Yudai Hayashi
A Best-of-Both Approach to Improve Match Predictions and Reciprocal Recommendations for Job Search
Sep 18, 2024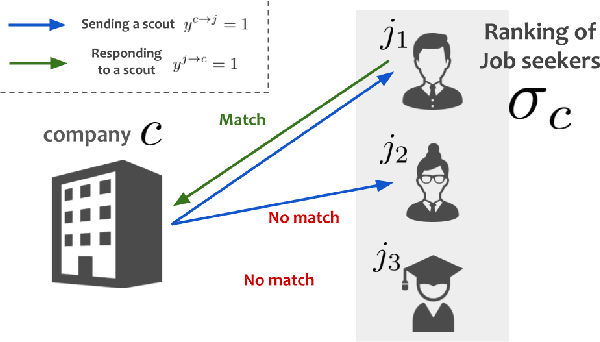
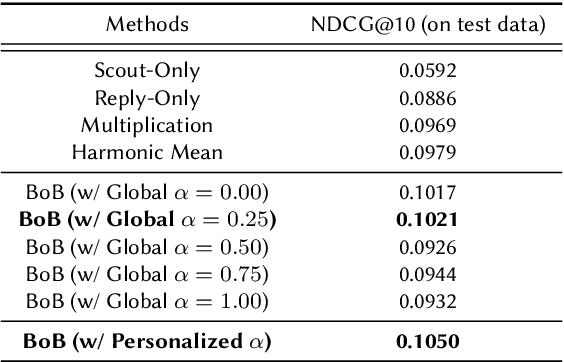
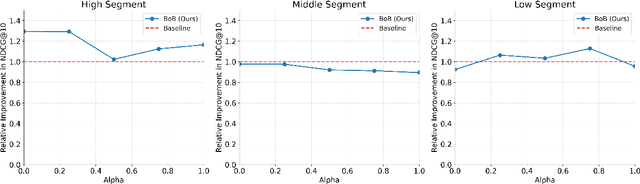
Abstract:Matching users with mutual preferences is a critical aspect of services driven by reciprocal recommendations, such as job search. To produce recommendations in such scenarios, one can predict match probabilities and construct rankings based on these predictions. However, this direct match prediction approach often underperforms due to the extreme sparsity of match labels. Therefore, most existing methods predict preferences separately for each direction (e.g., job seeker to employer and employer to job seeker) and then aggregate the predictions to generate overall matching scores and produce recommendations. However, this typical approach often leads to practical issues, such as biased error propagation between the two models. This paper introduces and demonstrates a novel and practical solution to improve reciprocal recommendations in production by leveraging pseudo-match scores. Specifically, our approach generates dense and more directly relevant pseudo-match scores by combining the true match labels, which are accurate but sparse, with relatively inaccurate but dense match predictions. We then train a meta-model to output the final match predictions by minimizing the prediction loss against the pseudo-match scores. Our method can be seen as a best-of-both (BoB) approach, as it combines the high-level ideas of both direct match prediction and the two separate models approach. It also allows for user-specific weights to construct personalized pseudo-match scores, achieving even better matching performance through appropriate tuning of the weights. Offline experiments on real-world job search data demonstrate the superior performance of our BoB method, particularly with personalized pseudo-match scores, compared to existing approaches in terms of finding potential matches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge