Haochen Shi
History-Guided Iterative Visual Reasoning with Self-Correction
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Self-consistency methods are the core technique for improving the reasoning reliability of multimodal large language models (MLLMs). By generating multiple reasoning results through repeated sampling and selecting the best answer via voting, they play an important role in cross-modal tasks. However, most existing self-consistency methods are limited to a fixed ``repeated sampling and voting'' paradigm and do not reuse historical reasoning information. As a result, models struggle to actively correct visual understanding errors and dynamically adjust their reasoning during iteration. Inspired by the human reasoning behavior of repeated verification and dynamic error correction, we propose the H-GIVR framework. During iterative reasoning, the MLLM observes the image multiple times and uses previously generated answers as references for subsequent steps, enabling dynamic correction of errors and improving answer accuracy. We conduct comprehensive experiments on five datasets and three models. The results show that the H-GIVR framework can significantly improve cross-modal reasoning accuracy while maintaining low computational cost. For instance, using \texttt{Llama3.2-vision:11b} on the ScienceQA dataset, the model requires an average of 2.57 responses per question to achieve an accuracy of 78.90\%, representing a 107\% improvement over the baseline.
NAACL: Noise-AwAre Verbal Confidence Calibration for LLMs in RAG Systems
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Accurately assessing model confidence is essential for deploying large language models (LLMs) in mission-critical factual domains. While retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is widely adopted to improve grounding, confidence calibration in RAG settings remains poorly understood. We conduct a systematic study across four benchmarks, revealing that LLMs exhibit poor calibration performance due to noisy retrieved contexts. Specifically, contradictory or irrelevant evidence tends to inflate the model's false certainty, leading to severe overconfidence. To address this, we propose NAACL Rules (Noise-AwAre Confidence CaLibration Rules) to provide a principled foundation for resolving overconfidence under noise. We further design NAACL, a noise-aware calibration framework that synthesizes supervision from about 2K HotpotQA examples guided by these rules. By performing supervised fine-tuning (SFT) with this data, NAACL equips models with intrinsic noise awareness without relying on stronger teacher models. Empirical results show that NAACL yields substantial gains, improving ECE scores by 10.9% in-domain and 8.0% out-of-domain. By bridging the gap between retrieval noise and verbal calibration, NAACL paves the way for both accurate and epistemically reliable LLMs.
Locomotion Beyond Feet
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Most locomotion methods for humanoid robots focus on leg-based gaits, yet natural bipeds frequently rely on hands, knees, and elbows to establish additional contacts for stability and support in complex environments. This paper introduces Locomotion Beyond Feet, a comprehensive system for whole-body humanoid locomotion across extremely challenging terrains, including low-clearance spaces under chairs, knee-high walls, knee-high platforms, and steep ascending and descending stairs. Our approach addresses two key challenges: contact-rich motion planning and generalization across diverse terrains. To this end, we combine physics-grounded keyframe animation with reinforcement learning. Keyframes encode human knowledge of motor skills, are embodiment-specific, and can be readily validated in simulation or on hardware, while reinforcement learning transforms these references into robust, physically accurate motions. We further employ a hierarchical framework consisting of terrain-specific motion-tracking policies, failure recovery mechanisms, and a vision-based skill planner. Real-world experiments demonstrate that Locomotion Beyond Feet achieves robust whole-body locomotion and generalizes across obstacle sizes, obstacle instances, and terrain sequences.
Evolving Programmatic Skill Networks
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:We study continual skill acquisition in open-ended embodied environments where an agent must construct, refine, and reuse an expanding library of executable skills. We introduce the Programmatic Skill Network (PSN), a framework in which skills are executable symbolic programs forming a compositional network that evolves through experience. PSN defines three core mechanisms instantiated via large language models: (1)REFLECT for structured fault localization over skill compositions, (2) progressive optimization with maturity-aware update gating that stabilizes reliable skills while maintaining plasticity for uncertain ones, and (3) canonical structural refactoring under rollback validation that maintains network compactness. We further show that PSN's learning dynamics exhibit structural parallels to neural network training. Experiments on MineDojo and Crafter demonstrate robust skill reuse, rapid adaptation, and strong generalization across open-ended task distributions.\footnote{We plan to open-source the code.
Safety Compliance: Rethinking LLM Safety Reasoning through the Lens of Compliance
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:The proliferation of Large Language Models (LLMs) has demonstrated remarkable capabilities, elevating the critical importance of LLM safety. However, existing safety methods rely on ad-hoc taxonomy and lack a rigorous, systematic protection, failing to ensure safety for the nuanced and complex behaviors of modern LLM systems. To address this problem, we solve LLM safety from legal compliance perspectives, named safety compliance. In this work, we posit relevant established legal frameworks as safety standards for defining and measuring safety compliance, including the EU AI Act and GDPR, which serve as core legal frameworks for AI safety and data security in Europe. To bridge the gap between LLM safety and legal compliance, we first develop a new benchmark for safety compliance by generating realistic LLM safety scenarios seeded with legal statutes. Subsequently, we align Qwen3-8B using Group Policy Optimization (GRPO) to construct a safety reasoner, Compliance Reasoner, which effectively aligns LLMs with legal standards to mitigate safety risks. Our comprehensive experiments demonstrate that the Compliance Reasoner achieves superior performance on the new benchmark, with average improvements of +10.45% for the EU AI Act and +11.85% for GDPR.
Robot Trains Robot: Automatic Real-World Policy Adaptation and Learning for Humanoids
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:Simulation-based reinforcement learning (RL) has significantly advanced humanoid locomotion tasks, yet direct real-world RL from scratch or adapting from pretrained policies remains rare, limiting the full potential of humanoid robots. Real-world learning, despite being crucial for overcoming the sim-to-real gap, faces substantial challenges related to safety, reward design, and learning efficiency. To address these limitations, we propose Robot-Trains-Robot (RTR), a novel framework where a robotic arm teacher actively supports and guides a humanoid robot student. The RTR system provides protection, learning schedule, reward, perturbation, failure detection, and automatic resets. It enables efficient long-term real-world humanoid training with minimal human intervention. Furthermore, we propose a novel RL pipeline that facilitates and stabilizes sim-to-real transfer by optimizing a single dynamics-encoded latent variable in the real world. We validate our method through two challenging real-world humanoid tasks: fine-tuning a walking policy for precise speed tracking and learning a humanoid swing-up task from scratch, illustrating the promising capabilities of real-world humanoid learning realized by RTR-style systems. See https://robot-trains-robot.github.io/ for more info.
INFERENCEDYNAMICS: Efficient Routing Across LLMs through Structured Capability and Knowledge Profiling
May 22, 2025


Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) routing is a pivotal technique for navigating a diverse landscape of LLMs, aiming to select the best-performing LLMs tailored to the domains of user queries, while managing computational resources. However, current routing approaches often face limitations in scalability when dealing with a large pool of specialized LLMs, or in their adaptability to extending model scope and evolving capability domains. To overcome those challenges, we propose InferenceDynamics, a flexible and scalable multi-dimensional routing framework by modeling the capability and knowledge of models. We operate it on our comprehensive dataset RouteMix, and demonstrate its effectiveness and generalizability in group-level routing using modern benchmarks including MMLU-Pro, GPQA, BigGenBench, and LiveBench, showcasing its ability to identify and leverage top-performing models for given tasks, leading to superior outcomes with efficient resource utilization. The broader adoption of Inference Dynamics can empower users to harness the full specialized potential of the LLM ecosystem, and our code will be made publicly available to encourage further research.
Towards Multi-Agent Reasoning Systems for Collaborative Expertise Delegation: An Exploratory Design Study
May 12, 2025Abstract:Designing effective collaboration structure for multi-agent LLM systems to enhance collective reasoning is crucial yet remains under-explored. In this paper, we systematically investigate how collaborative reasoning performance is affected by three key design dimensions: (1) Expertise-Domain Alignment, (2) Collaboration Paradigm (structured workflow vs. diversity-driven integration), and (3) System Scale. Our findings reveal that expertise alignment benefits are highly domain-contingent, proving most effective for contextual reasoning tasks. Furthermore, collaboration focused on integrating diverse knowledge consistently outperforms rigid task decomposition. Finally, we empirically explore the impact of scaling the multi-agent system with expertise specialization and study the computational trade off, highlighting the need for more efficient communication protocol design. This work provides concrete guidelines for configuring specialized multi-agent system and identifies critical architectural trade-offs and bottlenecks for scalable multi-agent reasoning. The code will be made available upon acceptance.
The Curse of CoT: On the Limitations of Chain-of-Thought in In-Context Learning
Apr 07, 2025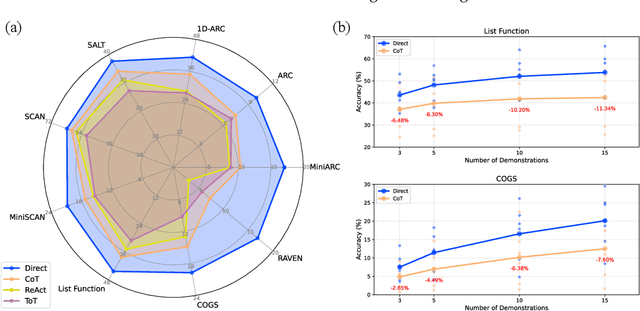
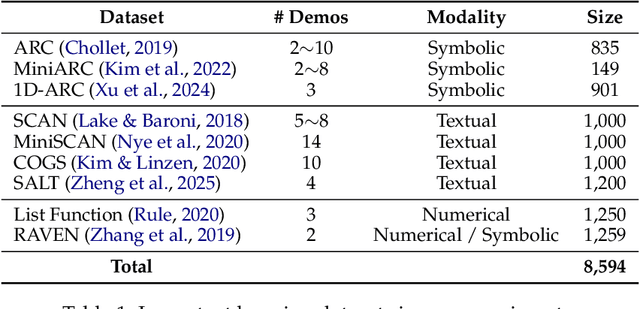
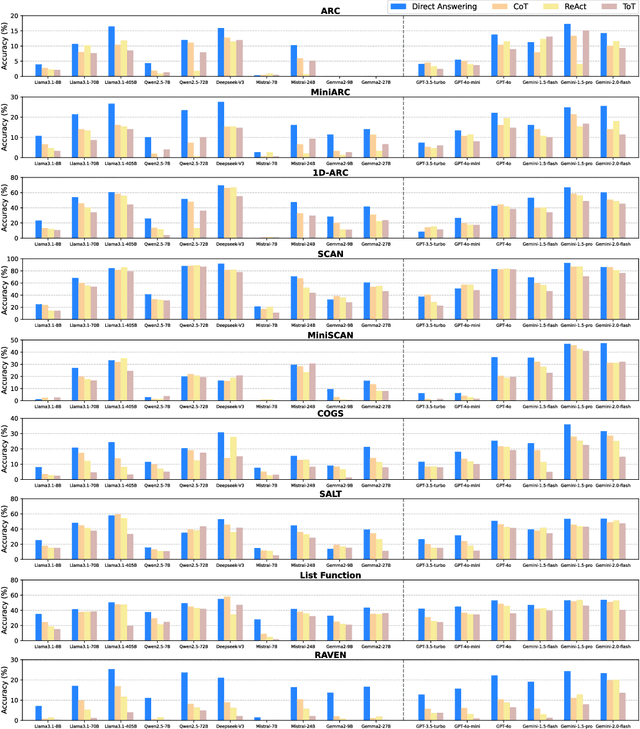
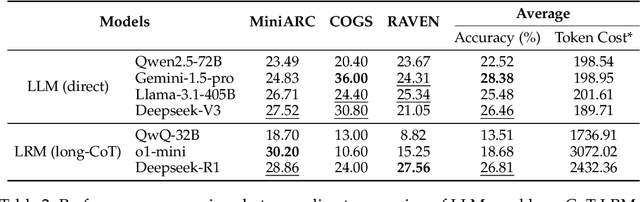
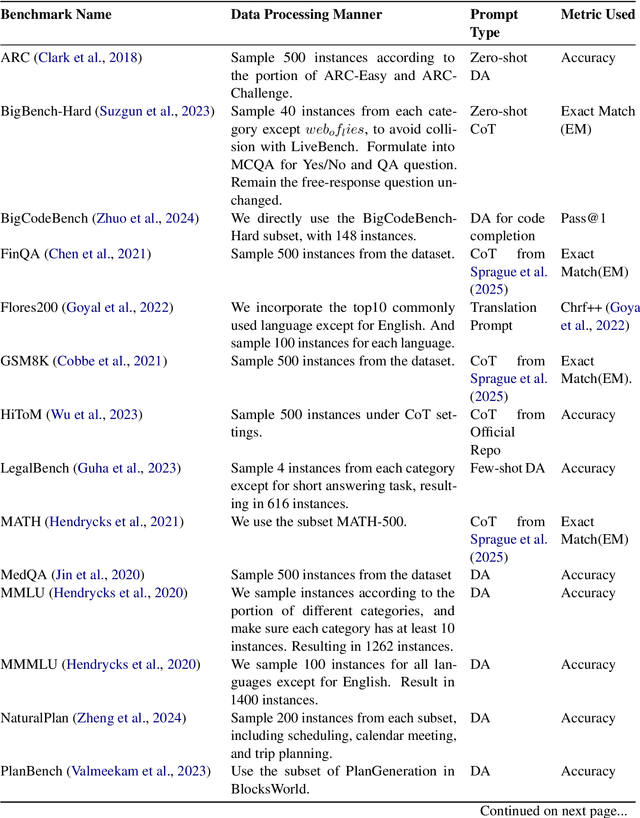
Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has been widely recognized for its ability to enhance reasoning capabilities in large language models (LLMs) through the generation of explicit explanatory rationales. However, our study reveals a surprising contradiction to this prevailing perspective. Through extensive experiments involving 16 state-of-the-art LLMs and nine diverse pattern-based in-context learning (ICL) datasets, we demonstrate that CoT and its reasoning variants consistently underperform direct answering across varying model scales and benchmark complexities. To systematically investigate this unexpected phenomenon, we designed extensive experiments to validate several hypothetical explanations. Our analysis uncovers a fundamental explicit-implicit duality driving CoT's performance in pattern-based ICL: while explicit reasoning falters due to LLMs' struggles to infer underlying patterns from demonstrations, implicit reasoning-disrupted by the increased contextual distance of CoT rationales-often compensates, delivering correct answers despite flawed rationales. This duality explains CoT's relative underperformance, as noise from weak explicit inference undermines the process, even as implicit mechanisms partially salvage outcomes. Notably, even long-CoT reasoning models, which excel in abstract and symbolic reasoning, fail to fully overcome these limitations despite higher computational costs. Our findings challenge existing assumptions regarding the universal efficacy of CoT, yielding novel insights into its limitations and guiding future research toward more nuanced and effective reasoning methodologies for LLMs.
Advances and Challenges in Foundation Agents: From Brain-Inspired Intelligence to Evolutionary, Collaborative, and Safe Systems
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:The advent of large language models (LLMs) has catalyzed a transformative shift in artificial intelligence, paving the way for advanced intelligent agents capable of sophisticated reasoning, robust perception, and versatile action across diverse domains. As these agents increasingly drive AI research and practical applications, their design, evaluation, and continuous improvement present intricate, multifaceted challenges. This survey provides a comprehensive overview, framing intelligent agents within a modular, brain-inspired architecture that integrates principles from cognitive science, neuroscience, and computational research. We structure our exploration into four interconnected parts. First, we delve into the modular foundation of intelligent agents, systematically mapping their cognitive, perceptual, and operational modules onto analogous human brain functionalities, and elucidating core components such as memory, world modeling, reward processing, and emotion-like systems. Second, we discuss self-enhancement and adaptive evolution mechanisms, exploring how agents autonomously refine their capabilities, adapt to dynamic environments, and achieve continual learning through automated optimization paradigms, including emerging AutoML and LLM-driven optimization strategies. Third, we examine collaborative and evolutionary multi-agent systems, investigating the collective intelligence emerging from agent interactions, cooperation, and societal structures, highlighting parallels to human social dynamics. Finally, we address the critical imperative of building safe, secure, and beneficial AI systems, emphasizing intrinsic and extrinsic security threats, ethical alignment, robustness, and practical mitigation strategies necessary for trustworthy real-world deployment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge