Wenting Zhao
Scaling Agentic Verifier for Competitive Coding
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong coding capabilities but still struggle to solve competitive programming problems correctly in a single attempt. Execution-based re-ranking offers a promising test-time scaling strategy, yet existing methods are constrained by either difficult test case generation or inefficient random input sampling. To address this limitation, we propose Agentic Verifier, an execution-based agent that actively reasons about program behaviors and searches for highly discriminative test inputs that expose behavioral discrepancies among candidate solutions. Through multi-turn interaction with code execution environments, the verifier iteratively refines the candidate input generator and produces targeted counterexamples rather than blindly sampling inputs. We train the verifier to acquire this discriminative input generation capability via a scalable pipeline combining large-scale data synthesis, rejection fine-tuning, and agentic reinforcement learning. Extensive experiments across five competitive programming benchmarks demonstrate consistent improvements over strong execution-based baselines, achieving up to +10-15% absolute gains in Best@K accuracy. Further analysis reveals clear test-time scaling behavior and highlights the verifier's broader potential beyond reranking.
SWE-Universe: Scale Real-World Verifiable Environments to Millions
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We propose SWE-Universe, a scalable and efficient framework for automatically constructing real-world software engineering (SWE) verifiable environments from GitHub pull requests (PRs). To overcome the prevalent challenges of automatic building, such as low production yield, weak verifiers, and prohibitive cost, our framework utilizes a building agent powered by an efficient custom-trained model. This agent employs iterative self-verification and in-loop hacking detection to ensure the reliable generation of high-fidelity, verifiable tasks. Using this method, we scale the number of real-world multilingual SWE environments to a million scale (807,693). We demonstrate the profound value of our environments through large-scale agentic mid-training and reinforcement learning. Finally, we applied this technique to Qwen3-Max-Thinking and achieved a score of 75.3% on SWE-Bench Verified. Our work provides both a critical resource and a robust methodology to advance the next generation of coding agents.
SweRank+: Multilingual, Multi-Turn Code Ranking for Software Issue Localization
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Maintaining large-scale, multilingual codebases hinges on accurately localizing issues, which requires mapping natural-language error descriptions to the relevant functions that need to be modified. However, existing ranking approaches are often Python-centric and perform a single-pass search over the codebase. This work introduces SweRank+, a framework that couples SweRankMulti, a cross-lingual code ranking tool, with SweRankAgent, an agentic search setup, for iterative, multi-turn reasoning over the code repository. SweRankMulti comprises a code embedding retriever and a listwise LLM reranker, and is trained using a carefully curated large-scale issue localization dataset spanning multiple popular programming languages. SweRankAgent adopts an agentic search loop that moves beyond single-shot localization with a memory buffer to reason and accumulate relevant localization candidates over multiple turns. Our experiments on issue localization benchmarks spanning various languages demonstrate new state-of-the-art performance with SweRankMulti, while SweRankAgent further improves localization over single-pass ranking.
Self-Abstraction from Grounded Experience for Plan-Guided Policy Refinement
Nov 08, 2025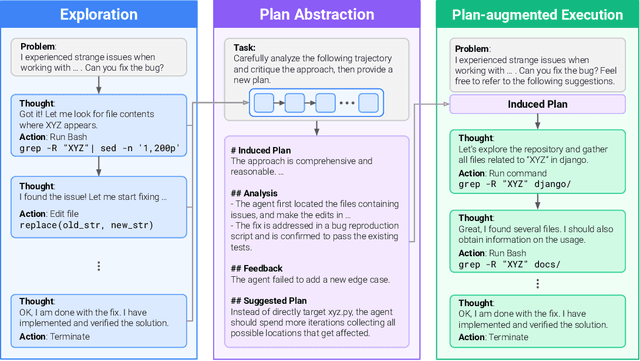
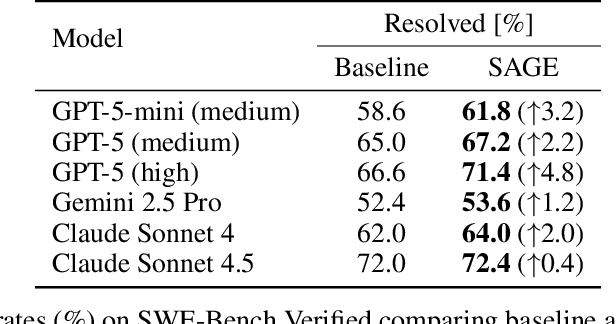
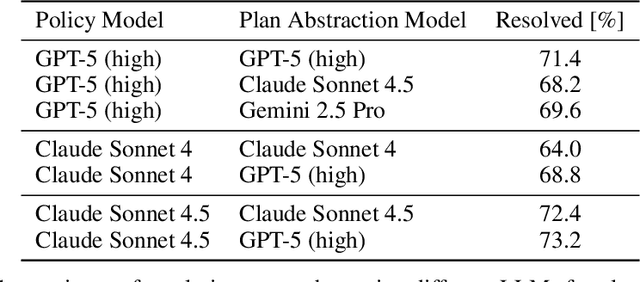
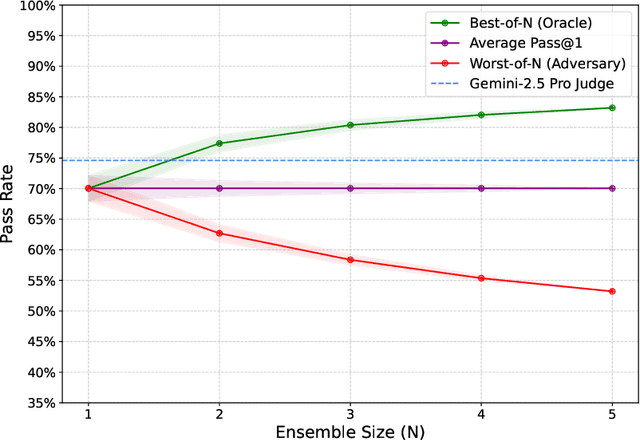
Abstract:Large language model (LLM) based agents are increasingly used to tackle software engineering tasks that require multi-step reasoning and code modification, demonstrating promising yet limited performance. However, most existing LLM agents typically operate within static execution frameworks, lacking a principled mechanism to learn and self-improve from their own experience and past rollouts. As a result, their performance remains bounded by the initial framework design and the underlying LLM's capabilities. We propose Self-Abstraction from Grounded Experience (SAGE), a framework that enables agents to learn from their own task executions and refine their behavior through self-abstraction. After an initial rollout, the agent induces a concise plan abstraction from its grounded experience, distilling key steps, dependencies, and constraints. This learned abstraction is then fed back as contextual guidance, refining the agent's policy and supporting more structured, informed subsequent executions. Empirically, SAGE delivers consistent performance gains across diverse LLM backbones and agent architectures. Notably, it yields a 7.2% relative performance improvement over the strong Mini-SWE-Agent baseline when paired with the GPT-5 (high) backbone. SAGE further achieves strong overall performance on SWE-Bench Verified benchmark, reaching 73.2% and 74% Pass@1 resolve rates with the Mini-SWE-Agent and OpenHands CodeAct agent framework, respectively.
StepWiser: Stepwise Generative Judges for Wiser Reasoning
Aug 27, 2025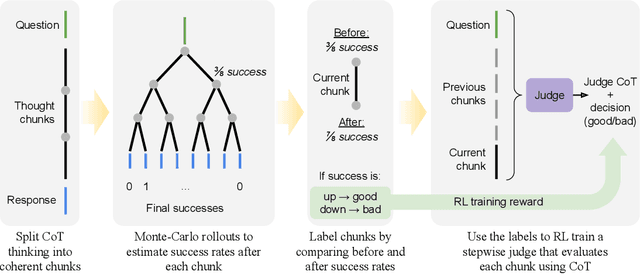


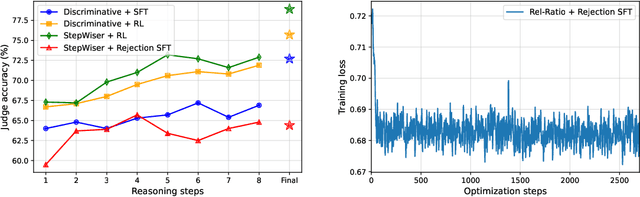
Abstract:As models increasingly leverage multi-step reasoning strategies to solve complex problems, supervising the logical validity of these intermediate steps has become a critical research challenge. Process reward models address this by providing step-by-step feedback, but current approaches have two major drawbacks: they typically function as classifiers without providing explanations, and their reliance on supervised fine-tuning with static datasets limits generalization. Inspired by recent advances, we reframe stepwise reward modeling from a classification task to a reasoning task itself. We thus propose a generative judge that reasons about the policy model's reasoning steps (i.e., meta-reasons), outputting thinking tokens before delivering a final verdict. Our model, StepWiser, is trained by reinforcement learning using relative outcomes of rollouts. We show it provides (i) better judgment accuracy on intermediate steps than existing methods; (ii) can be used to improve the policy model at training time; and (iii) improves inference-time search.
Towards LLM Agents for Earth Observation
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Earth Observation (EO) provides critical planetary data for environmental monitoring, disaster management, climate science, and other scientific domains. Here we ask: Are AI systems ready for reliable Earth Observation? We introduce \datasetnamenospace, a benchmark of 140 yes/no questions from NASA Earth Observatory articles across 13 topics and 17 satellite sensors. Using Google Earth Engine API as a tool, LLM agents can only achieve an accuracy of 33% because the code fails to run over 58% of the time. We improve the failure rate for open models by fine-tuning synthetic data, allowing much smaller models (Llama-3.1-8B) to achieve comparable accuracy to much larger ones (e.g., DeepSeek-R1). Taken together, our findings identify significant challenges to be solved before AI agents can automate earth observation, and suggest paths forward. The project page is available at https://iandrover.github.io/UnivEarth.
Multi-Turn Code Generation Through Single-Step Rewards
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:We address the problem of code generation from multi-turn execution feedback. Existing methods either generate code without feedback or use complex, hierarchical reinforcement learning to optimize multi-turn rewards. We propose a simple yet scalable approach, $\mu$Code, that solves multi-turn code generation using only single-step rewards. Our key insight is that code generation is a one-step recoverable MDP, where the correct code can be recovered from any intermediate code state in a single turn. $\mu$Code iteratively trains both a generator to provide code solutions conditioned on multi-turn execution feedback and a verifier to score the newly generated code. Experimental evaluations show that our approach achieves significant improvements over the state-of-the-art baselines. We provide analysis of the design choices of the reward models and policy, and show the efficacy of $\mu$Code at utilizing the execution feedback. Our code is available at https://github.com/portal-cornell/muCode.
ProjectTest: A Project-level LLM Unit Test Generation Benchmark and Impact of Error Fixing Mechanisms
Feb 11, 2025



Abstract:Unit test generation has become a promising and important use case of LLMs. However, existing evaluation benchmarks for assessing LLM unit test generation capabilities focus on function- or class-level code rather than more practical and challenging project-level codebases. To address such limitation, we propose ProjectTest, a project-level benchmark for unit test generation covering Python, Java, and JavaScript. ProjectTest features 20 moderate-sized and high-quality projects per language. We evaluate nine frontier LLMs on ProjectTest and the results show that all frontier LLMs tested exhibit moderate performance on ProjectTest on Python and Java, highlighting the difficulty of ProjectTest. We also conduct a thorough error analysis, which shows that even frontier LLMs, such as Claude-3.5-Sonnet, have significant simple errors, including compilation and cascade errors. Motivated by this observation, we further evaluate all frontier LLMs under manual error-fixing and self-error-fixing scenarios to assess their potential when equipped with error-fixing mechanisms.
ProjectTest: A Project-level Unit Test Generation Benchmark and Impact of Error Fixing Mechanisms
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Unit test generation has become a promising and important use case of LLMs. However, existing evaluation benchmarks for assessing LLM unit test generation capabilities focus on function- or class-level code rather than more practical and challenging project-level codebases. To address such limitation, we propose ProjectTest, a project-level benchmark for unit test generation covering Python, Java, and JavaScript. ProjectTest features 20 moderate-sized and high-quality projects per language. We evaluate nine frontier LLMs on ProjectTest and the results show that all frontier LLMs tested exhibit moderate performance on ProjectTest on Python and Java, highlighting the difficulty of ProjectTest. We also conduct a thorough error analysis, which shows that even frontier LLMs, such as Claude-3.5-Sonnet, have significant simple errors, including compilation and cascade errors. Motivated by this observation, we further evaluate all frontier LLMs under manual error-fixing and self-error-fixing scenarios to assess their potential when equipped with error-fixing mechanisms.
Commit0: Library Generation from Scratch
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:With the goal of benchmarking generative systems beyond expert software development ability, we introduce Commit0, a benchmark that challenges AI agents to write libraries from scratch. Agents are provided with a specification document outlining the library's API as well as a suite of interactive unit tests, with the goal of producing an implementation of this API accordingly. The implementation is validated through running these unit tests. As a benchmark, Commit0 is designed to move beyond static one-shot code generation towards agents that must process long-form natural language specifications, adapt to multi-stage feedback, and generate code with complex dependencies. Commit0 also offers an interactive environment where models receive static analysis and execution feedback on the code they generate. Our experiments demonstrate that while current agents can pass some unit tests, none can yet fully reproduce full libraries. Results also show that interactive feedback is quite useful for models to generate code that passes more unit tests, validating the benchmarks that facilitate its use.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge