Chirag Shah
iAgentBench: Benchmarking Sensemaking Capabilities of Information-Seeking Agents on High-Traffic Topics
Mar 04, 2026Abstract:With the emergence of search-enabled generative QA systems, users are increasingly turning to tools that browse, aggregate, and reconcile evidence across multiple sources on their behalf. Yet many widely used QA benchmarks remain answerable by retrieving a single relevant passage, making them poorly suited for measuring cross-source sensemaking, such as integrating evidence, tracking causal links, and resolving dependencies across facets of a topic. We present iAgentBench, a dynamic ODQA benchmark that targets these higher-level information needs while keeping questions natural and grounded in realistic information-seeking behavior. iAgentBench draws seed topics from real-world attention signals and uses common user intent patterns to construct user-like questions whose answers require combining evidence from multiple sources, not just extracting a single snippet. Each instance is released with traceable evidence and auditable intermediate artifacts that support contamination checks and enable fine-grained diagnosis of failures in retrieval versus synthesis. Experiments across multiple LLMs show that retrieval improves accuracy, but retrieval alone does not reliably resolve these questions, underscoring the need to evaluate evidence use, not just evidence access.
Knowing Isn't Understanding: Re-grounding Generative Proactivity with Epistemic and Behavioral Insight
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Generative AI agents equate understanding with resolving explicit queries, an assumption that confines interaction to what users can articulate. This assumption breaks down when users themselves lack awareness of what is missing, risky, or worth considering. In such conditions, proactivity is not merely an efficiency enhancement, but an epistemic necessity. We refer to this condition as epistemic incompleteness: where progress depends on engaging with unknown unknowns for effective partnership. Existing approaches to proactivity remain narrowly anticipatory, extrapolating from past behavior and presuming that goals are already well defined, thereby failing to support users meaningfully. However, surfacing possibilities beyond a user's current awareness is not inherently beneficial. Unconstrained proactive interventions can misdirect attention, overwhelm users, or introduce harm. Proactive agents, therefore, require behavioral grounding: principled constraints on when, how, and to what extent an agent should intervene. We advance the position that generative proactivity must be grounded both epistemically and behaviorally. Drawing on the philosophy of ignorance and research on proactive behavior, we argue that these theories offer critical guidance for designing agents that can engage responsibly and foster meaningful partnerships.
ClaimDB: A Fact Verification Benchmark over Large Structured Data
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Despite substantial progress in fact-verification benchmarks, claims grounded in large-scale structured data remain underexplored. In this work, we introduce ClaimDB, the first fact-verification benchmark where the evidence for claims is derived from compositions of millions of records and multiple tables. ClaimDB consists of 80 unique real-life databases covering a wide range of domains, from governance and healthcare to media, education and the natural sciences. At this scale, verification approaches that rely on "reading" the evidence break down, forcing a timely shift toward reasoning in executable programs. We conduct extensive experiments with 30 state-of-the-art proprietary and open-source (below 70B) LLMs and find that none exceed 83% accuracy, with more than half below 55%. Our analysis also reveals that both closed- and open-source models struggle with abstention -- the ability to admit that there is no evidence to decide -- raising doubts about their reliability in high-stakes data analysis. We release the benchmark, code, and the LLM leaderboard at https://claimdb.github.io .
The PROPER Approach to Proactivity: Benchmarking and Advancing Knowledge Gap Navigation
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Most language-based assistants follow a reactive ask-and-respond paradigm, requiring users to explicitly state their needs. As a result, relevant but unexpressed needs often go unmet. Existing proactive agents attempt to address this gap either by eliciting further clarification, preserving this burden, or by extrapolating future needs from context, often leading to unnecessary or mistimed interventions. We introduce ProPer, Proactivity-driven Personalized agents, a novel two-agent architecture consisting of a Dimension Generating Agent (DGA) and a Response Generating Agent (RGA). DGA, a fine-tuned LLM agent, leverages explicit user data to generate multiple implicit dimensions (latent aspects relevant to the user's task but not considered by the user) or knowledge gaps. These dimensions are selectively filtered using a reranker based on quality, diversity, and task relevance. RGA then balances explicit and implicit dimensions to tailor personalized responses with timely and proactive interventions. We evaluate ProPer across multiple domains using a structured, gap-aware rubric that measures coverage, initiative appropriateness, and intent alignment. Our results show that ProPer improves quality scores and win rates across all domains, achieving up to 84% gains in single-turn evaluation and consistent dominance in multi-turn interactions.
I Think, Therefore I Am Under-Qualified? A Benchmark for Evaluating Linguistic Shibboleth Detection in LLM Hiring Evaluations
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating how Large Language Models (LLMs) respond to linguistic shibboleths: subtle linguistic markers that can inadvertently reveal demographic attributes such as gender, social class, or regional background. Through carefully constructed interview simulations using 100 validated question-response pairs, we demonstrate how LLMs systematically penalize certain linguistic patterns, particularly hedging language, despite equivalent content quality. Our benchmark generates controlled linguistic variations that isolate specific phenomena while maintaining semantic equivalence, which enables the precise measurement of demographic bias in automated evaluation systems. We validate our approach along multiple linguistic dimensions, showing that hedged responses receive 25.6% lower ratings on average, and demonstrate the benchmark's effectiveness in identifying model-specific biases. This work establishes a foundational framework for detecting and measuring linguistic discrimination in AI systems, with broad applications to fairness in automated decision-making contexts.
LLM-Driven Usefulness Judgment for Web Search Evaluation
Apr 19, 2025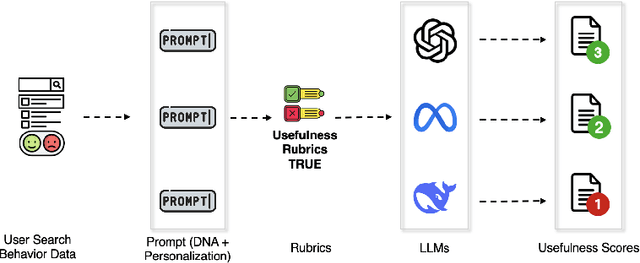
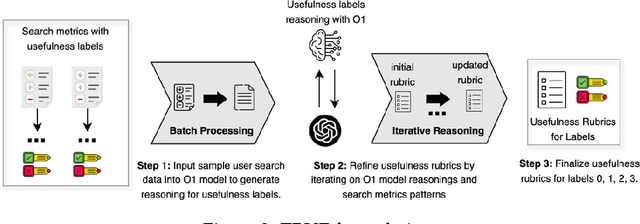
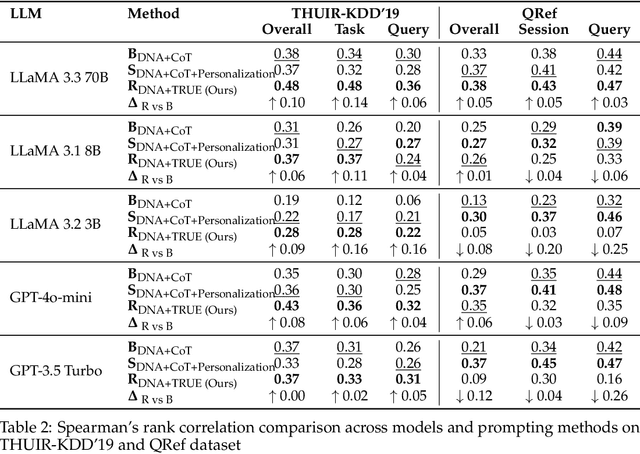
Abstract:Evaluation is fundamental in optimizing search experiences and supporting diverse user intents in Information Retrieval (IR). Traditional search evaluation methods primarily rely on relevance labels, which assess how well retrieved documents match a user's query. However, relevance alone fails to capture a search system's effectiveness in helping users achieve their search goals, making usefulness a critical evaluation criterion. In this paper, we explore an alternative approach: LLM-generated usefulness labels, which incorporate both implicit and explicit user behavior signals to evaluate document usefulness. We propose Task-aware Rubric-based Usefulness Evaluation (TRUE), a rubric-driven evaluation method that employs iterative sampling and reasoning to model complex search behavior patterns. Our findings show that (i) LLMs can generate moderate usefulness labels by leveraging comprehensive search session history incorporating personalization and contextual understanding, and (ii) fine-tuned LLMs improve usefulness judgments when provided with structured search session contexts. Additionally, we examine whether LLMs can distinguish between relevance and usefulness, particularly in cases where this divergence impacts search success. We also conduct an ablation study to identify key metrics for accurate usefulness label generation, optimizing for token efficiency and cost-effectiveness in real-world applications. This study advances LLM-based usefulness evaluation by refining key user metrics, exploring LLM-generated label reliability, and ensuring feasibility for large-scale search systems.
LLM-Driven Usefulness Labeling for IR Evaluation
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:In the information retrieval (IR) domain, evaluation plays a crucial role in optimizing search experiences and supporting diverse user intents. In the recent LLM era, research has been conducted to automate document relevance labels, as these labels have traditionally been assigned by crowd-sourced workers - a process that is both time and consuming and costly. This study focuses on LLM-generated usefulness labels, a crucial evaluation metric that considers the user's search intents and task objectives, an aspect where relevance falls short. Our experiment utilizes task-level, query-level, and document-level features along with user search behavior signals, which are essential in defining the usefulness of a document. Our research finds that (i) pre-trained LLMs can generate moderate usefulness labels by understanding the comprehensive search task session, (ii) pre-trained LLMs perform better judgement in short search sessions when provided with search session contexts. Additionally, we investigated whether LLMs can capture the unique divergence between relevance and usefulness, along with conducting an ablation study to identify the most critical metrics for accurate usefulness label generation. In conclusion, this work explores LLM-generated usefulness labels by evaluating critical metrics and optimizing for practicality in real-world settings.
Dynamic-KGQA: A Scalable Framework for Generating Adaptive Question Answering Datasets
Mar 06, 2025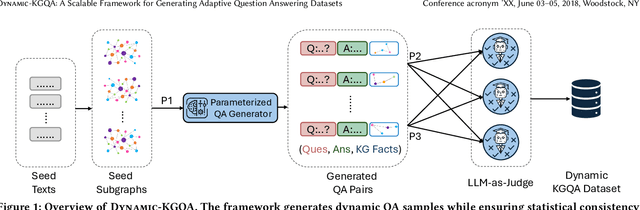
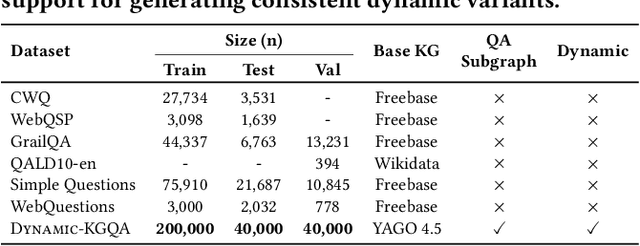
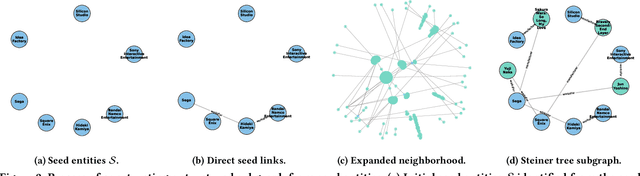
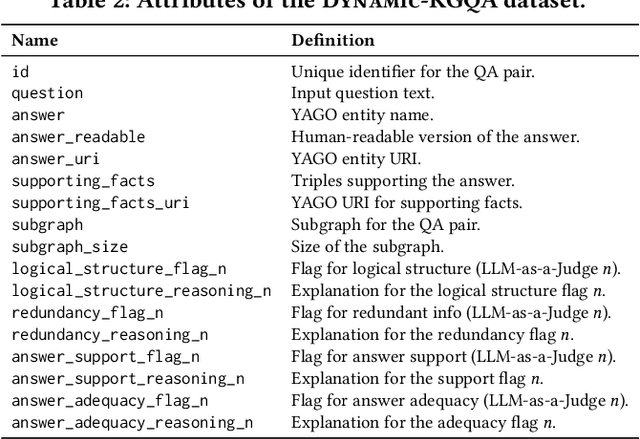
Abstract:As question answering (QA) systems advance alongside the rapid evolution of foundation models, the need for robust, adaptable, and large-scale evaluation benchmarks becomes increasingly critical. Traditional QA benchmarks are often static and publicly available, making them susceptible to data contamination and memorization by large language models (LLMs). Consequently, static benchmarks may overestimate model generalization and hinder a reliable assessment of real-world performance. In this work, we introduce Dynamic-KGQA, a scalable framework for generating adaptive QA datasets from knowledge graphs (KGs), designed to mitigate memorization risks while maintaining statistical consistency across iterations. Unlike fixed benchmarks, Dynamic-KGQA generates a new dataset variant on every run while preserving the underlying distribution, enabling fair and reproducible evaluations. Furthermore, our framework provides fine-grained control over dataset characteristics, supporting domain-specific and topic-focused QA dataset generation. Additionally, Dynamic-KGQA produces compact, semantically coherent subgraphs that facilitate both training and evaluation of KGQA models, enhancing their ability to leverage structured knowledge effectively. To align with existing evaluation protocols, we also provide static large-scale train/test/validation splits, ensuring comparability with prior methods. By introducing a dynamic, customizable benchmarking paradigm, Dynamic-KGQA enables a more rigorous and adaptable evaluation of QA systems.
Feedback-Aware Monte Carlo Tree Search for Efficient Information Seeking in Goal-Oriented Conversations
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:The ability to identify and acquire missing information is a critical component of effective decision making and problem solving. With the rise of conversational artificial intelligence (AI) systems, strategically formulating information-seeking questions becomes crucial and demands efficient methods to guide the search process. We introduce a novel approach to adaptive question-asking through a combination of Large Language Models (LLM) for generating questions that maximize information gain, Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) for constructing and leveraging a decision tree across multiple samples, and a hierarchical feedback mechanism to learn from past interactions. We present two key innovations: (1) an adaptive MCTS algorithm that balances exploration and exploitation for efficient search over potential questions; and (2) a clustering-based feedback algorithm that leverages prior experience to guide future interactions. Each incoming sample is assigned to a cluster based on its semantic similarity with previously observed samples. Our UCT (Upper Confidence bound for Trees) formulation selects optimal questions by combining expected rewards, a function of information gain, with a cluster-specific bonus that decays with depth, to emphasize the importance of early-stage questions that have proven effective for narrowing the solution space in similar samples. Experiments across three domains, including medical diagnosis and troubleshooting, demonstrate that our method leads to an average of 12% improvement in success rates and a 10x reduction in the average number of LLM calls made per conversation for the search process, in comparison to the state of the art.
Agents Are Not Enough
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:In the midst of the growing integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into various aspects of our lives, agents are experiencing a resurgence. These autonomous programs that act on behalf of humans are neither new nor exclusive to the mainstream AI movement. By exploring past incarnations of agents, we can understand what has been done previously, what worked, and more importantly, what did not pan out and why. This understanding lets us to examine what distinguishes the current focus on agents. While generative AI is appealing, this technology alone is insufficient to make new generations of agents more successful. To make the current wave of agents effective and sustainable, we envision an ecosystem that includes not only agents but also Sims, which represent user preferences and behaviors, as well as Assistants, which directly interact with the user and coordinate the execution of user tasks with the help of the agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge