Liyu Zhang
InstructDiff: Domain-Adaptive Data Selection via Differential Entropy for Efficient LLM Fine-Tuning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Supervised fine-tuning (SFT) is fundamental to adapting large language models, yet training on complete datasets incurs prohibitive costs with diminishing returns. Existing data selection methods suffer from severe domain specificity: techniques optimized for general instruction-following fail on reasoning tasks, and vice versa. We observe that measuring entropy differences between base models and minimally instruction-tuned calibrated models reveals a pattern -- samples with the lowest differential entropy consistently yield optimal performance across domains, yet this principle manifests domain-adaptively: reasoning tasks favor entropy increase (cognitive expansion), while general tasks favor entropy decrease (cognitive compression). We introduce InstructDiff, a unified framework that operationalizes differential entropy as a domain-adaptive selection criterion through warmup calibration, bi-directional NLL filtering, and entropy-based ranking. Extensive experiments show that InstructDiff achieves 17\% relative improvement over full data training on mathematical reasoning and 52\% for general instruction-following, outperforming prior baselines while using only 10\% of the data.
Chorus: Harmonizing Context and Sensing Signals for Data-Free Model Customization in IoT
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:In real-world IoT applications, sensor data is usually collected under diverse and dynamic contextual conditions where factors such as sensor placements or ambient environments can significantly affect data patterns and downstream performance. Traditional domain adaptation or generalization methods often ignore such context information or use simplistic integration strategies, making them ineffective in handling unseen context shifts after deployment. In this paper, we propose Chorus, a context-aware, data-free model customization approach that adapts models to unseen deployment conditions without requiring target-domain data. The key idea is to learn effective context representations that capture their influence on sensor data patterns and to adaptively integrate them based on the degree of context shift. Specifically, Chorus first performs unsupervised cross-modal reconstruction between unlabeled sensor data and language-based context embeddings, while regularizing the context embedding space to learn robust, generalizable context representations. Then, it trains a lightweight gated head on limited labeled samples to dynamically balance sensor and context contributions-favoring context when sensor evidence is ambiguous and vice versa. To further reduce inference latency, Chorus employs a context-caching mechanism that reuses cached context representations and updates only upon detected context shifts. Experiments on IMU, speech, and WiFi sensing tasks under diverse context shifts show that Chorus outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by up to 11.3% in unseen contexts, while maintaining comparable latency on smartphone and edge devices.
Synthesize-on-Graph: Knowledgeable Synthetic Data Generation for Continue Pre-training of Large Language Models
May 02, 2025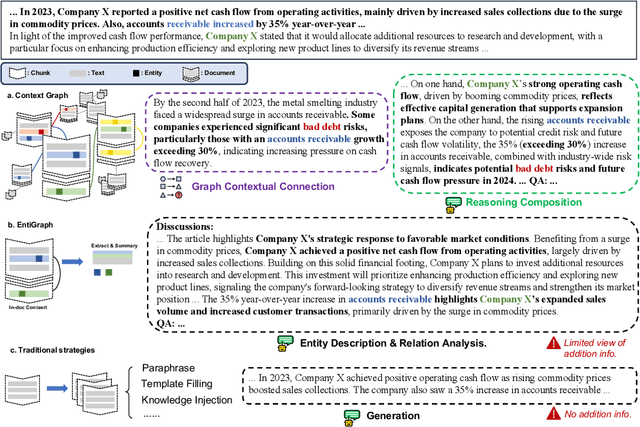
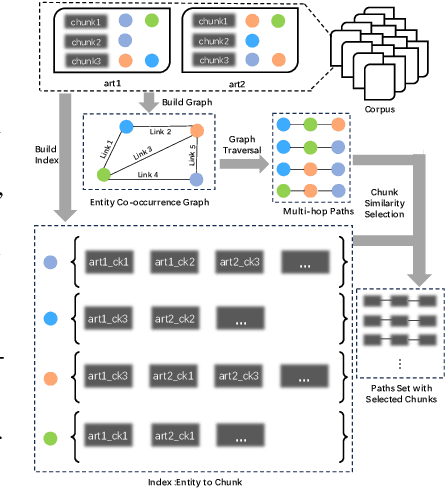
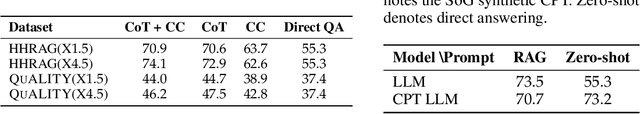
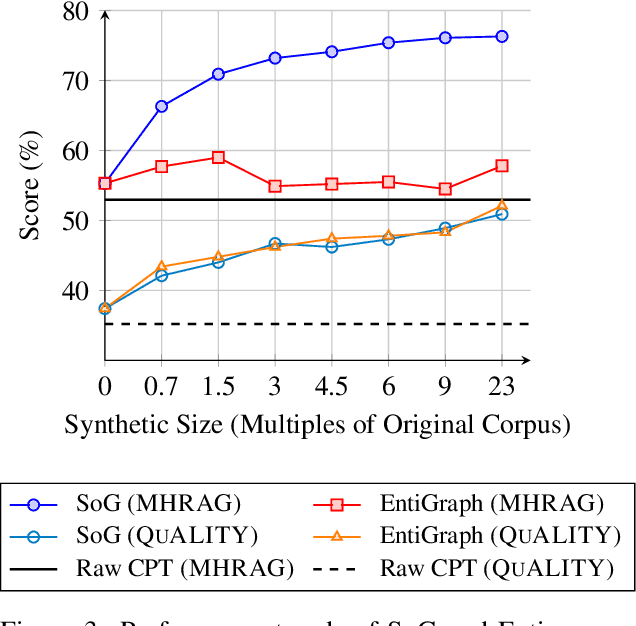
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success but remain data-inefficient, especially when learning from small, specialized corpora with limited and proprietary data. Existing synthetic data generation methods for continue pre-training focus on intra-document content and overlook cross-document knowledge associations, limiting content diversity and depth. We propose Synthetic-on-Graph (SoG), a synthetic data generation framework that incorporates cross-document knowledge associations for efficient corpus expansion. SoG constructs a context graph by extracting entities and concepts from the original corpus, representing cross-document associations, and employing a graph walk strategy for knowledge-associated sampling. This enhances synthetic data diversity and coherence, enabling models to learn complex knowledge structures and handle rare knowledge. To further improve synthetic data quality, we integrate Chain-of-Thought (CoT) and Contrastive Clarifying (CC) synthetic, enhancing reasoning processes and discriminative power. Experiments show that SoG outperforms the state-of-the-art (SOTA) method in a multi-hop document Q&A dataset while performing comparably to the SOTA method on the reading comprehension task datasets, which also underscores the better generalization capability of SoG. Our work advances synthetic data generation and provides practical solutions for efficient knowledge acquisition in LLMs, especially in domains with limited data availability.
ConceptEdit: Conceptualization-Augmented Knowledge Editing in Large Language Models for Commonsense Reasoning
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge Editing (KE) aims to adjust a Large Language Model's (LLM) internal representations and parameters to correct inaccuracies and improve output consistency without incurring the computational expense of re-training the entire model. However, editing commonsense knowledge still faces difficulties, including limited knowledge coverage in existing resources, the infeasibility of annotating labels for an overabundance of commonsense knowledge, and the strict knowledge formats of current editing methods. In this paper, we address these challenges by presenting ConceptEdit, a framework that integrates conceptualization and instantiation into the KE pipeline for LLMs to enhance their commonsense reasoning capabilities. ConceptEdit dynamically diagnoses implausible commonsense knowledge within an LLM using another verifier LLM and augments the source knowledge to be edited with conceptualization for stronger generalizability. Experimental results demonstrate that LLMs enhanced with ConceptEdit successfully generate commonsense knowledge with improved plausibility compared to other baselines and achieve stronger performance across multiple question answering benchmarks.
SAMG: State-Action-Aware Offline-to-Online Reinforcement Learning with Offline Model Guidance
Oct 24, 2024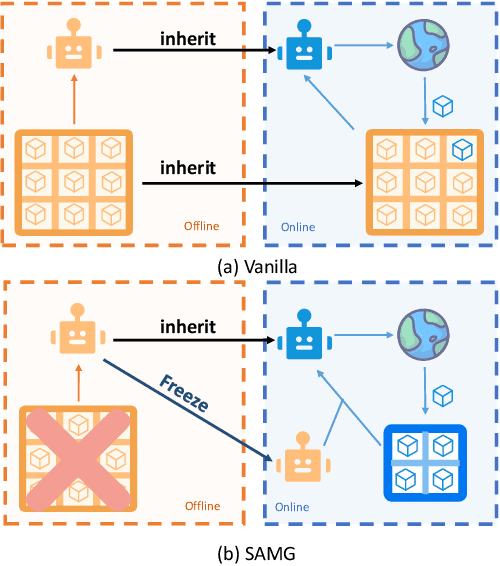
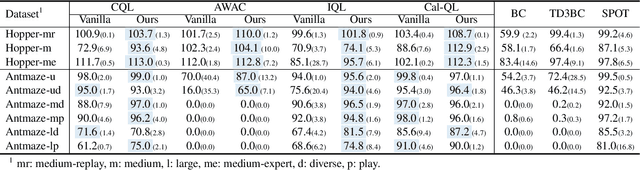
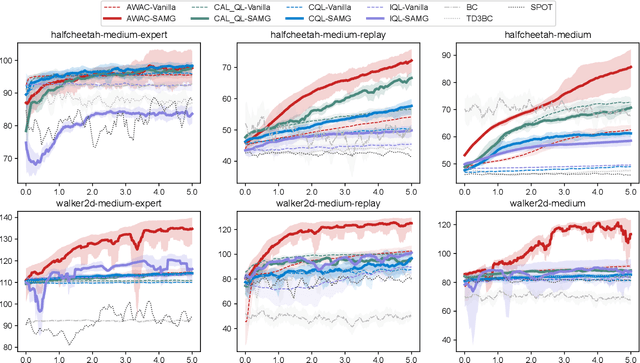
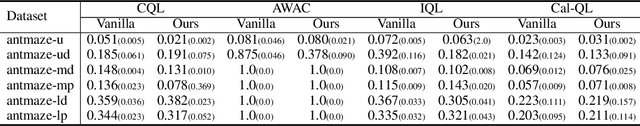
Abstract:The offline-to-online (O2O) paradigm in reinforcement learning (RL) utilizes pre-trained models on offline datasets for subsequent online fine-tuning. However, conventional O2O RL algorithms typically require maintaining and retraining the large offline datasets to mitigate the effects of out-of-distribution (OOD) data, which limits their efficiency in exploiting online samples. To address this challenge, we introduce a new paradigm called SAMG: State-Action-Conditional Offline-to-Online Reinforcement Learning with Offline Model Guidance. In particular, rather than directly training on offline data, SAMG freezes the pre-trained offline critic to provide offline values for each state-action pair to deliver compact offline information. This framework eliminates the need for retraining with offline data by freezing and leveraging these values of the offline model. These are then incorporated with the online target critic using a Bellman equation weighted by a policy state-action-aware coefficient. This coefficient, derived from a conditional variational auto-encoder (C-VAE), aims to capture the reliability of the offline data on a state-action level. SAMG could be easily integrated with existing Q-function based O2O RL algorithms. Theoretical analysis shows good optimality and lower estimation error of SAMG. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that SAMG outperforms four state-of-the-art O2O RL algorithms in the D4RL benchmark.
On the Role of Entity and Event Level Conceptualization in Generalizable Reasoning: A Survey of Tasks, Methods, Applications, and Future Directions
Jun 16, 2024



Abstract:Entity- and event-level conceptualization, as fundamental elements of human cognition, plays a pivotal role in generalizable reasoning. This process involves abstracting specific instances into higher-level concepts and forming abstract knowledge that can be applied in unfamiliar or novel situations, which can enhance models' inferential capabilities and support the effective transfer of knowledge across various domains. Despite its significance, there is currently a lack of a systematic overview that comprehensively examines existing works in the definition, execution, and application of conceptualization to enhance reasoning tasks. In this paper, we address this gap by presenting the first comprehensive survey of 150+ papers, categorizing various definitions, resources, methods, and downstream applications related to conceptualization into a unified taxonomy, with a focus on the entity and event levels. Furthermore, we shed light on potential future directions in this field and hope to garner more attention from the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge