Jiayi Tong
Empowering Clinical Trial Design through AI: A Randomized Evaluation of PowerGPT
Sep 15, 2025



Abstract:Sample size calculations for power analysis are critical for clinical research and trial design, yet their complexity and reliance on statistical expertise create barriers for many researchers. We introduce PowerGPT, an AI-powered system integrating large language models (LLMs) with statistical engines to automate test selection and sample size estimation in trial design. In a randomized trial to evaluate its effectiveness, PowerGPT significantly improved task completion rates (99.3% vs. 88.9% for test selection, 99.3% vs. 77.8% for sample size calculation) and accuracy (94.1% vs. 55.4% in sample size estimation, p < 0.001), while reducing average completion time (4.0 vs. 9.3 minutes, p < 0.001). These gains were consistent across various statistical tests and benefited both statisticians and non-statisticians as well as bridging expertise gaps. Already under deployment across multiple institutions, PowerGPT represents a scalable AI-driven approach that enhances accessibility, efficiency, and accuracy in statistical power analysis for clinical research.
Enabling Inclusive Systematic Reviews: Incorporating Preprint Articles with Large Language Model-Driven Evaluations
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Background. Systematic reviews in comparative effectiveness research require timely evidence synthesis. Preprints accelerate knowledge dissemination but vary in quality, posing challenges for systematic reviews. Methods. We propose AutoConfidence (automated confidence assessment), an advanced framework for predicting preprint publication, which reduces reliance on manual curation and expands the range of predictors, including three key advancements: (1) automated data extraction using natural language processing techniques, (2) semantic embeddings of titles and abstracts, and (3) large language model (LLM)-driven evaluation scores. Additionally, we employed two prediction models: a random forest classifier for binary outcome and a survival cure model that predicts both binary outcome and publication risk over time. Results. The random forest classifier achieved AUROC 0.692 with LLM-driven scores, improving to 0.733 with semantic embeddings and 0.747 with article usage metrics. The survival cure model reached AUROC 0.716 with LLM-driven scores, improving to 0.731 with semantic embeddings. For publication risk prediction, it achieved a concordance index of 0.658, increasing to 0.667 with semantic embeddings. Conclusion. Our study advances the framework for preprint publication prediction through automated data extraction and multiple feature integration. By combining semantic embeddings with LLM-driven evaluations, AutoConfidence enhances predictive performance while reducing manual annotation burden. The framework has the potential to facilitate systematic incorporation of preprint articles in evidence-based medicine, supporting researchers in more effective evaluation and utilization of preprint resources.
Federated Learning Algorithms for Generalized Mixed-effects Model (GLMM) on Horizontally Partitioned Data from Distributed Sources
Sep 28, 2021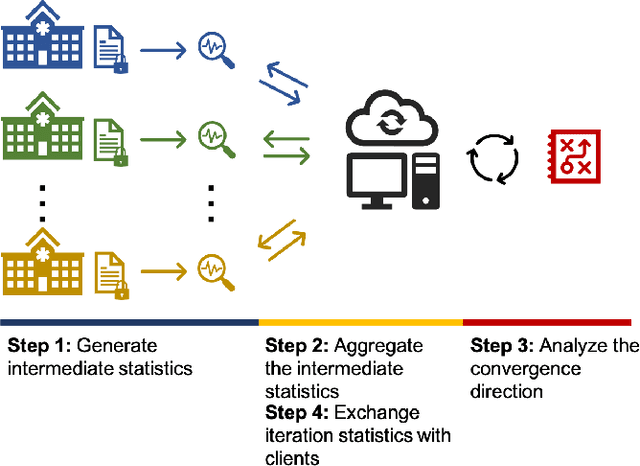

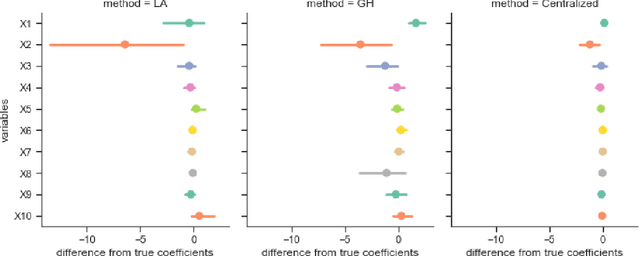
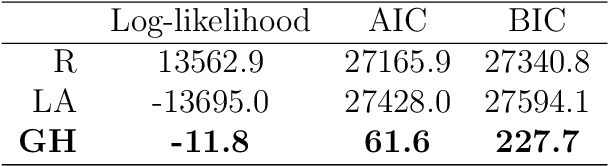
Abstract:Objectives: This paper develops two algorithms to achieve federated generalized linear mixed effect models (GLMM), and compares the developed model's outcomes with each other, as well as that from the standard R package (`lme4'). Methods: The log-likelihood function of GLMM is approximated by two numerical methods (Laplace approximation and Gaussian Hermite approximation), which supports federated decomposition of GLMM to bring computation to data. Results: Our developed method can handle GLMM to accommodate hierarchical data with multiple non-independent levels of observations in a federated setting. The experiment results demonstrate comparable (Laplace) and superior (Gaussian-Hermite) performances with simulated and real-world data. Conclusion: We developed and compared federated GLMMs with different approximations, which can support researchers in analyzing biomedical data to accommodate mixed effects and address non-independence due to hierarchical structures (i.e., institutes, region, country, etc.).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge