Barry Wang
Command-V: Pasting LLM Behaviors via Activation Profiles
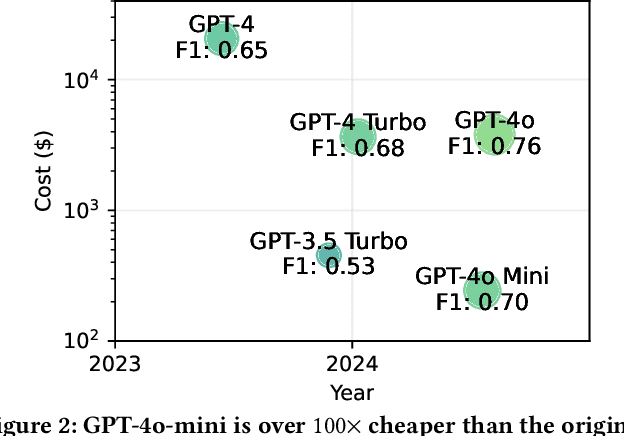
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:Retrofitting large language models (LLMs) with new behaviors typically requires full finetuning or distillation-costly steps that must be repeated for every architecture. In this work, we introduce Command-V, a backpropagation-free behavior transfer method that copies an existing residual activation adapter from a donor model and pastes its effect into a recipient model. Command-V profiles layer activations on a small prompt set, derives linear converters between corresponding layers, and applies the donor intervention in the recipient's activation space. This process does not require access to the original training data and needs minimal compute. In three case studies-safety-refusal enhancement, jailbreak facilitation, and automatic chain-of-thought reasoning--Command-V matches or exceeds the performance of direct finetuning while using orders of magnitude less compute. Our code and data are accessible at https://github.com/GithuBarry/Command-V/.
LLMs unlock new paths to monetizing exploits
May 16, 2025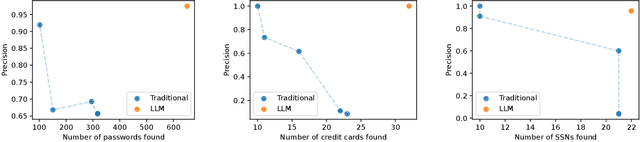
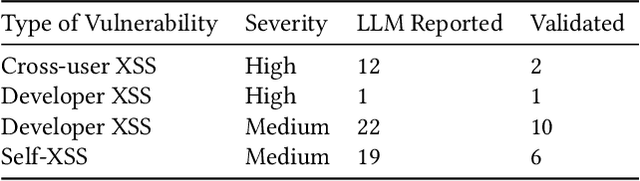

Abstract:We argue that Large language models (LLMs) will soon alter the economics of cyberattacks. Instead of attacking the most commonly used software and monetizing exploits by targeting the lowest common denominator among victims, LLMs enable adversaries to launch tailored attacks on a user-by-user basis. On the exploitation front, instead of human attackers manually searching for one difficult-to-identify bug in a product with millions of users, LLMs can find thousands of easy-to-identify bugs in products with thousands of users. And on the monetization front, instead of generic ransomware that always performs the same attack (encrypt all your data and request payment to decrypt), an LLM-driven ransomware attack could tailor the ransom demand based on the particular content of each exploited device. We show that these two attacks (and several others) are imminently practical using state-of-the-art LLMs. For example, we show that without any human intervention, an LLM finds highly sensitive personal information in the Enron email dataset (e.g., an executive having an affair with another employee) that could be used for blackmail. While some of our attacks are still too expensive to scale widely today, the incentives to implement these attacks will only increase as LLMs get cheaper. Thus, we argue that LLMs create a need for new defense-in-depth approaches.
NoveltyBench: Evaluating Language Models for Humanlike Diversity
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Language models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities on standard benchmarks, yet they struggle increasingly from mode collapse, the inability to generate diverse and novel outputs. Our work introduces NoveltyBench, a benchmark specifically designed to evaluate the ability of language models to produce multiple distinct and high-quality outputs. NoveltyBench utilizes prompts curated to elicit diverse answers and filtered real-world user queries. Evaluating 20 leading language models, we find that current state-of-the-art systems generate significantly less diversity than human writers. Notably, larger models within a family often exhibit less diversity than their smaller counterparts, challenging the notion that capability on standard benchmarks translates directly to generative utility. While prompting strategies like in-context regeneration can elicit diversity, our findings highlight a fundamental lack of distributional diversity in current models, reducing their utility for users seeking varied responses and suggesting the need for new training and evaluation paradigms that prioritize diversity alongside quality.
Are Triggers Needed for Document-Level Event Extraction?
Nov 13, 2024Abstract:Most existing work on event extraction has focused on sentence-level texts and presumes the identification of a trigger-span -- a word or phrase in the input that evokes the occurrence of an event of interest. Event arguments are then extracted with respect to the trigger. Indeed, triggers are treated as integral to, and trigger detection as an essential component of, event extraction. In this paper, we provide the first investigation of the role of triggers for the more difficult and much less studied task of document-level event extraction. We analyze their usefulness in multiple end-to-end and pipelined neural event extraction models for three document-level event extraction datasets, measuring performance using triggers of varying quality (human-annotated, LLM-generated, keyword-based, and random). Our research shows that trigger effectiveness varies based on the extraction task's characteristics and data quality, with basic, automatically-generated triggers serving as a viable alternative to human-annotated ones. Furthermore, providing detailed event descriptions to the extraction model helps maintain robust performance even when trigger quality degrades. Perhaps surprisingly, we also find that the mere existence of trigger input, even random ones, is important for prompt-based LLM approaches to the task.
IQA-EVAL: Automatic Evaluation of Human-Model Interactive Question Answering
Aug 24, 2024



Abstract:To evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) for question answering (QA), traditional methods typically focus on directly assessing the immediate responses generated by the models based on the given question and context. In the common use case of humans seeking AI assistant's help in finding information, these non-interactive evaluations do not account for the dynamic nature of human-model conversations, and interaction-aware evaluations have shown that accurate QA models are preferred by humans (Lee et al., 2023). Recent works in human-computer interaction (HCI) have employed human evaluators to conduct interactions and evaluations, but they are often prohibitively expensive and time-consuming to scale. In this work, we introduce an automatic evaluation framework IQA-EVAL to Interactive Question Answering Evaluation. More specifically, we introduce LLM-based Evaluation Agent (LEA) that can: (1) simulate human behaviors to generate interactions with IQA models; (2) automatically evaluate the generated interactions. Moreover, we propose assigning personas to LEAs to better simulate groups of real human evaluators. We show that: (1) our evaluation framework with GPT-4 (or Claude) as the backbone model achieves a high correlation with human evaluations on the IQA task; (2) assigning personas to LEA to better represent the crowd further significantly improves correlations. Finally, we use our automatic metric to evaluate five recent representative LLMs with over 1000 questions from complex and ambiguous question answering tasks, which comes with a substantial cost of $5k if evaluated by humans.
Probing Representations for Document-level Event Extraction
Oct 23, 2023

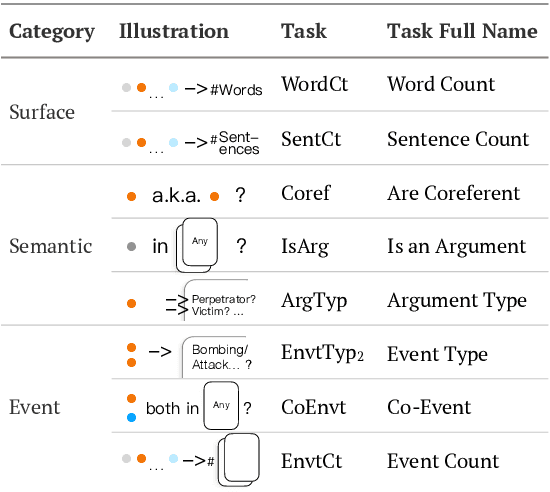

Abstract:The probing classifiers framework has been employed for interpreting deep neural network models for a variety of natural language processing (NLP) applications. Studies, however, have largely focused on sentencelevel NLP tasks. This work is the first to apply the probing paradigm to representations learned for document-level information extraction (IE). We designed eight embedding probes to analyze surface, semantic, and event-understanding capabilities relevant to document-level event extraction. We apply them to the representations acquired by learning models from three different LLM-based document-level IE approaches on a standard dataset. We found that trained encoders from these models yield embeddings that can modestly improve argument detections and labeling but only slightly enhance event-level tasks, albeit trade-offs in information helpful for coherence and event-type prediction. We further found that encoder models struggle with document length and cross-sentence discourse.
Automatic Error Analysis for Document-level Information Extraction
Sep 15, 2022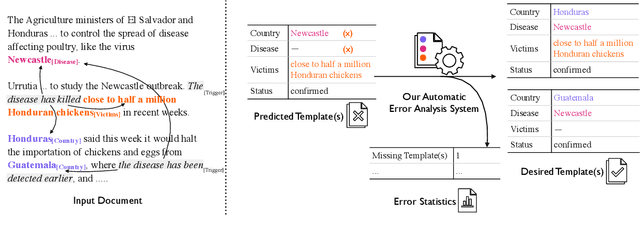
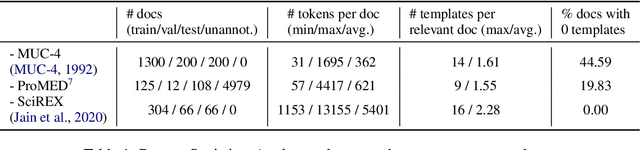
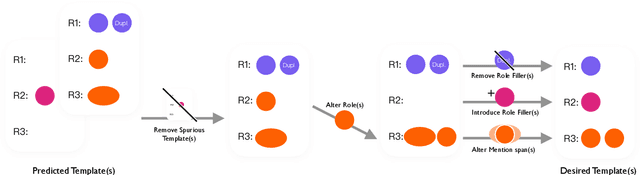
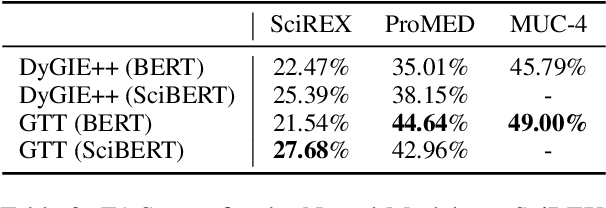
Abstract:Document-level information extraction (IE) tasks have recently begun to be revisited in earnest using the end-to-end neural network techniques that have been successful on their sentence-level IE counterparts. Evaluation of the approaches, however, has been limited in a number of dimensions. In particular, the precision/recall/F1 scores typically reported provide few insights on the range of errors the models make. We build on the work of Kummerfeld and Klein (2013) to propose a transformation-based framework for automating error analysis in document-level event and (N-ary) relation extraction. We employ our framework to compare two state-of-the-art document-level template-filling approaches on datasets from three domains; and then, to gauge progress in IE since its inception 30 years ago, vs. four systems from the MUC-4 (1992) evaluation.
* Accepted to ACL 2022 Main Conference. First three authors contributed equally to this work
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge