Ying Su
Unsupervised Feature Selection via Robust Autoencoder and Adaptive Graph Learning
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Effective feature selection is essential for high-dimensional data analysis and machine learning. Unsupervised feature selection (UFS) aims to simultaneously cluster data and identify the most discriminative features. Most existing UFS methods linearly project features into a pseudo-label space for clustering, but they suffer from two critical limitations: (1) an oversimplified linear mapping that fails to capture complex feature relationships, and (2) an assumption of uniform cluster distributions, ignoring outliers prevalent in real-world data. To address these issues, we propose the Robust Autoencoder-based Unsupervised Feature Selection (RAEUFS) model, which leverages a deep autoencoder to learn nonlinear feature representations while inherently improving robustness to outliers. We further develop an efficient optimization algorithm for RAEUFS. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art UFS approaches in both clean and outlier-contaminated data settings.
ActPlan-1K: Benchmarking the Procedural Planning Ability of Visual Language Models in Household Activities
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:Large language models~(LLMs) have been adopted to process textual task description and accomplish procedural planning in embodied AI tasks because of their powerful reasoning ability. However, there is still lack of study on how vision language models~(VLMs) behave when multi-modal task inputs are considered. Counterfactual planning that evaluates the model's reasoning ability over alternative task situations are also under exploited. In order to evaluate the planning ability of both multi-modal and counterfactual aspects, we propose ActPlan-1K. ActPlan-1K is a multi-modal planning benchmark constructed based on ChatGPT and household activity simulator iGibson2. The benchmark consists of 153 activities and 1,187 instances. Each instance describing one activity has a natural language task description and multiple environment images from the simulator. The gold plan of each instance is action sequences over the objects in provided scenes. Both the correctness and commonsense satisfaction are evaluated on typical VLMs. It turns out that current VLMs are still struggling at generating human-level procedural plans for both normal activities and counterfactual activities. We further provide automatic evaluation metrics by finetuning over BLEURT model to facilitate future research on our benchmark.
LLMs Assist NLP Researchers: Critique Paper (Meta-)Reviewing
Jun 25, 2024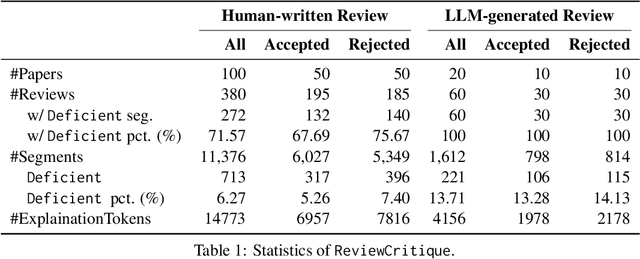
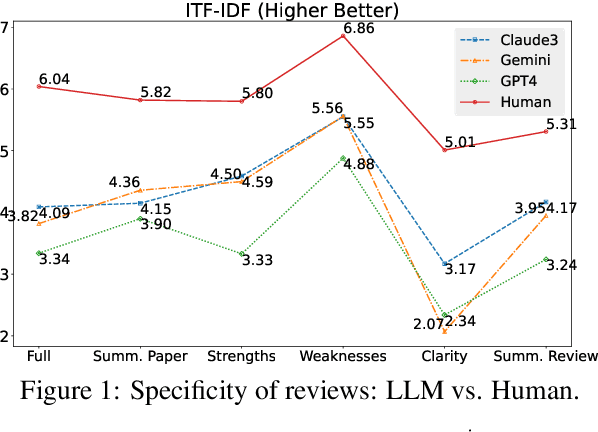
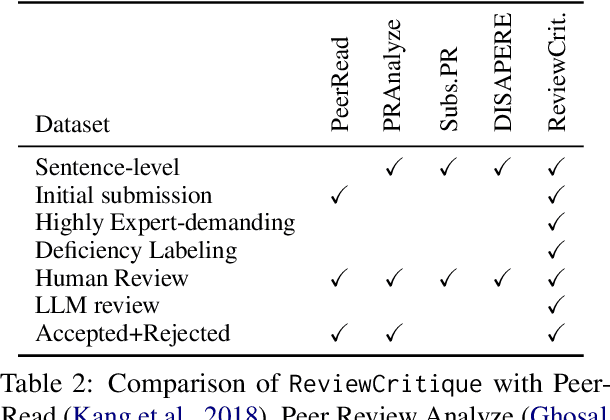
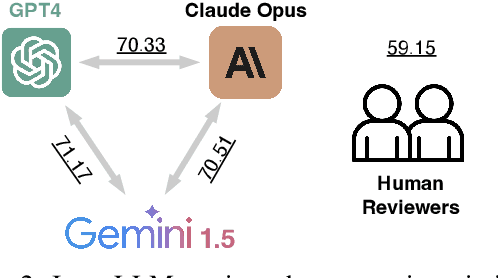
Abstract:This work is motivated by two key trends. On one hand, large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable versatility in various generative tasks such as writing, drawing, and question answering, significantly reducing the time required for many routine tasks. On the other hand, researchers, whose work is not only time-consuming but also highly expertise-demanding, face increasing challenges as they have to spend more time reading, writing, and reviewing papers. This raises the question: how can LLMs potentially assist researchers in alleviating their heavy workload? This study focuses on the topic of LLMs assist NLP Researchers, particularly examining the effectiveness of LLM in assisting paper (meta-)reviewing and its recognizability. To address this, we constructed the ReviewCritique dataset, which includes two types of information: (i) NLP papers (initial submissions rather than camera-ready) with both human-written and LLM-generated reviews, and (ii) each review comes with "deficiency" labels and corresponding explanations for individual segments, annotated by experts. Using ReviewCritique, this study explores two threads of research questions: (i) "LLMs as Reviewers", how do reviews generated by LLMs compare with those written by humans in terms of quality and distinguishability? (ii) "LLMs as Metareviewers", how effectively can LLMs identify potential issues, such as Deficient or unprofessional review segments, within individual paper reviews? To our knowledge, this is the first work to provide such a comprehensive analysis.
DPER: Diffusion Prior Driven Neural Representation for Limited Angle and Sparse View CT Reconstruction
Apr 27, 2024



Abstract:Limited-angle and sparse-view computed tomography (LACT and SVCT) are crucial for expanding the scope of X-ray CT applications. However, they face challenges due to incomplete data acquisition, resulting in diverse artifacts in the reconstructed CT images. Emerging implicit neural representation (INR) techniques, such as NeRF, NeAT, and NeRP, have shown promise in under-determined CT imaging reconstruction tasks. However, the unsupervised nature of INR architecture imposes limited constraints on the solution space, particularly for the highly ill-posed reconstruction task posed by LACT and ultra-SVCT. In this study, we introduce the Diffusion Prior Driven Neural Representation (DPER), an advanced unsupervised framework designed to address the exceptionally ill-posed CT reconstruction inverse problems. DPER adopts the Half Quadratic Splitting (HQS) algorithm to decompose the inverse problem into data fidelity and distribution prior sub-problems. The two sub-problems are respectively addressed by INR reconstruction scheme and pre-trained score-based diffusion model. This combination initially preserves the implicit image local consistency prior from INR. Additionally, it effectively augments the feasibility of the solution space for the inverse problem through the generative diffusion model, resulting in increased stability and precision in the solutions. We conduct comprehensive experiments to evaluate the performance of DPER on LACT and ultra-SVCT reconstruction with two public datasets (AAPM and LIDC). The results show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art reconstruction methods on in-domain datasets, while achieving significant performance improvements on out-of-domain datasets.
Rethinking the Bounds of LLM Reasoning: Are Multi-Agent Discussions the Key?
Feb 28, 2024Abstract:Recent progress in LLMs discussion suggests that multi-agent discussion improves the reasoning abilities of LLMs. In this work, we reevaluate this claim through systematic experiments, where we propose a novel group discussion framework to enrich the set of discussion mechanisms. Interestingly, our results show that a single-agent LLM with strong prompts can achieve almost the same performance as the best existing discussion approach on a wide range of reasoning tasks and backbone LLMs. We observe that the multi-agent discussion performs better than a single agent only when there is no demonstration in the prompt. Further study reveals the common interaction mechanisms of LLMs during the discussion.
EntailE: Introducing Textual Entailment in Commonsense Knowledge Graph Completion
Feb 15, 2024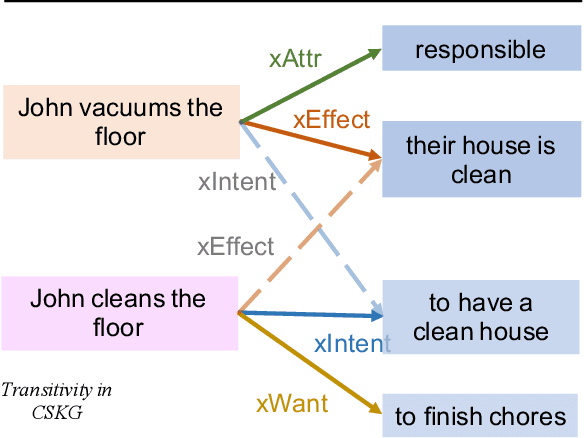
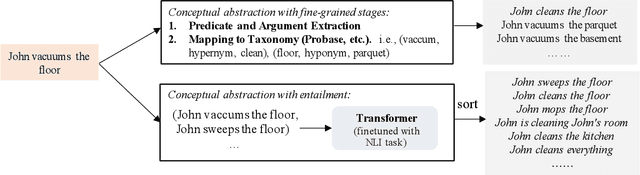
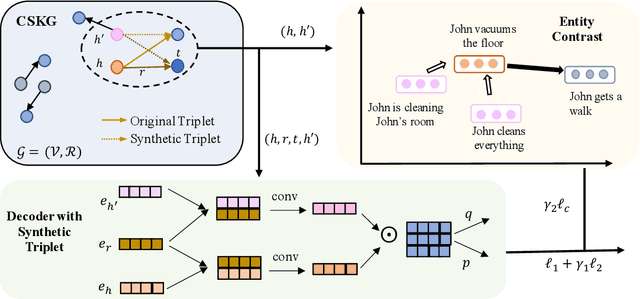
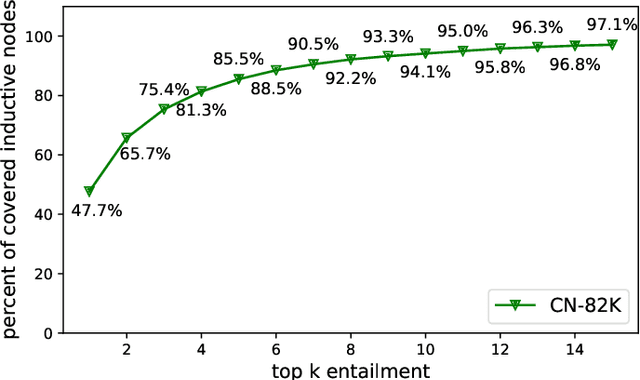
Abstract:Commonsense knowledge graph completion is a new challenge for commonsense knowledge graph construction and application. In contrast to factual knowledge graphs such as Freebase and YAGO, commonsense knowledge graphs (CSKGs; e.g., ConceptNet) utilize free-form text to represent named entities, short phrases, and events as their nodes. Such a loose structure results in large and sparse CSKGs, which makes the semantic understanding of these nodes more critical for learning rich commonsense knowledge graph embedding. While current methods leverage semantic similarities to increase the graph density, the semantic plausibility of the nodes and their relations are under-explored. Previous works adopt conceptual abstraction to improve the consistency of modeling (event) plausibility, but they are not scalable enough and still suffer from data sparsity. In this paper, we propose to adopt textual entailment to find implicit entailment relations between CSKG nodes, to effectively densify the subgraph connecting nodes within the same conceptual class, which indicates a similar level of plausibility. Each node in CSKG finds its top entailed nodes using a finetuned transformer over natural language inference (NLI) tasks, which sufficiently capture textual entailment signals. The entailment relation between these nodes are further utilized to: 1) build new connections between source triplets and entailed nodes to densify the sparse CSKGs; 2) enrich the generalization ability of node representations by comparing the node embeddings with a contrastive loss. Experiments on two standard CSKGs demonstrate that our proposed framework EntailE can improve the performance of CSKG completion tasks under both transductive and inductive settings.
PipeNet: Question Answering with Semantic Pruning over Knowledge Graphs
Jan 31, 2024Abstract:It is well acknowledged that incorporating explicit knowledge graphs (KGs) can benefit question answering. Existing approaches typically follow a grounding-reasoning pipeline in which entity nodes are first grounded for the query (question and candidate answers), and then a reasoning module reasons over the matched multi-hop subgraph for answer prediction. Although the pipeline largely alleviates the issue of extracting essential information from giant KGs, efficiency is still an open challenge when scaling up hops in grounding the subgraphs. In this paper, we target at finding semantically related entity nodes in the subgraph to improve the efficiency of graph reasoning with KG. We propose a grounding-pruning-reasoning pipeline to prune noisy nodes, remarkably reducing the computation cost and memory usage while also obtaining decent subgraph representation. In detail, the pruning module first scores concept nodes based on the dependency distance between matched spans and then prunes the nodes according to score ranks. To facilitate the evaluation of pruned subgraphs, we also propose a graph attention network (GAT) based module to reason with the subgraph data. Experimental results on CommonsenseQA and OpenBookQA demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
On the Discussion of Large Language Models: Symmetry of Agents and Interplay with Prompts
Nov 13, 2023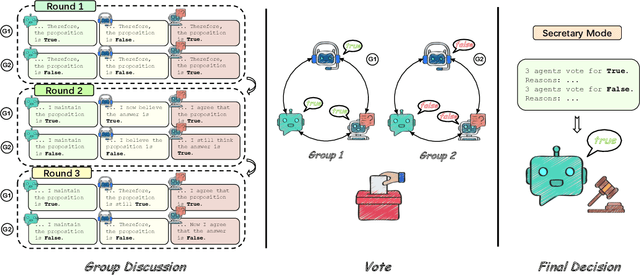

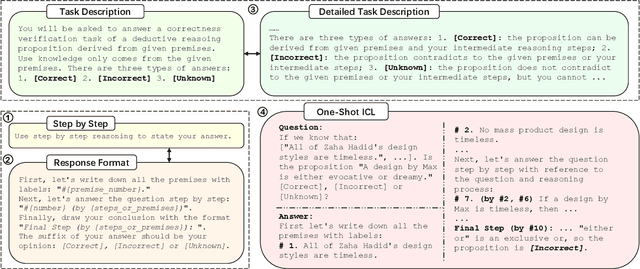
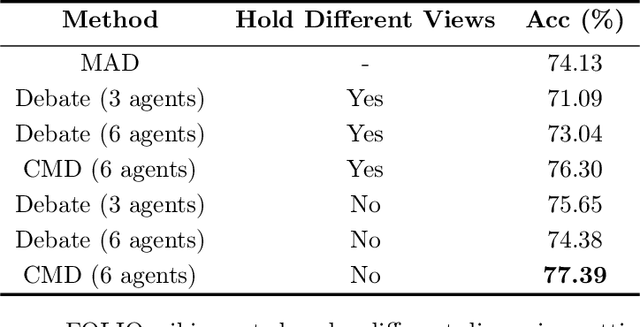
Abstract:Two ways has been discussed to unlock the reasoning capability of a large language model. The first one is prompt engineering and the second one is to combine the multiple inferences of large language models, or the multi-agent discussion. Theoretically, this paper justifies the multi-agent discussion mechanisms from the symmetry of agents. Empirically, this paper reports the empirical results of the interplay of prompts and discussion mechanisms, revealing the empirical state-of-the-art performance of complex multi-agent mechanisms can be approached by carefully developed prompt engineering. This paper also proposes a scalable discussion mechanism based on conquer and merge, providing a simple multi-agent discussion solution with simple prompts but state-of-the-art performance.
Are LLMs Rigorous Logical Reasoner? Empowering Natural Language Proof Generation with Contrastive Stepwise Decoding
Nov 12, 2023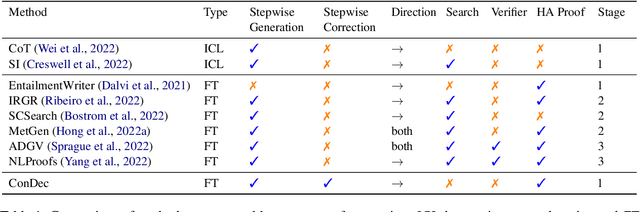
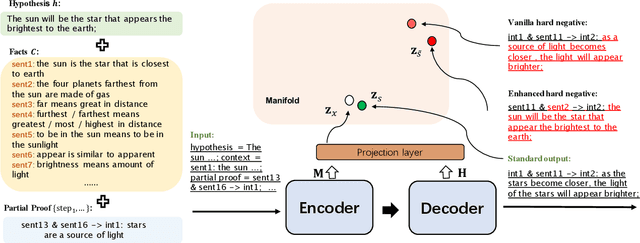
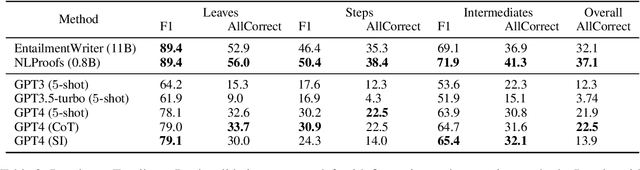
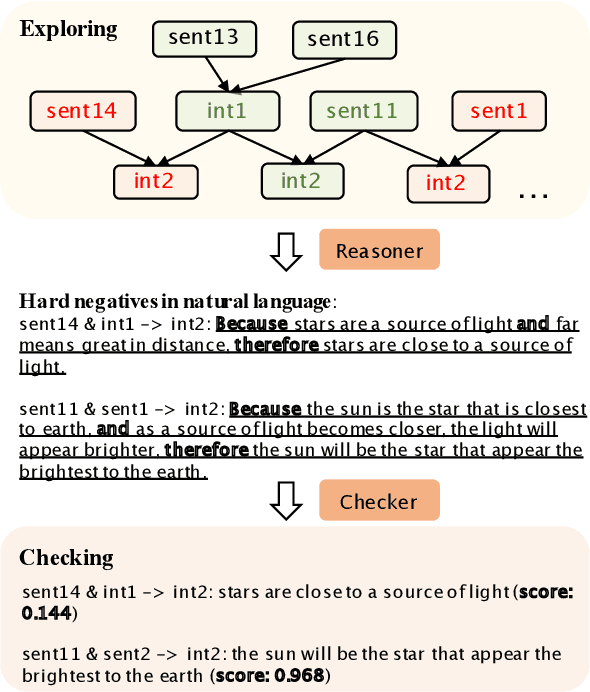
Abstract:Logical reasoning remains a pivotal component within the realm of artificial intelligence. The recent evolution of large language models (LLMs) has marked significant progress in this domain. The adoption of strategies like chain-of-thought (CoT) has enhanced the performance of LLMs across diverse reasoning tasks. Nonetheless, logical reasoning that involves proof planning, specifically those that necessitate the validation of explanation accuracy, continues to present stumbling blocks. In this study, we first evaluate the efficacy of LLMs with advanced CoT strategies concerning such tasks. Our analysis reveals that LLMs still struggle to navigate complex reasoning chains, which demand the meticulous linkage of premises to derive a cogent conclusion. To address this issue, we finetune a smaller-scale language model, equipping it to decompose proof objectives into more manageable subgoals. We also introduce contrastive decoding to stepwise proof generation, making use of negative reasoning paths to strengthen the model's capacity for logical deduction. Experiments on EntailmentBank underscore the success of our method in augmenting the proof planning abilities of language models.
MICO: A Multi-alternative Contrastive Learning Framework for Commonsense Knowledge Representation
Oct 14, 2022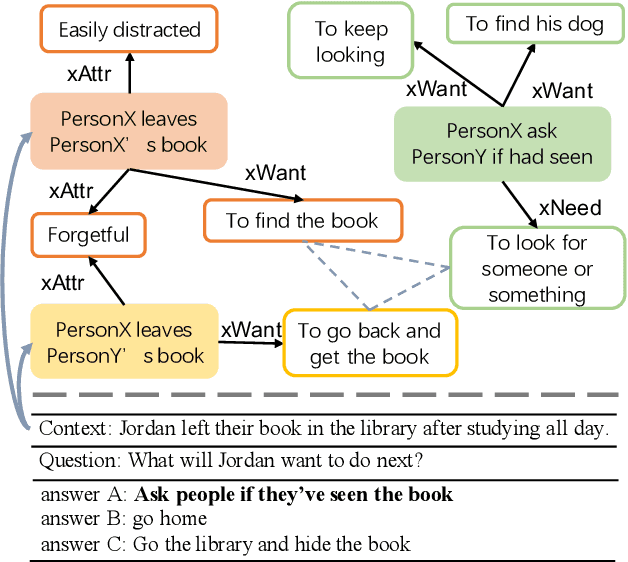
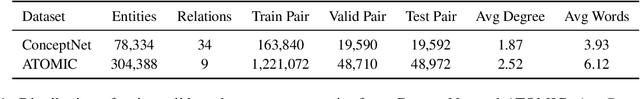

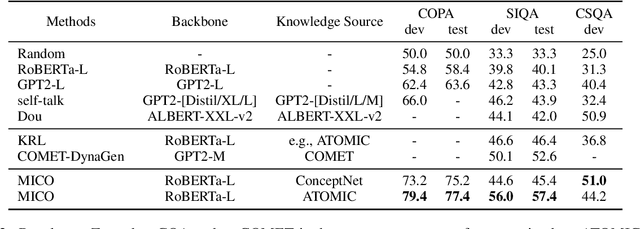
Abstract:Commonsense reasoning tasks such as commonsense knowledge graph completion and commonsense question answering require powerful representation learning. In this paper, we propose to learn commonsense knowledge representation by MICO, a Multi-alternative contrastve learning framework on COmmonsense knowledge graphs (MICO). MICO generates the commonsense knowledge representation by contextual interaction between entity nodes and relations with multi-alternative contrastive learning. In MICO, the head and tail entities in an $(h,r,t)$ knowledge triple are converted to two relation-aware sequence pairs (a premise and an alternative) in the form of natural language. Semantic representations generated by MICO can benefit the following two tasks by simply comparing the distance score between the representations: 1) zero-shot commonsense question answering task; 2) inductive commonsense knowledge graph completion task. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness of our method.
* 9 pages, 2 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge