S. Kevin Zhou
CausalSpatial: A Benchmark for Object-Centric Causal Spatial Reasoning
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Humans can look at a static scene and instantly predict what happens next -- will moving this object cause a collision? We call this ability Causal Spatial Reasoning. However, current multimodal large language models (MLLMs) cannot do this, as they remain largely restricted to static spatial perception, struggling to answer "what-if" questions in a 3D scene. We introduce CausalSpatial, a diagnostic benchmark evaluating whether models can anticipate consequences of object motions across four tasks: Collision, Compatibility, Occlusion, and Trajectory. Results expose a severe gap: humans score 84% while GPT-5 achieves only 54%. Why do MLLMs fail? Our analysis uncovers a fundamental deficiency: models over-rely on textual chain-of-thought reasoning that drifts from visual evidence, producing fluent but spatially ungrounded hallucinations. To address this, we propose the Causal Object World model (COW), a framework that externalizes the simulation process by generating videos of hypothetical dynamics. With explicit visual cues of causality, COW enables models to ground their reasoning in physical reality rather than linguistic priors. We make the dataset and code publicly available here: https://github.com/CausalSpatial/CausalSpatial
Equivariant Sampling for Improving Diffusion Model-based Image Restoration
Nov 13, 2025

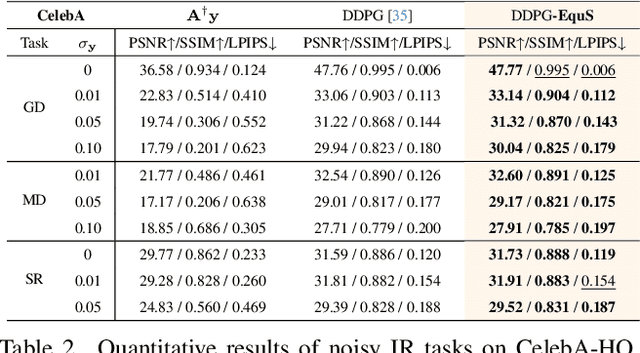

Abstract:Recent advances in generative models, especially diffusion models, have significantly improved image restoration (IR) performance. However, existing problem-agnostic diffusion model-based image restoration (DMIR) methods face challenges in fully leveraging diffusion priors, resulting in suboptimal performance. In this paper, we address the limitations of current problem-agnostic DMIR methods by analyzing their sampling process and providing effective solutions. We introduce EquS, a DMIR method that imposes equivariant information through dual sampling trajectories. To further boost EquS, we propose the Timestep-Aware Schedule (TAS) and introduce EquS$^+$. TAS prioritizes deterministic steps to enhance certainty and sampling efficiency. Extensive experiments on benchmarks demonstrate that our method is compatible with previous problem-agnostic DMIR methods and significantly boosts their performance without increasing computational costs. Our code is available at https://github.com/FouierL/EquS.
RadGS-Reg: Registering Spine CT with Biplanar X-rays via Joint 3D Radiative Gaussians Reconstruction and 3D/3D Registration
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Computed Tomography (CT)/X-ray registration in image-guided navigation remains challenging because of its stringent requirements for high accuracy and real-time performance. Traditional "render and compare" methods, relying on iterative projection and comparison, suffer from spatial information loss and domain gap. 3D reconstruction from biplanar X-rays supplements spatial and shape information for 2D/3D registration, but current methods are limited by dense-view requirements and struggles with noisy X-rays. To address these limitations, we introduce RadGS-Reg, a novel framework for vertebral-level CT/X-ray registration through joint 3D Radiative Gaussians (RadGS) reconstruction and 3D/3D registration. Specifically, our biplanar X-rays vertebral RadGS reconstruction module explores learning-based RadGS reconstruction method with a Counterfactual Attention Learning (CAL) mechanism, focusing on vertebral regions in noisy X-rays. Additionally, a patient-specific pre-training strategy progressively adapts the RadGS-Reg from simulated to real data while simultaneously learning vertebral shape prior knowledge. Experiments on in-house datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance for both tasks, surpassing existing methods. The code is available at: https://github.com/shenao1995/RadGS_Reg.
Dyna3DGR: 4D Cardiac Motion Tracking with Dynamic 3D Gaussian Representation
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Accurate analysis of cardiac motion is crucial for evaluating cardiac function. While dynamic cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) can capture detailed tissue motion throughout the cardiac cycle, the fine-grained 4D cardiac motion tracking remains challenging due to the homogeneous nature of myocardial tissue and the lack of distinctive features. Existing approaches can be broadly categorized into image based and representation-based, each with its limitations. Image-based methods, including both raditional and deep learning-based registration approaches, either struggle with topological consistency or rely heavily on extensive training data. Representation-based methods, while promising, often suffer from loss of image-level details. To address these limitations, we propose Dynamic 3D Gaussian Representation (Dyna3DGR), a novel framework that combines explicit 3D Gaussian representation with implicit neural motion field modeling. Our method simultaneously optimizes cardiac structure and motion in a self-supervised manner, eliminating the need for extensive training data or point-to-point correspondences. Through differentiable volumetric rendering, Dyna3DGR efficiently bridges continuous motion representation with image-space alignment while preserving both topological and temporal consistency. Comprehensive evaluations on the ACDC dataset demonstrate that our approach surpasses state-of-the-art deep learning-based diffeomorphic registration methods in tracking accuracy. The code will be available in https://github.com/windrise/Dyna3DGR.
U-RWKV: Lightweight medical image segmentation with direction-adaptive RWKV
Jul 15, 2025Abstract:Achieving equity in healthcare accessibility requires lightweight yet high-performance solutions for medical image segmentation, particularly in resource-limited settings. Existing methods like U-Net and its variants often suffer from limited global Effective Receptive Fields (ERFs), hindering their ability to capture long-range dependencies. To address this, we propose U-RWKV, a novel framework leveraging the Recurrent Weighted Key-Value(RWKV) architecture, which achieves efficient long-range modeling at O(N) computational cost. The framework introduces two key innovations: the Direction-Adaptive RWKV Module(DARM) and the Stage-Adaptive Squeeze-and-Excitation Module(SASE). DARM employs Dual-RWKV and QuadScan mechanisms to aggregate contextual cues across images, mitigating directional bias while preserving global context and maintaining high computational efficiency. SASE dynamically adapts its architecture to different feature extraction stages, balancing high-resolution detail preservation and semantic relationship capture. Experiments demonstrate that U-RWKV achieves state-of-the-art segmentation performance with high computational efficiency, offering a practical solution for democratizing advanced medical imaging technologies in resource-constrained environments. The code is available at https://github.com/hbyecoding/U-RWKV.
NeRF-based CBCT Reconstruction needs Normalization and Initialization
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is widely used in medical imaging. However, the limited number and intensity of X-ray projections make reconstruction an ill-posed problem with severe artifacts. NeRF-based methods have achieved great success in this task. However, they suffer from a local-global training mismatch between their two key components: the hash encoder and the neural network. Specifically, in each training step, only a subset of the hash encoder's parameters is used (local sparse), whereas all parameters in the neural network participate (global dense). Consequently, hash features generated in each step are highly misaligned, as they come from different subsets of the hash encoder. These misalignments from different training steps are then fed into the neural network, causing repeated inconsistent global updates in training, which leads to unstable training, slower convergence, and degraded reconstruction quality. Aiming to alleviate the impact of this local-global optimization mismatch, we introduce a Normalized Hash Encoder, which enhances feature consistency and mitigates the mismatch. Additionally, we propose a Mapping Consistency Initialization(MCI) strategy that initializes the neural network before training by leveraging the global mapping property from a well-trained model. The initialized neural network exhibits improved stability during early training, enabling faster convergence and enhanced reconstruction performance. Our method is simple yet effective, requiring only a few lines of code while substantially improving training efficiency on 128 CT cases collected from 4 different datasets, covering 7 distinct anatomical regions.
MVP-CBM:Multi-layer Visual Preference-enhanced Concept Bottleneck Model for Explainable Medical Image Classification
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:The concept bottleneck model (CBM), as a technique improving interpretability via linking predictions to human-understandable concepts, makes high-risk and life-critical medical image classification credible. Typically, existing CBM methods associate the final layer of visual encoders with concepts to explain the model's predictions. However, we empirically discover the phenomenon of concept preference variation, that is, the concepts are preferably associated with the features at different layers than those only at the final layer; yet a blind last-layer-based association neglects such a preference variation and thus weakens the accurate correspondences between features and concepts, impairing model interpretability. To address this issue, we propose a novel Multi-layer Visual Preference-enhanced Concept Bottleneck Model (MVP-CBM), which comprises two key novel modules: (1) intra-layer concept preference modeling, which captures the preferred association of different concepts with features at various visual layers, and (2) multi-layer concept sparse activation fusion, which sparsely aggregates concept activations from multiple layers to enhance performance. Thus, by explicitly modeling concept preferences, MVP-CBM can comprehensively leverage multi-layer visual information to provide a more nuanced and accurate explanation of model decisions. Extensive experiments on several public medical classification benchmarks demonstrate that MVP-CBM achieves state-of-the-art accuracy and interoperability, verifying its superiority. Code is available at https://github.com/wcj6/MVP-CBM.
* 7 pages, 6 figures,
SridBench: Benchmark of Scientific Research Illustration Drawing of Image Generation Model
May 28, 2025Abstract:Recent years have seen rapid advances in AI-driven image generation. Early diffusion models emphasized perceptual quality, while newer multimodal models like GPT-4o-image integrate high-level reasoning, improving semantic understanding and structural composition. Scientific illustration generation exemplifies this evolution: unlike general image synthesis, it demands accurate interpretation of technical content and transformation of abstract ideas into clear, standardized visuals. This task is significantly more knowledge-intensive and laborious, often requiring hours of manual work and specialized tools. Automating it in a controllable, intelligent manner would provide substantial practical value. Yet, no benchmark currently exists to evaluate AI on this front. To fill this gap, we introduce SridBench, the first benchmark for scientific figure generation. It comprises 1,120 instances curated from leading scientific papers across 13 natural and computer science disciplines, collected via human experts and MLLMs. Each sample is evaluated along six dimensions, including semantic fidelity and structural accuracy. Experimental results reveal that even top-tier models like GPT-4o-image lag behind human performance, with common issues in text/visual clarity and scientific correctness. These findings highlight the need for more advanced reasoning-driven visual generation capabilities.
Disentangled Human Body Representation Based on Unsupervised Semantic-Aware Learning
May 25, 2025Abstract:In recent years, more and more attention has been paid to the learning of 3D human representation. However, the complexity of lots of hand-defined human body constraints and the absence of supervision data limit that the existing works controllably and accurately represent the human body in views of semantics and representation ability. In this paper, we propose a human body representation with controllable fine-grained semantics and high precison of reconstruction in an unsupervised learning framework. In particularly, we design a whole-aware skeleton-grouped disentangle strategy to learn a correspondence between geometric semantical measurement of body and latent codes, which facilitates the control of shape and posture of human body by modifying latent coding paramerers. With the help of skeleton-grouped whole-aware encoder and unsupervised disentanglement losses, our representation model is learned by an unsupervised manner. Besides, a based-template residual learning scheme is injected into the encoder to ease of learning human body latent parameter in complicated body shape and pose spaces. Because of the geometrically meaningful latent codes, it can be used in a wide range of applications, from human body pose transfer to bilinear latent code interpolation. Further more, a part-aware decoder is utlized to promote the learning of controllable fine-grained semantics. The experimental results on public 3D human datasets show that the method has the ability of precise reconstruction.
A General Knowledge Injection Framework for ICD Coding
May 24, 2025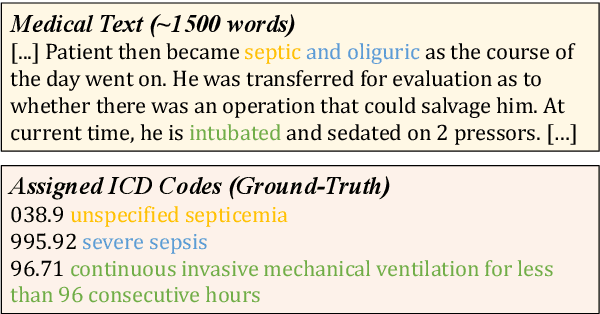
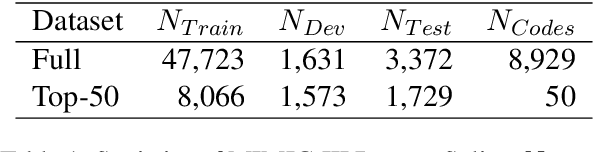
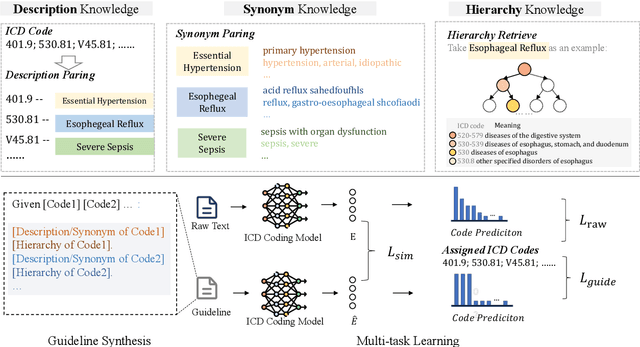
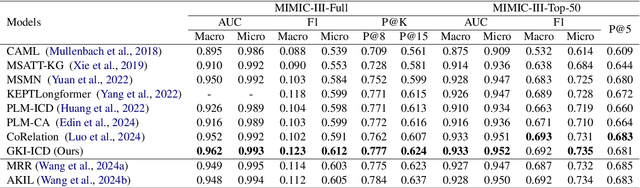
Abstract:ICD Coding aims to assign a wide range of medical codes to a medical text document, which is a popular and challenging task in the healthcare domain. To alleviate the problems of long-tail distribution and the lack of annotations of code-specific evidence, many previous works have proposed incorporating code knowledge to improve coding performance. However, existing methods often focus on a single type of knowledge and design specialized modules that are complex and incompatible with each other, thereby limiting their scalability and effectiveness. To address this issue, we propose GKI-ICD, a novel, general knowledge injection framework that integrates three key types of knowledge, namely ICD Description, ICD Synonym, and ICD Hierarchy, without specialized design of additional modules. The comprehensive utilization of the above knowledge, which exhibits both differences and complementarity, can effectively enhance the ICD coding performance. Extensive experiments on existing popular ICD coding benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of GKI-ICD, which achieves the state-of-the-art performance on most evaluation metrics. Code is available at https://github.com/xuzhang0112/GKI-ICD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge