Chuan Hong
Department of Biostatistics and Bioinformatics, Duke University, Durham, USA
Adversarial Drift-Aware Predictive Transfer: Toward Durable Clinical AI
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Clinical AI systems frequently suffer performance decay post-deployment due to temporal data shifts, such as evolving populations, diagnostic coding updates (e.g., ICD-9 to ICD-10), and systemic shocks like the COVID-19 pandemic. Addressing this ``aging'' effect via frequent retraining is often impractical due to computational costs and privacy constraints. To overcome these hurdles, we introduce Adversarial Drift-Aware Predictive Transfer (ADAPT), a novel framework designed to confer durability against temporal drift with minimal retraining. ADAPT innovatively constructs an uncertainty set of plausible future models by combining historical source models and limited current data. By optimizing worst-case performance over this set, it balances current accuracy with robustness against degradation due to future drifts. Crucially, ADAPT requires only summary-level model estimators from historical periods, preserving data privacy and ensuring operational simplicity. Validated on longitudinal suicide risk prediction using electronic health records from Mass General Brigham (2005--2021) and Duke University Health Systems, ADAPT demonstrated superior stability across coding transitions and pandemic-induced shifts. By minimizing annual performance decay without labeling or retraining future data, ADAPT offers a scalable pathway for sustaining reliable AI in high-stakes healthcare environments.
Toward Global Large Language Models in Medicine
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Despite continuous advances in medical technology, the global distribution of health care resources remains uneven. The development of large language models (LLMs) has transformed the landscape of medicine and holds promise for improving health care quality and expanding access to medical information globally. However, existing LLMs are primarily trained on high-resource languages, limiting their applicability in global medical scenarios. To address this gap, we constructed GlobMed, a large multilingual medical dataset, containing over 500,000 entries spanning 12 languages, including four low-resource languages. Building on this, we established GlobMed-Bench, which systematically assesses 56 state-of-the-art proprietary and open-weight LLMs across multiple multilingual medical tasks, revealing significant performance disparities across languages, particularly for low-resource languages. Additionally, we introduced GlobMed-LLMs, a suite of multilingual medical LLMs trained on GlobMed, with parameters ranging from 1.7B to 8B. GlobMed-LLMs achieved an average performance improvement of over 40% relative to baseline models, with a more than threefold increase in performance on low-resource languages. Together, these resources provide an important foundation for advancing the equitable development and application of LLMs globally, enabling broader language communities to benefit from technological advances.
TRACER: Transfer Learning based Real-time Adaptation for Clinical Evolving Risk
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Clinical decision support tools built on electronic health records often experience performance drift due to temporal population shifts, particularly when changes in the clinical environment initially affect only a subset of patients, resulting in a transition to mixed populations. Such case-mix changes commonly arise following system-level operational updates or the emergence of new diseases, such as COVID-19. We propose TRACER (Transfer Learning-based Real-time Adaptation for Clinical Evolving Risk), a framework that identifies encounter-level transition membership and adapts predictive models using transfer learning without full retraining. In simulation studies, TRACER outperformed static models trained on historical or contemporary data. In a real-world application predicting hospital admission following emergency department visits across the COVID-19 transition, TRACER improved both discrimination and calibration. TRACER provides a scalable approach for maintaining robust predictive performance under evolving and heterogeneous clinical conditions.
Leveraging LLMs for Title and Abstract Screening for Systematic Review: A Cost-Effective Dynamic Few-Shot Learning Approach
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Systematic reviews are a key component of evidence-based medicine, playing a critical role in synthesizing existing research evidence and guiding clinical decisions. However, with the rapid growth of research publications, conducting systematic reviews has become increasingly burdensome, with title and abstract screening being one of the most time-consuming and resource-intensive steps. To mitigate this issue, we designed a two-stage dynamic few-shot learning (DFSL) approach aimed at improving the efficiency and performance of large language models (LLMs) in the title and abstract screening task. Specifically, this approach first uses a low-cost LLM for initial screening, then re-evaluates low-confidence instances using a high-performance LLM, thereby enhancing screening performance while controlling computational costs. We evaluated this approach across 10 systematic reviews, and the results demonstrate its strong generalizability and cost-effectiveness, with potential to reduce manual screening burden and accelerate the systematic review process in practical applications.
An Agentic AI System for Multi-Framework Communication Coding
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Clinical communication is central to patient outcomes, yet large-scale human annotation of patient-provider conversation remains labor-intensive, inconsistent, and difficult to scale. Existing approaches based on large language models typically rely on single-task models that lack adaptability, interpretability, and reliability, especially when applied across various communication frameworks and clinical domains. In this study, we developed a Multi-framework Structured Agentic AI system for Clinical Communication (MOSAIC), built on a LangGraph-based architecture that orchestrates four core agents, including a Plan Agent for codebook selection and workflow planning, an Update Agent for maintaining up-to-date retrieval databases, a set of Annotation Agents that applies codebook-guided retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with dynamic few-shot prompting, and a Verification Agent that provides consistency checks and feedback. To evaluate performance, we compared MOSAIC outputs against gold-standard annotations created by trained human coders. We developed and evaluated MOSAIC using 26 gold standard annotated transcripts for training and 50 transcripts for testing, spanning rheumatology and OB/GYN domains. On the test set, MOSAIC achieved an overall F1 score of 0.928. Performance was highest in the Rheumatology subset (F1 = 0.962) and strongest for Patient Behavior (e.g., patients asking questions, expressing preferences, or showing assertiveness). Ablations revealed that MOSAIC outperforms baseline benchmarking.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Medicine: A Scoping Review of Technical Implementations, Clinical Applications, and Ethical Considerations
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth of medical knowledge and increasing complexity of clinical practice pose challenges. In this context, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated value; however, inherent limitations remain. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technologies show potential to enhance their clinical applicability. This study reviewed RAG applications in medicine. We found that research primarily relied on publicly available data, with limited application in private data. For retrieval, approaches commonly relied on English-centric embedding models, while LLMs were mostly generic, with limited use of medical-specific LLMs. For evaluation, automated metrics evaluated generation quality and task performance, whereas human evaluation focused on accuracy, completeness, relevance, and fluency, with insufficient attention to bias and safety. RAG applications were concentrated on question answering, report generation, text summarization, and information extraction. Overall, medical RAG remains at an early stage, requiring advances in clinical validation, cross-linguistic adaptation, and support for low-resource settings to enable trustworthy and responsible global use.
RELEAP: Reinforcement-Enhanced Label-Efficient Active Phenotyping for Electronic Health Records
Nov 08, 2025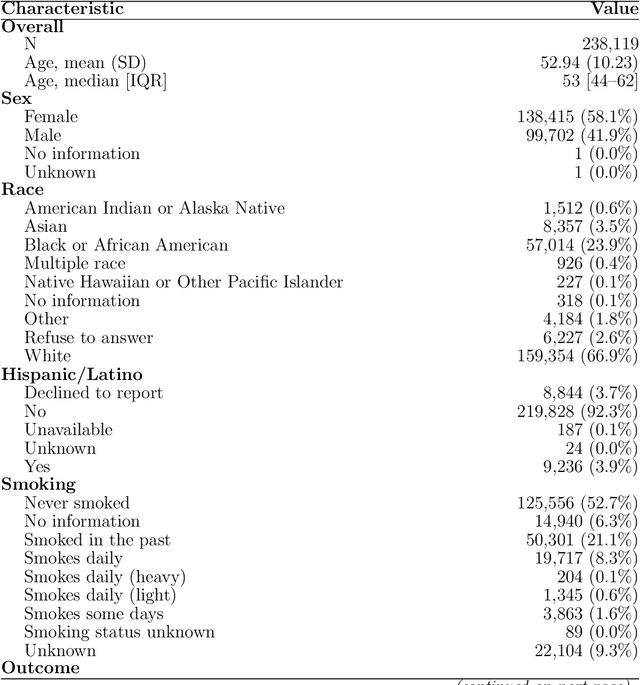
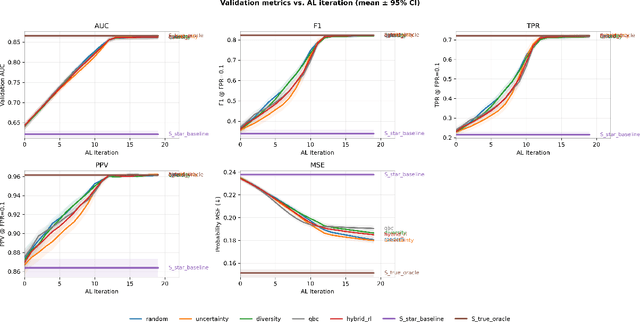

Abstract:Objective: Electronic health record (EHR) phenotyping often relies on noisy proxy labels, which undermine the reliability of downstream risk prediction. Active learning can reduce annotation costs, but most rely on fixed heuristics and do not ensure that phenotype refinement improves prediction performance. Our goal was to develop a framework that directly uses downstream prediction performance as feedback to guide phenotype correction and sample selection under constrained labeling budgets. Materials and Methods: We propose Reinforcement-Enhanced Label-Efficient Active Phenotyping (RELEAP), a reinforcement learning-based active learning framework. RELEAP adaptively integrates multiple querying strategies and, unlike prior methods, updates its policy based on feedback from downstream models. We evaluated RELEAP on a de-identified Duke University Health System (DUHS) cohort (2014-2024) for incident lung cancer risk prediction, using logistic regression and penalized Cox survival models. Performance was benchmarked against noisy-label baselines and single-strategy active learning. Results: RELEAP consistently outperformed all baselines. Logistic AUC increased from 0.774 to 0.805 and survival C-index from 0.718 to 0.752. Using downstream performance as feedback, RELEAP produced smoother and more stable gains than heuristic methods under the same labeling budget. Discussion: By linking phenotype refinement to prediction outcomes, RELEAP learns which samples most improve downstream discrimination and calibration, offering a more principled alternative to fixed active learning rules. Conclusion: RELEAP optimizes phenotype correction through downstream feedback, offering a scalable, label-efficient paradigm that reduces manual chart review and enhances the reliability of EHR-based risk prediction.
Equitable Survival Prediction: A Fairness-Aware Survival Modeling (FASM) Approach
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:As machine learning models become increasingly integrated into healthcare, structural inequities and social biases embedded in clinical data can be perpetuated or even amplified by data-driven models. In survival analysis, censoring and time dynamics can further add complexity to fair model development. Additionally, algorithmic fairness approaches often overlook disparities in cross-group rankings, e.g., high-risk Black patients may be ranked below lower-risk White patients who do not experience the event of mortality. Such misranking can reinforce biological essentialism and undermine equitable care. We propose a Fairness-Aware Survival Modeling (FASM), designed to mitigate algorithmic bias regarding both intra-group and cross-group risk rankings over time. Using breast cancer prognosis as a representative case and applying FASM to SEER breast cancer data, we show that FASM substantially improves fairness while preserving discrimination performance comparable to fairness-unaware survival models. Time-stratified evaluations show that FASM maintains stable fairness over a 10-year horizon, with the greatest improvements observed during the mid-term of follow-up. Our approach enables the development of survival models that prioritize both accuracy and equity in clinical decision-making, advancing fairness as a core principle in clinical care.
PEHRT: A Common Pipeline for Harmonizing Electronic Health Record data for Translational Research
Sep 10, 2025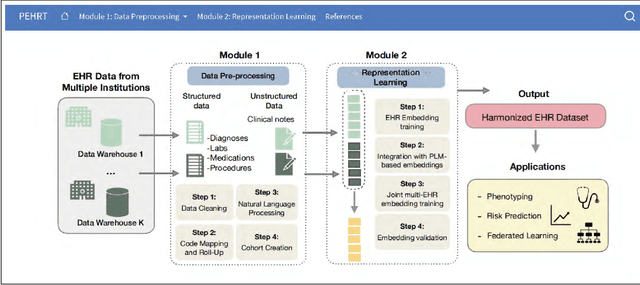
Abstract:Integrative analysis of multi-institutional Electronic Health Record (EHR) data enhances the reliability and generalizability of translational research by leveraging larger, more diverse patient cohorts and incorporating multiple data modalities. However, harmonizing EHR data across institutions poses major challenges due to data heterogeneity, semantic differences, and privacy concerns. To address these challenges, we introduce $\textit{PEHRT}$, a standardized pipeline for efficient EHR data harmonization consisting of two core modules: (1) data pre-processing and (2) representation learning. PEHRT maps EHR data to standard coding systems and uses advanced machine learning to generate research-ready datasets without requiring individual-level data sharing. Our pipeline is also data model agnostic and designed for streamlined execution across institutions based on our extensive real-world experience. We provide a complete suite of open source software, accompanied by a user-friendly tutorial, and demonstrate the utility of PEHRT in a variety of tasks using data from diverse healthcare systems.
Integrated Analysis for Electronic Health Records with Structured and Sporadic Missingness
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Objectives: We propose a novel imputation method tailored for Electronic Health Records (EHRs) with structured and sporadic missingness. Such missingness frequently arises in the integration of heterogeneous EHR datasets for downstream clinical applications. By addressing these gaps, our method provides a practical solution for integrated analysis, enhancing data utility and advancing the understanding of population health. Materials and Methods: We begin by demonstrating structured and sporadic missing mechanisms in the integrated analysis of EHR data. Following this, we introduce a novel imputation framework, Macomss, specifically designed to handle structurally and heterogeneously occurring missing data. We establish theoretical guarantees for Macomss, ensuring its robustness in preserving the integrity and reliability of integrated analyses. To assess its empirical performance, we conduct extensive simulation studies that replicate the complex missingness patterns observed in real-world EHR systems, complemented by validation using EHR datasets from the Duke University Health System (DUHS). Results: Simulation studies show that our approach consistently outperforms existing imputation methods. Using datasets from three hospitals within DUHS, Macomss achieves the lowest imputation errors for missing data in most cases and provides superior or comparable downstream prediction performance compared to benchmark methods. Conclusions: We provide a theoretically guaranteed and practically meaningful method for imputing structured and sporadic missing data, enabling accurate and reliable integrated analysis across multiple EHR datasets. The proposed approach holds significant potential for advancing research in population health.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge