Changmiao Wang
DGSAN: Dual-Graph Spatiotemporal Attention Network for Pulmonary Nodule Malignancy Prediction
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. Early detection and diagnosis of pulmonary nodules are essential for improving patient survival rates. Although previous research has integrated multimodal and multi-temporal information, outperforming single modality and single time point, the fusion methods are limited to inefficient vector concatenation and simple mutual attention, highlighting the need for more effective multimodal information fusion. To address these challenges, we introduce a Dual-Graph Spatiotemporal Attention Network, which leverages temporal variations and multimodal data to enhance the accuracy of predictions. Our methodology involves developing a Global-Local Feature Encoder to better capture the local, global, and fused characteristics of pulmonary nodules. Additionally, a Dual-Graph Construction method organizes multimodal features into inter-modal and intra-modal graphs. Furthermore, a Hierarchical Cross-Modal Graph Fusion Module is introduced to refine feature integration. We also compiled a novel multimodal dataset named the NLST-cmst dataset as a comprehensive source of support for related research. Our extensive experiments, conducted on both the NLST-cmst and curated CSTL-derived datasets, demonstrate that our DGSAN significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in classifying pulmonary nodules with exceptional computational efficiency.
MedGEN-Bench: Contextually entangled benchmark for open-ended multimodal medical generation
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:As Vision-Language Models (VLMs) increasingly gain traction in medical applications, clinicians are progressively expecting AI systems not only to generate textual diagnoses but also to produce corresponding medical images that integrate seamlessly into authentic clinical workflows. Despite the growing interest, existing medical visual benchmarks present notable limitations. They often rely on ambiguous queries that lack sufficient relevance to image content, oversimplify complex diagnostic reasoning into closed-ended shortcuts, and adopt a text-centric evaluation paradigm that overlooks the importance of image generation capabilities. To address these challenges, we introduce MedGEN-Bench, a comprehensive multimodal benchmark designed to advance medical AI research. MedGEN-Bench comprises 6,422 expert-validated image-text pairs spanning six imaging modalities, 16 clinical tasks, and 28 subtasks. It is structured into three distinct formats: Visual Question Answering, Image Editing, and Contextual Multimodal Generation. What sets MedGEN-Bench apart is its focus on contextually intertwined instructions that necessitate sophisticated cross-modal reasoning and open-ended generative outputs, moving beyond the constraints of multiple-choice formats. To evaluate the performance of existing systems, we employ a novel three-tier assessment framework that integrates pixel-level metrics, semantic text analysis, and expert-guided clinical relevance scoring. Using this framework, we systematically assess 10 compositional frameworks, 3 unified models, and 5 VLMs.
WDT-MD: Wavelet Diffusion Transformers for Microaneurysm Detection in Fundus Images
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Microaneurysms (MAs), the earliest pathognomonic signs of Diabetic Retinopathy (DR), present as sub-60 $μm$ lesions in fundus images with highly variable photometric and morphological characteristics, rendering manual screening not only labor-intensive but inherently error-prone. While diffusion-based anomaly detection has emerged as a promising approach for automated MA screening, its clinical application is hindered by three fundamental limitations. First, these models often fall prey to "identity mapping", where they inadvertently replicate the input image. Second, they struggle to distinguish MAs from other anomalies, leading to high false positives. Third, their suboptimal reconstruction of normal features hampers overall performance. To address these challenges, we propose a Wavelet Diffusion Transformer framework for MA Detection (WDT-MD), which features three key innovations: a noise-encoded image conditioning mechanism to avoid "identity mapping" by perturbing image conditions during training; pseudo-normal pattern synthesis via inpainting to introduce pixel-level supervision, enabling discrimination between MAs and other anomalies; and a wavelet diffusion Transformer architecture that combines the global modeling capability of diffusion Transformers with multi-scale wavelet analysis to enhance reconstruction of normal retinal features. Comprehensive experiments on the IDRiD and e-ophtha MA datasets demonstrate that WDT-MD outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both pixel-level and image-level MA detection. This advancement holds significant promise for improving early DR screening.
No Modality Left Behind: Adapting to Missing Modalities via Knowledge Distillation for Brain Tumor Segmentation
Sep 18, 2025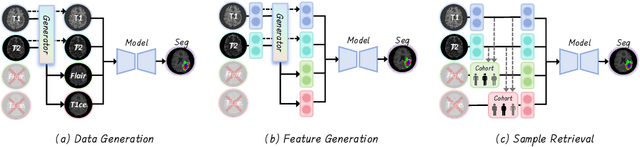
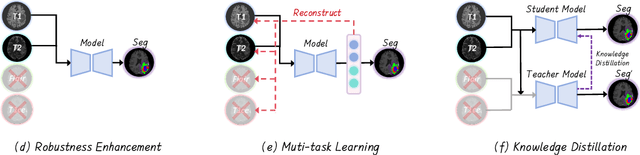
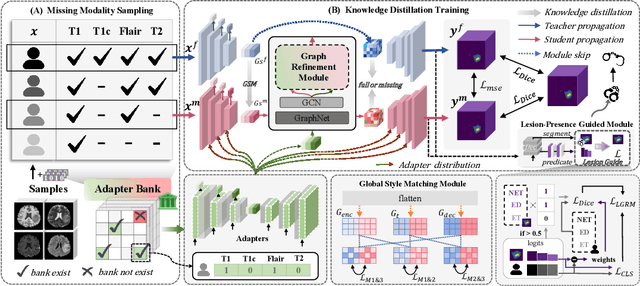
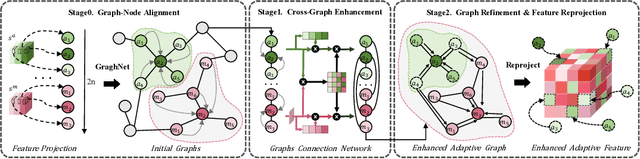
Abstract:Accurate brain tumor segmentation is essential for preoperative evaluation and personalized treatment. Multi-modal MRI is widely used due to its ability to capture complementary tumor features across different sequences. However, in clinical practice, missing modalities are common, limiting the robustness and generalizability of existing deep learning methods that rely on complete inputs, especially under non-dominant modality combinations. To address this, we propose AdaMM, a multi-modal brain tumor segmentation framework tailored for missing-modality scenarios, centered on knowledge distillation and composed of three synergistic modules. The Graph-guided Adaptive Refinement Module explicitly models semantic associations between generalizable and modality-specific features, enhancing adaptability to modality absence. The Bi-Bottleneck Distillation Module transfers structural and textural knowledge from teacher to student models via global style matching and adversarial feature alignment. The Lesion-Presence-Guided Reliability Module predicts prior probabilities of lesion types through an auxiliary classification task, effectively suppressing false positives under incomplete inputs. Extensive experiments on the BraTS 2018 and 2024 datasets demonstrate that AdaMM consistently outperforms existing methods, exhibiting superior segmentation accuracy and robustness, particularly in single-modality and weak-modality configurations. In addition, we conduct a systematic evaluation of six categories of missing-modality strategies, confirming the superiority of knowledge distillation and offering practical guidance for method selection and future research. Our source code is available at https://github.com/Quanato607/AdaMM.
Brain-HGCN: A Hyperbolic Graph Convolutional Network for Brain Functional Network Analysis
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) provides a powerful non-invasive window into the brain's functional organization by generating complex functional networks, typically modeled as graphs. These brain networks exhibit a hierarchical topology that is crucial for cognitive processing. However, due to inherent spatial constraints, standard Euclidean GNNs struggle to represent these hierarchical structures without high distortion, limiting their clinical performance. To address this limitation, we propose Brain-HGCN, a geometric deep learning framework based on hyperbolic geometry, which leverages the intrinsic property of negatively curved space to model the brain's network hierarchy with high fidelity. Grounded in the Lorentz model, our model employs a novel hyperbolic graph attention layer with a signed aggregation mechanism to distinctly process excitatory and inhibitory connections, ultimately learning robust graph-level representations via a geometrically sound Fr\'echet mean for graph readout. Experiments on two large-scale fMRI datasets for psychiatric disorder classification demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms a wide range of state-of-the-art Euclidean baselines. This work pioneers a new geometric deep learning paradigm for fMRI analysis, highlighting the immense potential of hyperbolic GNNs in the field of computational psychiatry.
Drawing2CAD: Sequence-to-Sequence Learning for CAD Generation from Vectorized Drawings
Aug 26, 2025



Abstract:Computer-Aided Design (CAD) generative modeling is driving significant innovations across industrial applications. Recent works have shown remarkable progress in creating solid models from various inputs such as point clouds, meshes, and text descriptions. However, these methods fundamentally diverge from traditional industrial workflows that begin with 2D engineering drawings. The automatic generation of parametric CAD models from these 2D vector drawings remains underexplored despite being a critical step in engineering design. To address this gap, our key insight is to reframe CAD generation as a sequence-to-sequence learning problem where vector drawing primitives directly inform the generation of parametric CAD operations, preserving geometric precision and design intent throughout the transformation process. We propose Drawing2CAD, a framework with three key technical components: a network-friendly vector primitive representation that preserves precise geometric information, a dual-decoder transformer architecture that decouples command type and parameter generation while maintaining precise correspondence, and a soft target distribution loss function accommodating inherent flexibility in CAD parameters. To train and evaluate Drawing2CAD, we create CAD-VGDrawing, a dataset of paired engineering drawings and parametric CAD models, and conduct thorough experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/lllssc/Drawing2CAD.
GraphMMP: A Graph Neural Network Model with Mutual Information and Global Fusion for Multimodal Medical Prognosis
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:In the field of multimodal medical data analysis, leveraging diverse types of data and understanding their hidden relationships continues to be a research focus. The main challenges lie in effectively modeling the complex interactions between heterogeneous data modalities with distinct characteristics while capturing both local and global dependencies across modalities. To address these challenges, this paper presents a two-stage multimodal prognosis model, GraphMMP, which is based on graph neural networks. The proposed model constructs feature graphs using mutual information and features a global fusion module built on Mamba, which significantly boosts prognosis performance. Empirical results show that GraphMMP surpasses existing methods on datasets related to liver prognosis and the METABRIC study, demonstrating its effectiveness in multimodal medical prognosis tasks.
Small Lesions-aware Bidirectional Multimodal Multiscale Fusion Network for Lung Disease Classification
Aug 06, 2025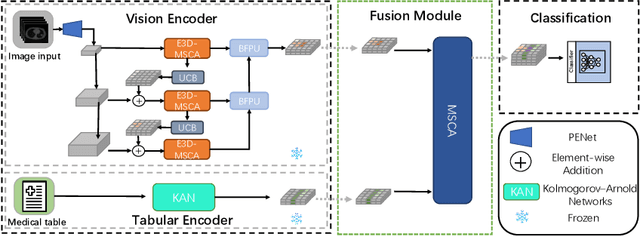
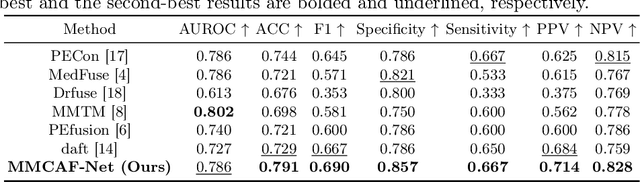
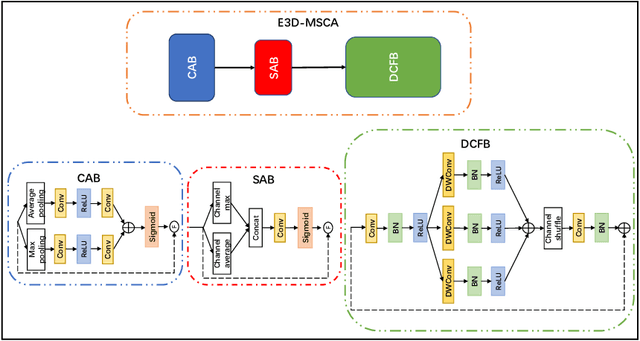
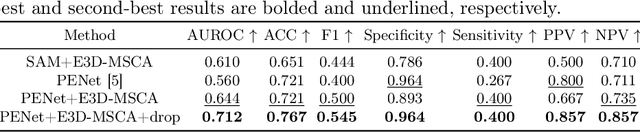
Abstract:The diagnosis of medical diseases faces challenges such as the misdiagnosis of small lesions. Deep learning, particularly multimodal approaches, has shown great potential in the field of medical disease diagnosis. However, the differences in dimensionality between medical imaging and electronic health record data present challenges for effective alignment and fusion. To address these issues, we propose the Multimodal Multiscale Cross-Attention Fusion Network (MMCAF-Net). This model employs a feature pyramid structure combined with an efficient 3D multi-scale convolutional attention module to extract lesion-specific features from 3D medical images. To further enhance multimodal data integration, MMCAF-Net incorporates a multi-scale cross-attention module, which resolves dimensional inconsistencies, enabling more effective feature fusion. We evaluated MMCAF-Net on the Lung-PET-CT-Dx dataset, and the results showed a significant improvement in diagnostic accuracy, surpassing current state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/yjx1234/MMCAF-Net
Bridging the Gap in Missing Modalities: Leveraging Knowledge Distillation and Style Matching for Brain Tumor Segmentation
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Accurate and reliable brain tumor segmentation, particularly when dealing with missing modalities, remains a critical challenge in medical image analysis. Previous studies have not fully resolved the challenges of tumor boundary segmentation insensitivity and feature transfer in the absence of key imaging modalities. In this study, we introduce MST-KDNet, aimed at addressing these critical issues. Our model features Multi-Scale Transformer Knowledge Distillation to effectively capture attention weights at various resolutions, Dual-Mode Logit Distillation to improve the transfer of knowledge, and a Global Style Matching Module that integrates feature matching with adversarial learning. Comprehensive experiments conducted on the BraTS and FeTS 2024 datasets demonstrate that MST-KDNet surpasses current leading methods in both Dice and HD95 scores, particularly in conditions with substantial modality loss. Our approach shows exceptional robustness and generalization potential, making it a promising candidate for real-world clinical applications. Our source code is available at https://github.com/Quanato607/MST-KDNet.
* 11 pages, 2 figures
Towards Practical Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis: A Lightweight and Interpretable Spiking Neural Model
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Early diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease (AD), especially at the mild cognitive impairment (MCI) stage, is vital yet hindered by subjective assessments and the high cost of multimodal imaging modalities. Although deep learning methods offer automated alternatives, their energy inefficiency and computational demands limit real-world deployment, particularly in resource-constrained settings. As a brain-inspired paradigm, spiking neural networks (SNNs) are inherently well-suited for modeling the sparse, event-driven patterns of neural degeneration in AD, offering a promising foundation for interpretable and low-power medical diagnostics. However, existing SNNs often suffer from weak expressiveness and unstable training, which restrict their effectiveness in complex medical tasks. To address these limitations, we propose FasterSNN, a hybrid neural architecture that integrates biologically inspired LIF neurons with region-adaptive convolution and multi-scale spiking attention. This design enables sparse, efficient processing of 3D MRI while preserving diagnostic accuracy. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that FasterSNN achieves competitive performance with substantially improved efficiency and stability, supporting its potential for practical AD screening. Our source code is available at https://github.com/wuchangw/FasterSNN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge