Yisong Yue
California Institute of Technology
NitroGen: An Open Foundation Model for Generalist Gaming Agents
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:We introduce NitroGen, a vision-action foundation model for generalist gaming agents that is trained on 40,000 hours of gameplay videos across more than 1,000 games. We incorporate three key ingredients: 1) an internet-scale video-action dataset constructed by automatically extracting player actions from publicly available gameplay videos, 2) a multi-game benchmark environment that can measure cross-game generalization, and 3) a unified vision-action model trained with large-scale behavior cloning. NitroGen exhibits strong competence across diverse domains, including combat encounters in 3D action games, high-precision control in 2D platformers, and exploration in procedurally generated worlds. It transfers effectively to unseen games, achieving up to 52% relative improvement in task success rates over models trained from scratch. We release the dataset, evaluation suite, and model weights to advance research on generalist embodied agents.
Embodied Learning of Reward for Musculoskeletal Control with Vision Language Models
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Discovering effective reward functions remains a fundamental challenge in motor control of high-dimensional musculoskeletal systems. While humans can describe movement goals explicitly such as "walking forward with an upright posture," the underlying control strategies that realize these goals are largely implicit, making it difficult to directly design rewards from high-level goals and natural language descriptions. We introduce Motion from Vision-Language Representation (MoVLR), a framework that leverages vision-language models (VLMs) to bridge the gap between goal specification and movement control. Rather than relying on handcrafted rewards, MoVLR iteratively explores the reward space through iterative interaction between control optimization and VLM feedback, aligning control policies with physically coordinated behaviors. Our approach transforms language and vision-based assessments into structured guidance for embodied learning, enabling the discovery and refinement of reward functions for high-dimensional musculoskeletal locomotion and manipulation. These results suggest that VLMs can effectively ground abstract motion descriptions in the implicit principles governing physiological motor control.
Feedforward 3D Editing via Text-Steerable Image-to-3D
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in image-to-3D has opened up immense possibilities for design, AR/VR, and robotics. However, to use AI-generated 3D assets in real applications, a critical requirement is the capability to edit them easily. We present a feedforward method, Steer3D, to add text steerability to image-to-3D models, which enables editing of generated 3D assets with language. Our approach is inspired by ControlNet, which we adapt to image-to-3D generation to enable text steering directly in a forward pass. We build a scalable data engine for automatic data generation, and develop a two-stage training recipe based on flow-matching training and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO). Compared to competing methods, Steer3D more faithfully follows the language instruction and maintains better consistency with the original 3D asset, while being 2.4x to 28.5x faster. Steer3D demonstrates that it is possible to add a new modality (text) to steer the generation of pretrained image-to-3D generative models with 100k data. Project website: https://glab-caltech.github.io/steer3d/
Learning Time-Scale Invariant Population-Level Neural Representations
Nov 17, 2025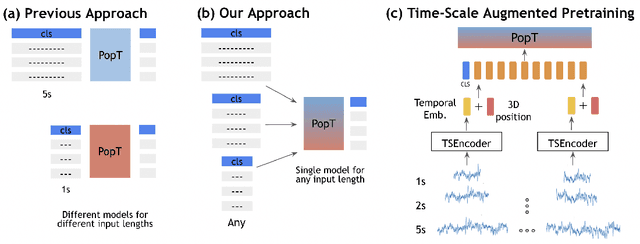
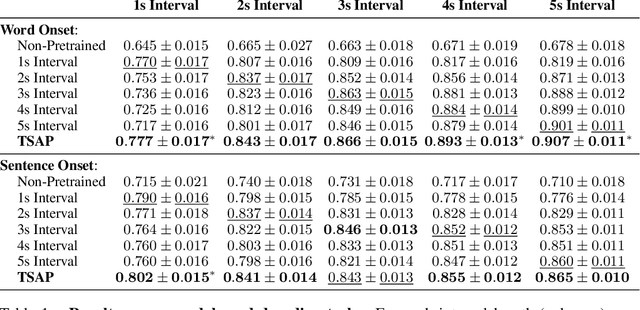
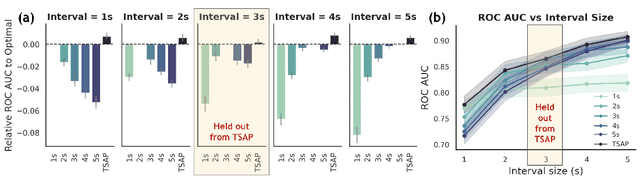
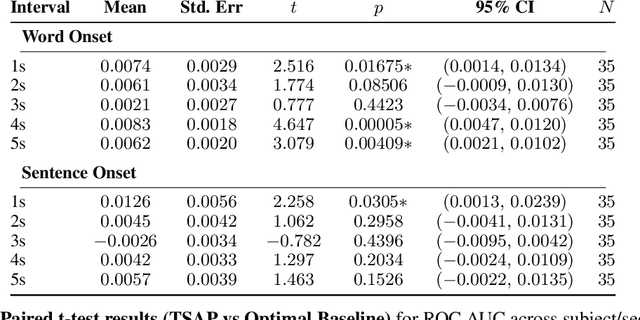
Abstract:General-purpose foundation models for neural time series can help accelerate neuroscientific discoveries and enable applications such as brain computer interfaces (BCIs). A key component in scaling these models is population-level representation learning, which leverages information across channels to capture spatial as well as temporal structure. Population-level approaches have recently shown that such representations can be both efficient to learn on top of pretrained temporal encoders and produce useful representations for decoding a variety of downstream tasks. However, these models remain sensitive to mismatches in preprocessing, particularly on time-scales, between pretraining and downstream settings. We systematically examine how time-scale mismatches affects generalization and find that existing representations lack invariance. To address this, we introduce Time-scale Augmented Pretraining (TSAP), which consistently improves robustness to different time-scales across decoding tasks and builds invariance in the representation space. These results highlight handling preprocessing diversity as a key step toward building generalizable neural foundation models.
A Narwhal-Inspired Sensing-to-Control Framework for Small Fixed-Wing Aircraft
Oct 08, 2025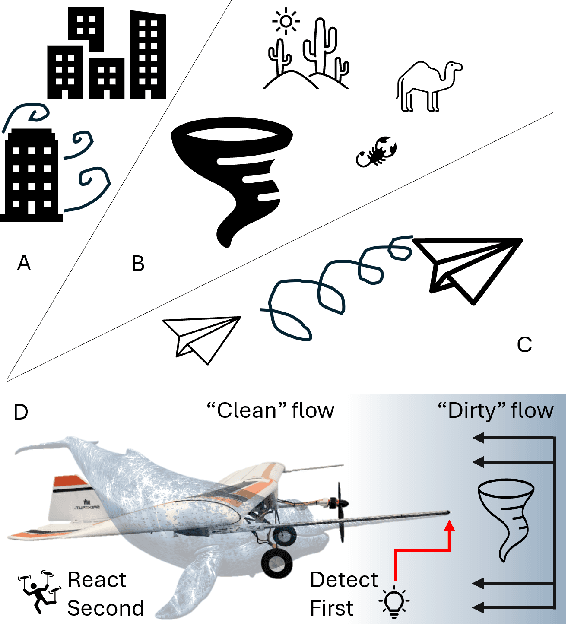
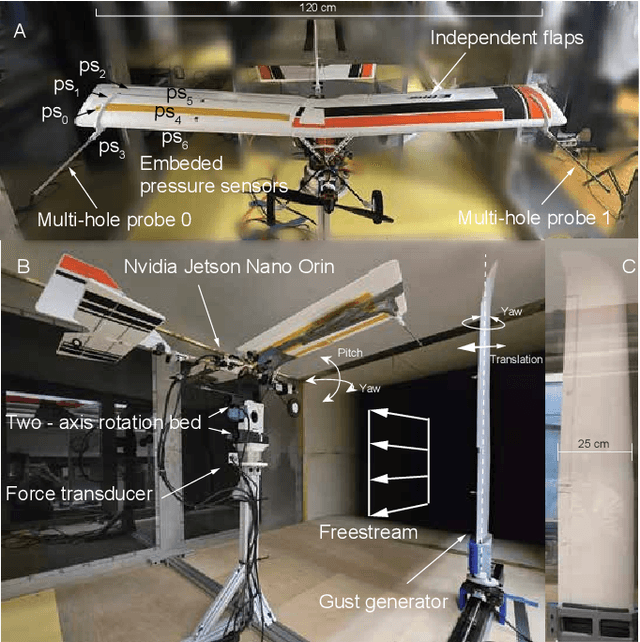
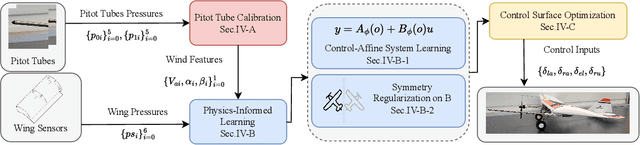
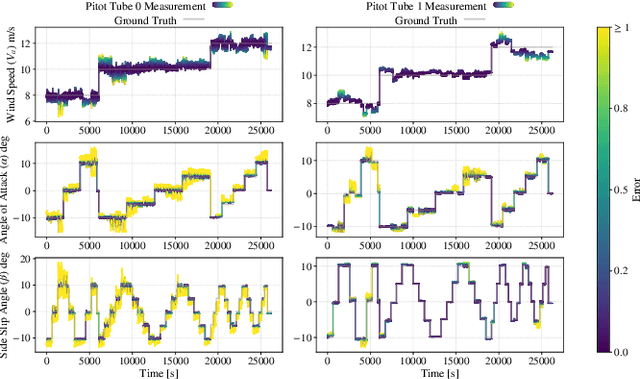
Abstract:Fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) offer endurance and efficiency but lack low-speed agility due to highly coupled dynamics. We present an end-to-end sensing-to-control pipeline that combines bio-inspired hardware, physics-informed dynamics learning, and convex control allocation. Measuring airflow on a small airframe is difficult because near-body aerodynamics, propeller slipstream, control-surface actuation, and ambient gusts distort pressure signals. Inspired by the narwhal's protruding tusk, we mount in-house multi-hole probes far upstream and complement them with sparse, carefully placed wing pressure sensors for local flow measurement. A data-driven calibration maps probe pressures to airspeed and flow angles. We then learn a control-affine dynamics model using the estimated airspeed/angles and sparse sensors. A soft left/right symmetry regularizer improves identifiability under partial observability and limits confounding between wing pressures and flaperon inputs. Desired wrenches (forces and moments) are realized by a regularized least-squares allocator that yields smooth, trimmed actuation. Wind-tunnel studies across a wide operating range show that adding wing pressures reduces force-estimation error by 25-30%, the proposed model degrades less under distribution shift (about 12% versus 44% for an unstructured baseline), and force tracking improves with smoother inputs, including a 27% reduction in normal-force RMSE versus a plain affine model and 34% versus an unstructured baseline.
TDRM: Smooth Reward Models with Temporal Difference for LLM RL and Inference
Sep 18, 2025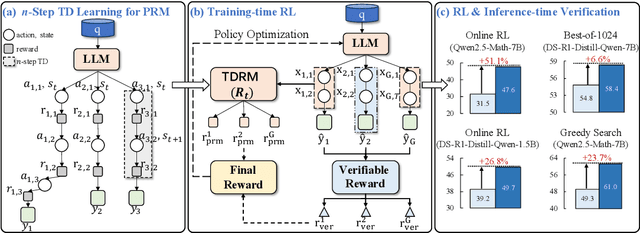
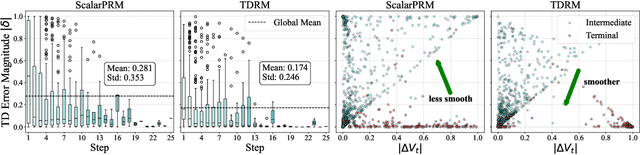
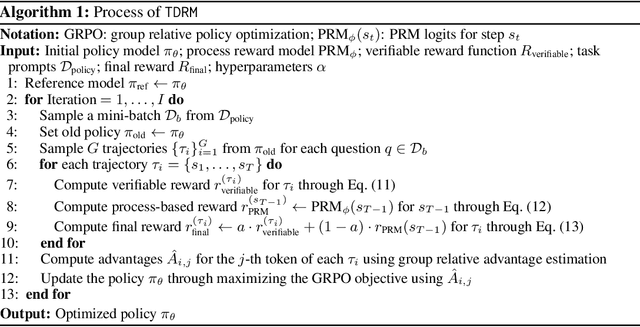
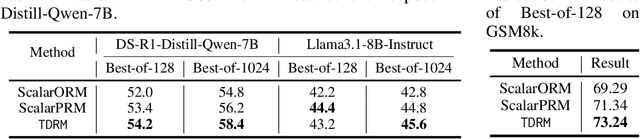
Abstract:Reward models are central to both reinforcement learning (RL) with language models and inference-time verification. However, existing reward models often lack temporal consistency, leading to ineffective policy updates and unstable RL training. We introduce TDRM, a method for learning smoother and more reliable reward models by minimizing temporal differences during training. This temporal-difference (TD) regularization produces smooth rewards and improves alignment with long-term objectives. Incorporating TDRM into the actor-critic style online RL loop yields consistent empirical gains. It is worth noting that TDRM is a supplement to verifiable reward methods, and both can be used in series. Experiments show that TD-trained process reward models (PRMs) improve performance across Best-of-N (up to 6.6%) and tree-search (up to 23.7%) settings. When combined with Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR), TD-trained PRMs lead to more data-efficient RL -- achieving comparable performance with just 2.5k data to what baseline methods require 50.1k data to attain -- and yield higher-quality language model policies on 8 model variants (5 series), e.g., Qwen2.5-(0.5B, 1,5B), GLM4-9B-0414, GLM-Z1-9B-0414, Qwen2.5-Math-(1.5B, 7B), and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-(1.5B, 7B). We release all code at https://github.com/THUDM/TDRM.
Kuramoto Orientation Diffusion Models
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Orientation-rich images, such as fingerprints and textures, often exhibit coherent angular directional patterns that are challenging to model using standard generative approaches based on isotropic Euclidean diffusion. Motivated by the role of phase synchronization in biological systems, we propose a score-based generative model built on periodic domains by leveraging stochastic Kuramoto dynamics in the diffusion process. In neural and physical systems, Kuramoto models capture synchronization phenomena across coupled oscillators -- a behavior that we re-purpose here as an inductive bias for structured image generation. In our framework, the forward process performs \textit{synchronization} among phase variables through globally or locally coupled oscillator interactions and attraction to a global reference phase, gradually collapsing the data into a low-entropy von Mises distribution. The reverse process then performs \textit{desynchronization}, generating diverse patterns by reversing the dynamics with a learned score function. This approach enables structured destruction during forward diffusion and a hierarchical generation process that progressively refines global coherence into fine-scale details. We implement wrapped Gaussian transition kernels and periodicity-aware networks to account for the circular geometry. Our method achieves competitive results on general image benchmarks and significantly improves generation quality on orientation-dense datasets like fingerprints and textures. Ultimately, this work demonstrates the promise of biologically inspired synchronization dynamics as structured priors in generative modeling.
Hybrid Data-Driven Predictive Control for Robust and Reactive Exoskeleton Locomotion Synthesis
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Robust bipedal locomotion in exoskeletons requires the ability to dynamically react to changes in the environment in real time. This paper introduces the hybrid data-driven predictive control (HDDPC) framework, an extension of the data-enabled predictive control, that addresses these challenges by simultaneously planning foot contact schedules and continuous domain trajectories. The proposed framework utilizes a Hankel matrix-based representation to model system dynamics, incorporating step-to-step (S2S) transitions to enhance adaptability in dynamic environments. By integrating contact scheduling with trajectory planning, the framework offers an efficient, unified solution for locomotion motion synthesis that enables robust and reactive walking through online replanning. We validate the approach on the Atalante exoskeleton, demonstrating improved robustness and adaptability.
Langevin Flows for Modeling Neural Latent Dynamics
Jul 15, 2025



Abstract:Neural populations exhibit latent dynamical structures that drive time-evolving spiking activities, motivating the search for models that capture both intrinsic network dynamics and external unobserved influences. In this work, we introduce LangevinFlow, a sequential Variational Auto-Encoder where the time evolution of latent variables is governed by the underdamped Langevin equation. Our approach incorporates physical priors -- such as inertia, damping, a learned potential function, and stochastic forces -- to represent both autonomous and non-autonomous processes in neural systems. Crucially, the potential function is parameterized as a network of locally coupled oscillators, biasing the model toward oscillatory and flow-like behaviors observed in biological neural populations. Our model features a recurrent encoder, a one-layer Transformer decoder, and Langevin dynamics in the latent space. Empirically, our method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on synthetic neural populations generated by a Lorenz attractor, closely matching ground-truth firing rates. On the Neural Latents Benchmark (NLB), the model achieves superior held-out neuron likelihoods (bits per spike) and forward prediction accuracy across four challenging datasets. It also matches or surpasses alternative methods in decoding behavioral metrics such as hand velocity. Overall, this work introduces a flexible, physics-inspired, high-performing framework for modeling complex neural population dynamics and their unobserved influences.
Escaping Platos Cave: JAM for Aligning Independently Trained Vision and Language Models
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:Independently trained vision and language models inhabit disjoint representational spaces, shaped by their respective modalities, objectives, and architectures. Yet an emerging hypothesis - the Platonic Representation Hypothesis - suggests that such models may nonetheless converge toward a shared statistical model of reality. This compatibility, if it exists, raises a fundamental question: can we move beyond post-hoc statistical detection of alignment and explicitly optimize for it between such disjoint representations? We cast this Platonic alignment problem as a multi-objective optimization task - preserve each modality's native structure while aligning for mutual coherence. We introduce the Joint Autoencoder Modulator (JAM) framework that jointly trains modality-specific autoencoders on the latent representations of pre-trained single modality models, encouraging alignment through both reconstruction and cross-modal objectives. By analogy, this framework serves as a method to escape Plato's Cave, enabling the emergence of shared structure from disjoint inputs. We evaluate this framework across three critical design axes: (i) the alignment objective - comparing contrastive loss (Con), its hard-negative variant (NegCon), and our Spread loss, (ii) the layer depth at which alignment is most effective, and (iii) the impact of foundation model scale on representational convergence. Our findings show that our lightweight Pareto-efficient framework reliably induces alignment, even across frozen, independently trained representations, offering both theoretical insight and practical pathways for transforming generalist unimodal foundations into specialist multimodal models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge