems and healthcare, yet OPE/L of CCB remains unexplored in the relevant literature. Typical OPE/L methods such as regression and importance sampling can be applied to the CCB problem, however, they face significant challenges due to high bias or variance, exacerbated by the exponential growth in the number of available subsets. To address these challenges, we introduce a concept of factored action space, which allows us to decompose each subset into binary indicators. This formulation allows us to distinguish between the ''main effect'' derived from the main actions, and the ''residual effect'', originating from the supplemental actions, facilitating more effective OPE. Specifically, our estimator, called OPCB, leverages an importance sampling-based approach to unbiasedly estimate the main effect, while employing regression-based approach to deal with the residual effect with low variance. OPCB achieves substantial variance reduction compared to conventional importance sampling methods and bias reduction relative to regression methods under certain conditions, as illustrated in our theoretical analysis. Experiments demonstrate OPCB's superior performance over typical methods in both OPE and OPL.
Long-term Off-Policy Evaluation and Learning
Apr 24, 2024Abstract:Short- and long-term outcomes of an algorithm often differ, with damaging downstream effects. A known example is a click-bait algorithm, which may increase short-term clicks but damage long-term user engagement. A possible solution to estimate the long-term outcome is to run an online experiment or A/B test for the potential algorithms, but it takes months or even longer to observe the long-term outcomes of interest, making the algorithm selection process unacceptably slow. This work thus studies the problem of feasibly yet accurately estimating the long-term outcome of an algorithm using only historical and short-term experiment data. Existing approaches to this problem either need a restrictive assumption about the short-term outcomes called surrogacy or cannot effectively use short-term outcomes, which is inefficient. Therefore, we propose a new framework called Long-term Off-Policy Evaluation (LOPE), which is based on reward function decomposition. LOPE works under a more relaxed assumption than surrogacy and effectively leverages short-term rewards to substantially reduce the variance. Synthetic experiments show that LOPE outperforms existing approaches particularly when surrogacy is severely violated and the long-term reward is noisy. In addition, real-world experiments on large-scale A/B test data collected on a music streaming platform show that LOPE can estimate the long-term outcome of actual algorithms more accurately than existing feasible methods.
Hyperparameter Optimization Can Even be Harmful in Off-Policy Learning and How to Deal with It
Apr 23, 2024Abstract:There has been a growing interest in off-policy evaluation in the literature such as recommender systems and personalized medicine. We have so far seen significant progress in developing estimators aimed at accurately estimating the effectiveness of counterfactual policies based on biased logged data. However, there are many cases where those estimators are used not only to evaluate the value of decision making policies but also to search for the best hyperparameters from a large candidate space. This work explores the latter hyperparameter optimization (HPO) task for off-policy learning. We empirically show that naively applying an unbiased estimator of the generalization performance as a surrogate objective in HPO can cause an unexpected failure, merely pursuing hyperparameters whose generalization performance is greatly overestimated. We then propose simple and computationally efficient corrections to the typical HPO procedure to deal with the aforementioned issues simultaneously. Empirical investigations demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed HPO algorithm in situations where the typical procedure fails severely.
Scalable and Provably Fair Exposure Control for Large-Scale Recommender Systems
Feb 22, 2024



Abstract:Typical recommendation and ranking methods aim to optimize the satisfaction of users, but they are often oblivious to their impact on the items (e.g., products, jobs, news, video) and their providers. However, there has been a growing understanding that the latter is crucial to consider for a wide range of applications, since it determines the utility of those being recommended. Prior approaches to fairness-aware recommendation optimize a regularized objective to balance user satisfaction and item fairness based on some notion such as exposure fairness. These existing methods have been shown to be effective in controlling fairness, however, most of them are computationally inefficient, limiting their applications to only unrealistically small-scale situations. This indeed implies that the literature does not yet provide a solution to enable a flexible control of exposure in the industry-scale recommender systems where millions of users and items exist. To enable a computationally efficient exposure control even for such large-scale systems, this work develops a scalable, fast, and fair method called \emph{\textbf{ex}posure-aware \textbf{ADMM} (\textbf{exADMM})}. exADMM is based on implicit alternating least squares (iALS), a conventional scalable algorithm for collaborative filtering, but optimizes a regularized objective to achieve a flexible control of accuracy-fairness tradeoff. A particular technical challenge in developing exADMM is the fact that the fairness regularizer destroys the separability of optimization subproblems for users and items, which is an essential property to ensure the scalability of iALS. Therefore, we develop a set of optimization tools to enable yet scalable fairness control with provable convergence guarantees as a basis of our algorithm.
POTEC: Off-Policy Learning for Large Action Spaces via Two-Stage Policy Decomposition
Feb 09, 2024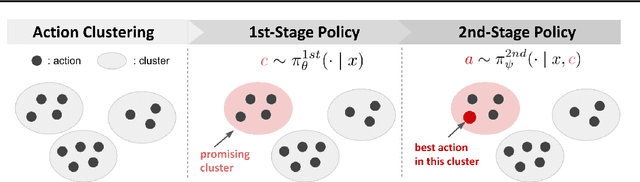
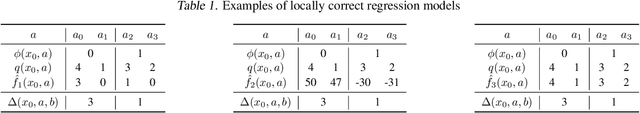
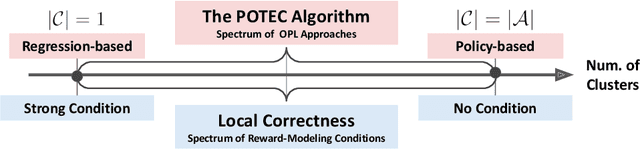
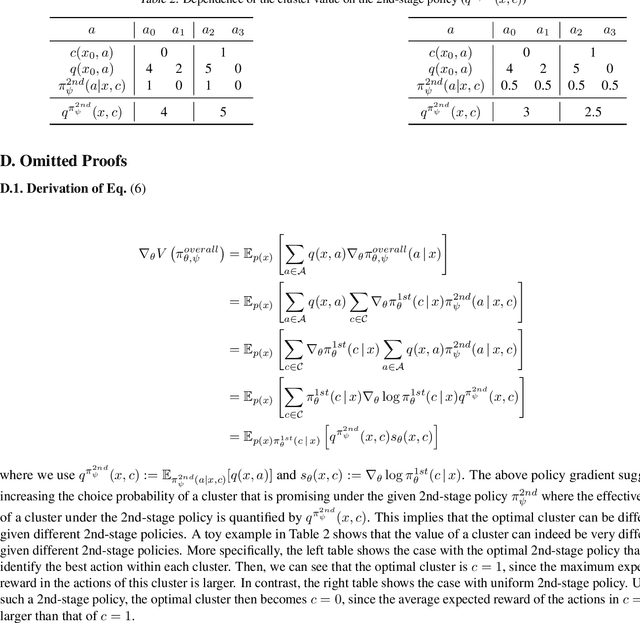
Abstract:We study off-policy learning (OPL) of contextual bandit policies in large discrete action spaces where existing methods -- most of which rely crucially on reward-regression models or importance-weighted policy gradients -- fail due to excessive bias or variance. To overcome these issues in OPL, we propose a novel two-stage algorithm, called Policy Optimization via Two-Stage Policy Decomposition (POTEC). It leverages clustering in the action space and learns two different policies via policy- and regression-based approaches, respectively. In particular, we derive a novel low-variance gradient estimator that enables to learn a first-stage policy for cluster selection efficiently via a policy-based approach. To select a specific action within the cluster sampled by the first-stage policy, POTEC uses a second-stage policy derived from a regression-based approach within each cluster. We show that a local correctness condition, which only requires that the regression model preserves the relative expected reward differences of the actions within each cluster, ensures that our policy-gradient estimator is unbiased and the second-stage policy is optimal. We also show that POTEC provides a strict generalization of policy- and regression-based approaches and their associated assumptions. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that POTEC provides substantial improvements in OPL effectiveness particularly in large and structured action spaces.
Off-Policy Evaluation of Slate Bandit Policies via Optimizing Abstraction
Feb 03, 2024
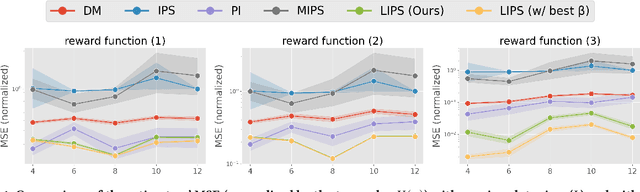
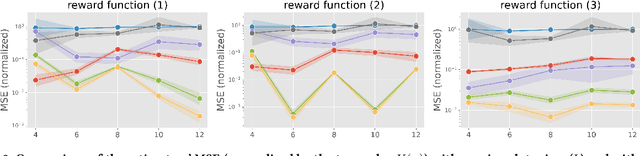

Abstract:We study off-policy evaluation (OPE) in the problem of slate contextual bandits where a policy selects multi-dimensional actions known as slates. This problem is widespread in recommender systems, search engines, marketing, to medical applications, however, the typical Inverse Propensity Scoring (IPS) estimator suffers from substantial variance due to large action spaces, making effective OPE a significant challenge. The PseudoInverse (PI) estimator has been introduced to mitigate the variance issue by assuming linearity in the reward function, but this can result in significant bias as this assumption is hard-to-verify from observed data and is often substantially violated. To address the limitations of previous estimators, we develop a novel estimator for OPE of slate bandits, called Latent IPS (LIPS), which defines importance weights in a low-dimensional slate abstraction space where we optimize slate abstractions to minimize the bias and variance of LIPS in a data-driven way. By doing so, LIPS can substantially reduce the variance of IPS without imposing restrictive assumptions on the reward function structure like linearity. Through empirical evaluation, we demonstrate that LIPS substantially outperforms existing estimators, particularly in scenarios with non-linear rewards and large slate spaces.
Towards Assessing and Benchmarking Risk-Return Tradeoff of Off-Policy Evaluation
Dec 04, 2023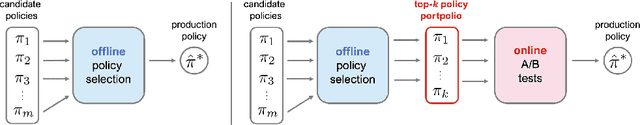
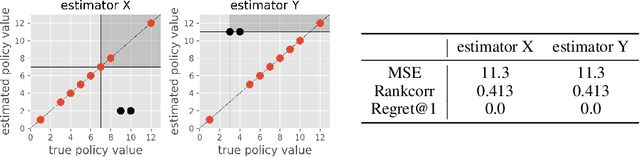
Abstract:Off-Policy Evaluation (OPE) aims to assess the effectiveness of counterfactual policies using only offline logged data and is often used to identify the top-k promising policies for deployment in online A/B tests. Existing evaluation metrics for OPE estimators primarily focus on the "accuracy" of OPE or that of downstream policy selection, neglecting risk-return tradeoff in the subsequent online policy deployment. To address this issue, we draw inspiration from portfolio evaluation in finance and develop a new metric, called SharpeRatio@k, which measures the risk-return tradeoff of policy portfolios formed by an OPE estimator under varying online evaluation budgets (k). We validate our metric in two example scenarios, demonstrating its ability to effectively distinguish between low-risk and high-risk estimators and to accurately identify the most efficient estimator. This efficient estimator is characterized by its capability to form the most advantageous policy portfolios, maximizing returns while minimizing risks during online deployment, a nuance that existing metrics typically overlook. To facilitate a quick, accurate, and consistent evaluation of OPE via SharpeRatio@k, we have also integrated this metric into an open-source software, SCOPE-RL. Employing SharpeRatio@k and SCOPE-RL, we conduct comprehensive benchmarking experiments on various estimators and RL tasks, focusing on their risk-return tradeoff. These experiments offer several interesting directions and suggestions for future OPE research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge