Mingxuan Liu
The Mask of Civility: Benchmarking Chinese Mock Politeness Comprehension in Large Language Models
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:From a pragmatic perspective, this study systematically evaluates the differences in performance among representative large language models (LLMs) in recognizing politeness, impoliteness, and mock politeness phenomena in Chinese. Addressing the existing gaps in pragmatic comprehension, the research adopts the frameworks of Rapport Management Theory and the Model of Mock Politeness to construct a three-category dataset combining authentic and simulated Chinese discourse. Six representative models, including GPT-5.1 and DeepSeek, were selected as test subjects and evaluated under four prompting conditions: zero-shot, few-shot, knowledge-enhanced, and hybrid strategies. This study serves as a meaningful attempt within the paradigm of ``Great Linguistics,'' offering a novel approach to applying pragmatic theory in the age of technological transformation. It also responds to the contemporary question of how technology and the humanities may coexist, representing an interdisciplinary endeavor that bridges linguistic technology and humanistic reflection.
AnyAD: Unified Any-Modality Anomaly Detection in Incomplete Multi-Sequence MRI
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Reliable anomaly detection in brain MRI remains challenging due to the scarcity of annotated abnormal cases and the frequent absence of key imaging modalities in real clinical workflows. Existing single-class or multi-class anomaly detection (AD) models typically rely on fixed modality configurations, require repetitive training, or fail to generalize to unseen modality combinations, limiting their clinical scalability. In this work, we present a unified Any-Modality AD framework that performs robust anomaly detection and localization under arbitrary MRI modality availability. The framework integrates a dual-pathway DINOv2 encoder with a feature distribution alignment mechanism that statistically aligns incomplete-modality features with full-modality representations, enabling stable inference even with severe modality dropout. To further enhance semantic consistency, we introduce an Intrinsic Normal Prototypes (INPs) extractor and an INP-guided decoder that reconstruct only normal anatomical patterns while naturally amplifying abnormal deviations. Through randomized modality masking and indirect feature completion during training, the model learns to adapt to all modality configurations without re-training. Extensive experiments on BraTS2018, MU-Glioma-Post, and Pretreat-MetsToBrain-Masks demonstrate that our approach consistently surpasses state-of-the-art industrial and medical AD baselines across 7 modality combinations, achieving superior generalization. This study establishes a scalable paradigm for multimodal medical AD under real-world, imperfect modality conditions. Our source code is available at https://github.com/wuchangw/AnyAD.
Equitable Survival Prediction: A Fairness-Aware Survival Modeling (FASM) Approach
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:As machine learning models become increasingly integrated into healthcare, structural inequities and social biases embedded in clinical data can be perpetuated or even amplified by data-driven models. In survival analysis, censoring and time dynamics can further add complexity to fair model development. Additionally, algorithmic fairness approaches often overlook disparities in cross-group rankings, e.g., high-risk Black patients may be ranked below lower-risk White patients who do not experience the event of mortality. Such misranking can reinforce biological essentialism and undermine equitable care. We propose a Fairness-Aware Survival Modeling (FASM), designed to mitigate algorithmic bias regarding both intra-group and cross-group risk rankings over time. Using breast cancer prognosis as a representative case and applying FASM to SEER breast cancer data, we show that FASM substantially improves fairness while preserving discrimination performance comparable to fairness-unaware survival models. Time-stratified evaluations show that FASM maintains stable fairness over a 10-year horizon, with the greatest improvements observed during the mid-term of follow-up. Our approach enables the development of survival models that prioritize both accuracy and equity in clinical decision-making, advancing fairness as a core principle in clinical care.
Knowledge to Sight: Reasoning over Visual Attributes via Knowledge Decomposition for Abnormality Grounding
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:In this work, we address the problem of grounding abnormalities in medical images, where the goal is to localize clinical findings based on textual descriptions. While generalist Vision-Language Models (VLMs) excel in natural grounding tasks, they often struggle in the medical domain due to rare, compositional, and domain-specific terms that are poorly aligned with visual patterns. Specialized medical VLMs address this challenge via large-scale domain pretraining, but at the cost of substantial annotation and computational resources. To overcome these limitations, we propose \textbf{Knowledge to Sight (K2Sight)}, a framework that introduces structured semantic supervision by decomposing clinical concepts into interpretable visual attributes, such as shape, density, and anatomical location. These attributes are distilled from domain ontologies and encoded into concise instruction-style prompts, which guide region-text alignment during training. Unlike conventional report-level supervision, our approach explicitly bridges domain knowledge and spatial structure, enabling data-efficient training of compact models. We train compact models with 0.23B and 2B parameters using only 1.5\% of the data required by state-of-the-art medical VLMs. Despite their small size and limited training data, these models achieve performance on par with or better than 7B+ medical VLMs, with up to 9.82\% improvement in $mAP_{50}$. Code and models: \href{https://lijunrio.github.io/K2Sight/}{\textcolor{SOTAPink}{https://lijunrio.github.io/K2Sight/}}.
RIS-MAE: A Self-Supervised Modulation Classification Method Based on Raw IQ Signals and Masked Autoencoder
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:Automatic modulation classification (AMC) is a basic technology in intelligent wireless communication systems. It is important for tasks such as spectrum monitoring, cognitive radio, and secure communications. In recent years, deep learning methods have made great progress in AMC. However, mainstream methods still face two key problems. First, they often use time-frequency images instead of raw signals. This causes loss of key modulation features and reduces adaptability to different communication conditions. Second, most methods rely on supervised learning. This needs a large amount of labeled data, which is hard to get in real-world environments. To solve these problems, we propose a self-supervised learning framework called RIS-MAE. RIS-MAE uses masked autoencoders to learn signal features from unlabeled data. It takes raw IQ sequences as input. By applying random masking and reconstruction, it captures important time-domain features such as amplitude, phase, etc. This helps the model learn useful and transferable representations. RIS-MAE is tested on four datasets. The results show that it performs better than existing methods in few-shot and cross-domain tasks. Notably, it achieves high classification accuracy on previously unseen datasets with only a small number of fine-tuning samples, confirming its generalization ability and potential for real-world deployment.
Towards Practical Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis: A Lightweight and Interpretable Spiking Neural Model
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Early diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease (AD), especially at the mild cognitive impairment (MCI) stage, is vital yet hindered by subjective assessments and the high cost of multimodal imaging modalities. Although deep learning methods offer automated alternatives, their energy inefficiency and computational demands limit real-world deployment, particularly in resource-constrained settings. As a brain-inspired paradigm, spiking neural networks (SNNs) are inherently well-suited for modeling the sparse, event-driven patterns of neural degeneration in AD, offering a promising foundation for interpretable and low-power medical diagnostics. However, existing SNNs often suffer from weak expressiveness and unstable training, which restrict their effectiveness in complex medical tasks. To address these limitations, we propose FasterSNN, a hybrid neural architecture that integrates biologically inspired LIF neurons with region-adaptive convolution and multi-scale spiking attention. This design enables sparse, efficient processing of 3D MRI while preserving diagnostic accuracy. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that FasterSNN achieves competitive performance with substantially improved efficiency and stability, supporting its potential for practical AD screening. Our source code is available at https://github.com/wuchangw/FasterSNN.
WLTCL: Wide Field-of-View 3-D LiDAR Truck Compartment Automatic Localization System
Apr 26, 2025Abstract:As an essential component of logistics automation, the automated loading system is becoming a critical technology for enhancing operational efficiency and safety. Precise automatic positioning of the truck compartment, which serves as the loading area, is the primary step in automated loading. However, existing methods have difficulty adapting to truck compartments of various sizes, do not establish a unified coordinate system for LiDAR and mobile manipulators, and often exhibit reliability issues in cluttered environments. To address these limitations, our study focuses on achieving precise automatic positioning of key points in large, medium, and small fence-style truck compartments in cluttered scenarios. We propose an innovative wide field-of-view 3-D LiDAR vehicle compartment automatic localization system. For vehicles of various sizes, this system leverages the LiDAR to generate high-density point clouds within an extensive field-of-view range. By incorporating parking area constraints, our vehicle point cloud segmentation method more effectively segments vehicle point clouds within the scene. Our compartment key point positioning algorithm utilizes the geometric features of the compartments to accurately locate the corner points, providing stackable spatial regions. Extensive experiments on our collected data and public datasets demonstrate that this system offers reliable positioning accuracy and reduced computational resource consumption, leading to its application and promotion in relevant fields.
seeBias: A Comprehensive Tool for Assessing and Visualizing AI Fairness
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Fairness in artificial intelligence (AI) prediction models is increasingly emphasized to support responsible adoption in high-stakes domains such as health care and criminal justice. Guidelines and implementation frameworks highlight the importance of both predictive accuracy and equitable outcomes. However, current fairness toolkits often evaluate classification performance disparities in isolation, with limited attention to other critical aspects such as calibration. To address these gaps, we present seeBias, an R package for comprehensive evaluation of model fairness and predictive performance. seeBias offers an integrated evaluation across classification, calibration, and other performance domains, providing a more complete view of model behavior. It includes customizable visualizations to support transparent reporting and responsible AI implementation. Using public datasets from criminal justice and healthcare, we demonstrate how seeBias supports fairness evaluations, and uncovers disparities that conventional fairness metrics may overlook. The R package is available on GitHub, and a Python version is under development.
A Plug-and-Play Temporal Normalization Module for Robust Remote Photoplethysmography
Nov 22, 2024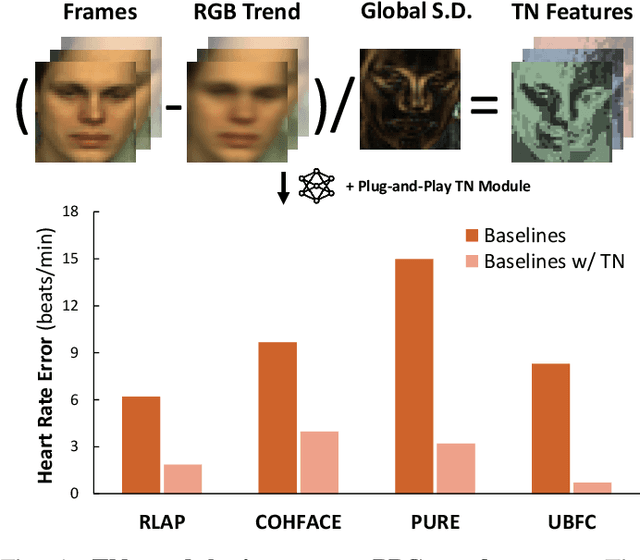
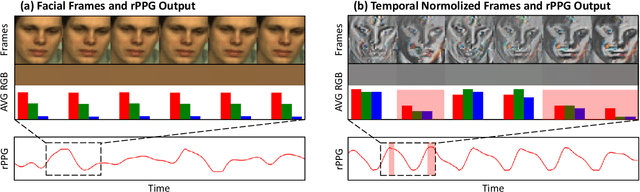
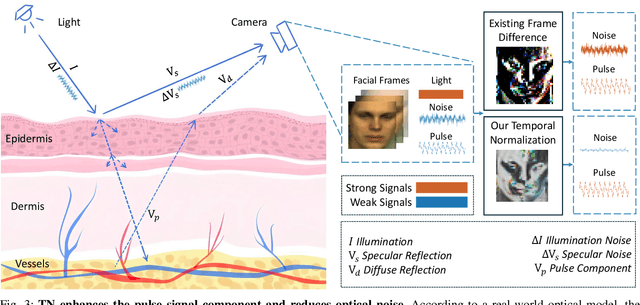
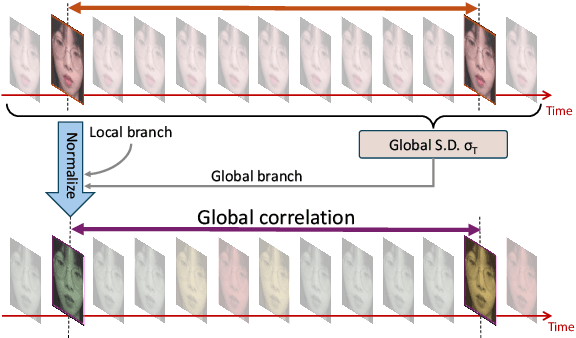
Abstract:Remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) extracts PPG signals from subtle color changes in facial videos, showing strong potential for health applications. However, most rPPG methods rely on intensity differences between consecutive frames, missing long-term signal variations affected by motion or lighting artifacts, which reduces accuracy. This paper introduces Temporal Normalization (TN), a flexible plug-and-play module compatible with any end-to-end rPPG network architecture. By capturing long-term temporally normalized features following detrending, TN effectively mitigates motion and lighting artifacts, significantly boosting the rPPG prediction performance. When integrated into four state-of-the-art rPPG methods, TN delivered performance improvements ranging from 34.3% to 94.2% in heart rate measurement tasks across four widely-used datasets. Notably, TN showed even greater performance gains in smaller models. We further discuss and provide insights into the mechanisms behind TN's effectiveness.
Organizing Unstructured Image Collections using Natural Language
Oct 07, 2024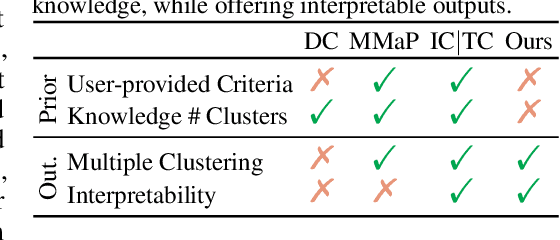

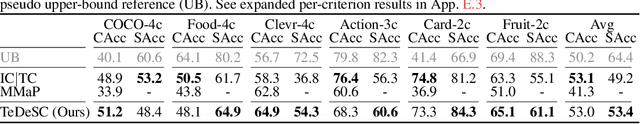
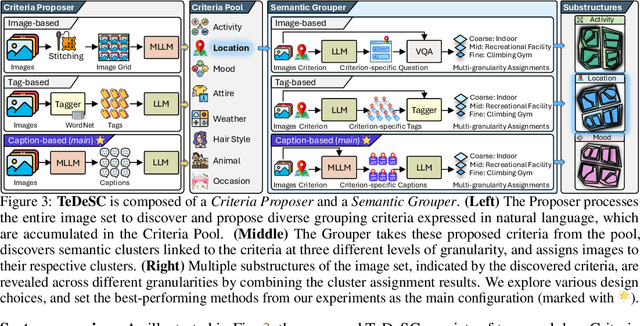
Abstract:Organizing unstructured visual data into semantic clusters is a key challenge in computer vision. Traditional deep clustering (DC) approaches focus on a single partition of data, while multiple clustering (MC) methods address this limitation by uncovering distinct clustering solutions. The rise of large language models (LLMs) and multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) has enhanced MC by allowing users to define clustering criteria in natural language. However, manually specifying criteria for large datasets is impractical. In this work, we introduce the task Semantic Multiple Clustering (SMC) that aims to automatically discover clustering criteria from large image collections, uncovering interpretable substructures without requiring human input. Our framework, Text Driven Semantic Multiple Clustering (TeDeSC), uses text as a proxy to concurrently reason over large image collections, discover partitioning criteria, expressed in natural language, and reveal semantic substructures. To evaluate TeDeSC, we introduce the COCO-4c and Food-4c benchmarks, each containing four grouping criteria and ground-truth annotations. We apply TeDeSC to various applications, such as discovering biases and analyzing social media image popularity, demonstrating its utility as a tool for automatically organizing image collections and revealing novel insights.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge