Junming Liu
EpiPlanAgent: Agentic Automated Epidemic Response Planning
Dec 12, 2025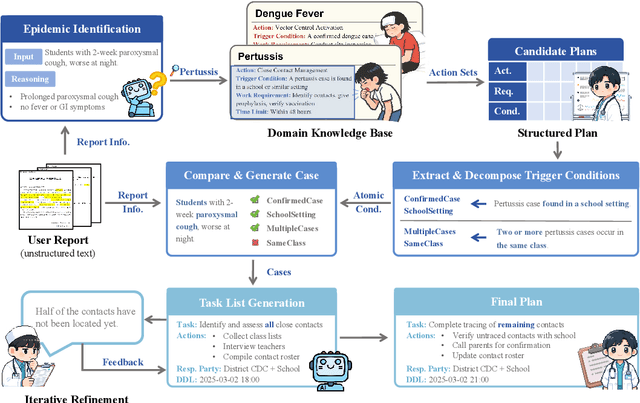
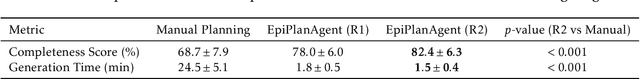
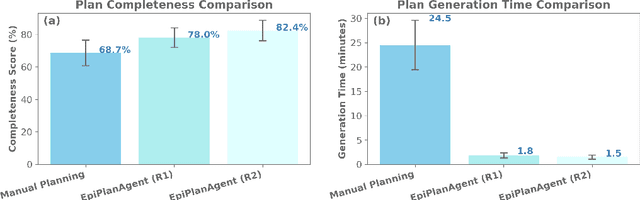
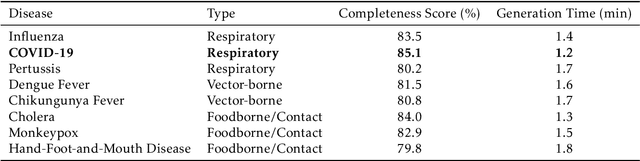
Abstract:Epidemic response planning is essential yet traditionally reliant on labor-intensive manual methods. This study aimed to design and evaluate EpiPlanAgent, an agent-based system using large language models (LLMs) to automate the generation and validation of digital emergency response plans. The multi-agent framework integrated task decomposition, knowledge grounding, and simulation modules. Public health professionals tested the system using real-world outbreak scenarios in a controlled evaluation. Results demonstrated that EpiPlanAgent significantly improved the completeness and guideline alignment of plans while drastically reducing development time compared to manual workflows. Expert evaluation confirmed high consistency between AI-generated and human-authored content. User feedback indicated strong perceived utility. In conclusion, EpiPlanAgent provides an effective, scalable solution for intelligent epidemic response planning, demonstrating the potential of agentic AI to transform public health preparedness.
Mosaic: Data-Free Knowledge Distillation via Mixture-of-Experts for Heterogeneous Distributed Environments
May 26, 2025



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a decentralized machine learning paradigm that enables clients to collaboratively train models while preserving data privacy. However, the coexistence of model and data heterogeneity gives rise to inconsistent representations and divergent optimization dynamics across clients, ultimately hindering robust global performance. To transcend these challenges, we propose Mosaic, a novel data-free knowledge distillation framework tailored for heterogeneous distributed environments. Mosaic first trains local generative models to approximate each client's personalized distribution, enabling synthetic data generation that safeguards privacy through strict separation from real data. Subsequently, Mosaic forms a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) from client models based on their specialized knowledge, and distills it into a global model using the generated data. To further enhance the MoE architecture, Mosaic integrates expert predictions via a lightweight meta model trained on a few representative prototypes. Extensive experiments on standard image classification benchmarks demonstrate that Mosaic consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches under both model and data heterogeneity. The source code has been published at https://github.com/Wings-Of-Disaster/Mosaic.
FedRecon: Missing Modality Reconstruction in Distributed Heterogeneous Environments
Apr 14, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal data are often incomplete and exhibit Non-Independent and Identically Distributed (Non-IID) characteristics in real-world scenarios. These inherent limitations lead to both modality heterogeneity through partial modality absence and data heterogeneity from distribution divergence, creating fundamental challenges for effective federated learning (FL). To address these coupled challenges, we propose FedRecon, the first method targeting simultaneous missing modality reconstruction and Non-IID adaptation in multimodal FL. Our approach first employs a lightweight Multimodal Variational Autoencoder (MVAE) to reconstruct missing modalities while preserving cross-modal consistency. Distinct from conventional imputation methods, we achieve sample-level alignment through a novel distribution mapping mechanism that guarantees both data consistency and completeness. Additionally, we introduce a strategy employing global generator freezing to prevent catastrophic forgetting, which in turn mitigates Non-IID fluctuations. Extensive evaluations on multimodal datasets demonstrate FedRecon's superior performance in modality reconstruction under Non-IID conditions, surpassing state-of-the-art methods.
HM-RAG: Hierarchical Multi-Agent Multimodal Retrieval Augmented Generation
Apr 13, 2025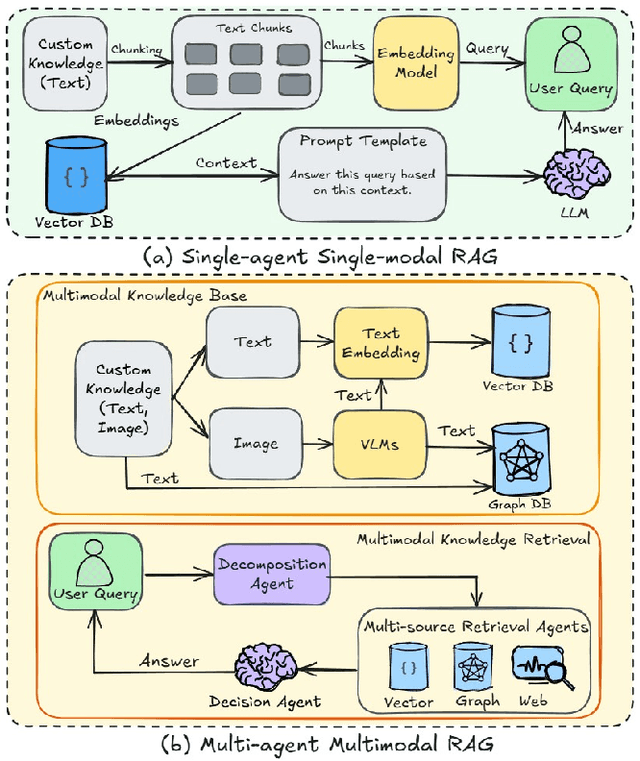
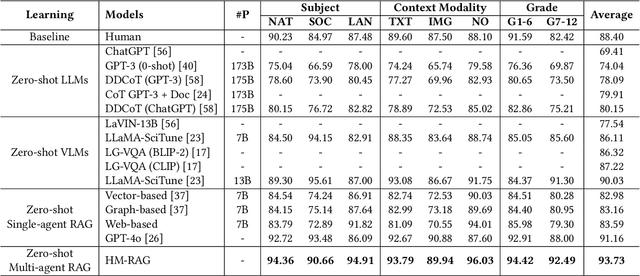
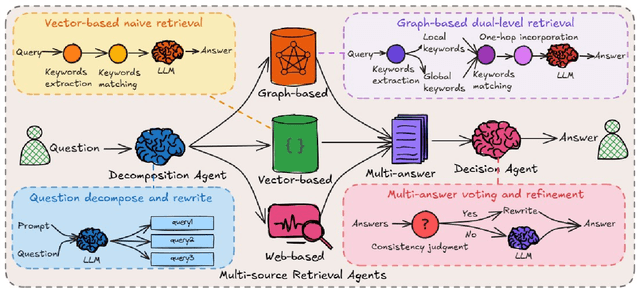
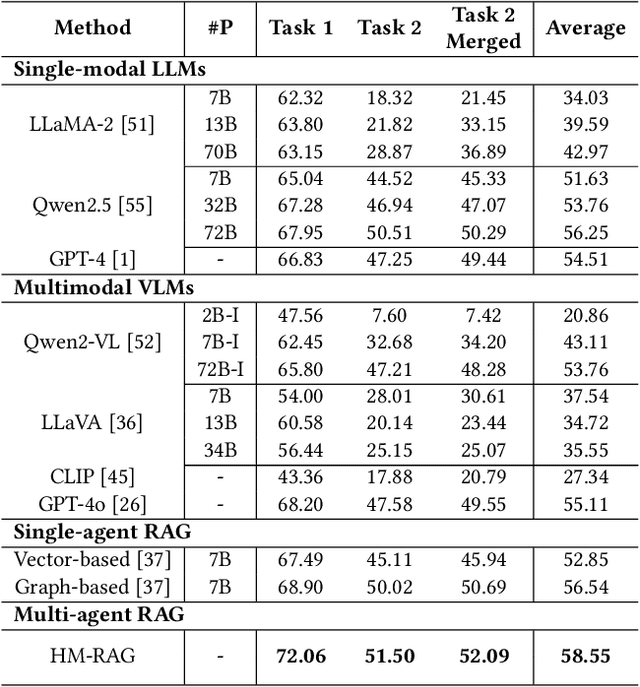
Abstract:While Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) augments Large Language Models (LLMs) with external knowledge, conventional single-agent RAG remains fundamentally limited in resolving complex queries demanding coordinated reasoning across heterogeneous data ecosystems. We present HM-RAG, a novel Hierarchical Multi-agent Multimodal RAG framework that pioneers collaborative intelligence for dynamic knowledge synthesis across structured, unstructured, and graph-based data. The framework is composed of three-tiered architecture with specialized agents: a Decomposition Agent that dissects complex queries into contextually coherent sub-tasks via semantic-aware query rewriting and schema-guided context augmentation; Multi-source Retrieval Agents that carry out parallel, modality-specific retrieval using plug-and-play modules designed for vector, graph, and web-based databases; and a Decision Agent that uses consistency voting to integrate multi-source answers and resolve discrepancies in retrieval results through Expert Model Refinement. This architecture attains comprehensive query understanding by combining textual, graph-relational, and web-derived evidence, resulting in a remarkable 12.95% improvement in answer accuracy and a 3.56% boost in question classification accuracy over baseline RAG systems on the ScienceQA and CrisisMMD benchmarks. Notably, HM-RAG establishes state-of-the-art results in zero-shot settings on both datasets. Its modular architecture ensures seamless integration of new data modalities while maintaining strict data governance, marking a significant advancement in addressing the critical challenges of multimodal reasoning and knowledge synthesis in RAG systems. Code is available at https://github.com/ocean-luna/HMRAG.
Aligning Vision to Language: Text-Free Multimodal Knowledge Graph Construction for Enhanced LLMs Reasoning
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Multimodal reasoning in Large Language Models (LLMs) struggles with incomplete knowledge and hallucination artifacts, challenges that textual Knowledge Graphs (KGs) only partially mitigate due to their modality isolation. While Multimodal Knowledge Graphs (MMKGs) promise enhanced cross-modal understanding, their practical construction is impeded by semantic narrowness of manual text annotations and inherent noise in visual-semantic entity linkages. In this paper, we propose Vision-align-to-Language integrated Knowledge Graph (VaLiK), a novel approach for constructing MMKGs that enhances LLMs reasoning through cross-modal information supplementation. Specifically, we cascade pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to align image features with text, transforming them into descriptions that encapsulate image-specific information. Furthermore, we developed a cross-modal similarity verification mechanism to quantify semantic consistency, effectively filtering out noise introduced during feature alignment. Even without manually annotated image captions, the refined descriptions alone suffice to construct the MMKG. Compared to conventional MMKGs construction paradigms, our approach achieves substantial storage efficiency gains while maintaining direct entity-to-image linkage capability. Experimental results on multimodal reasoning tasks demonstrate that LLMs augmented with VaLiK outperform previous state-of-the-art models. Our code is published at https://github.com/Wings-Of-Disaster/VaLiK.
How ChatGPT is Solving Vulnerability Management Problem
Nov 11, 2023
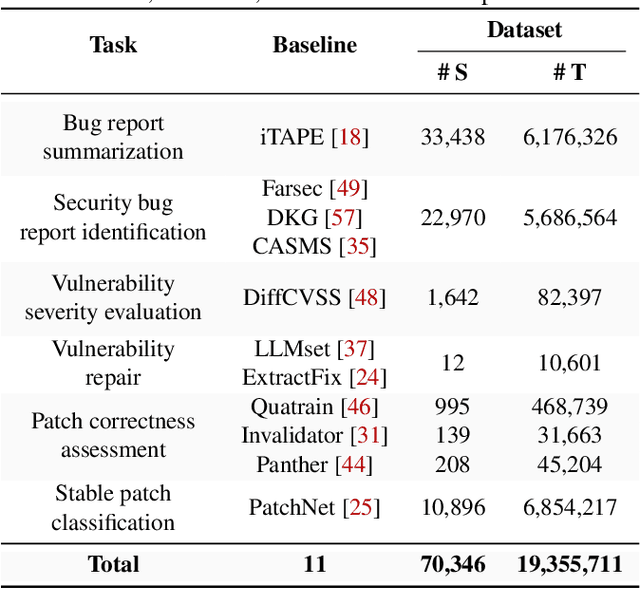


Abstract:Recently, ChatGPT has attracted great attention from the code analysis domain. Prior works show that ChatGPT has the capabilities of processing foundational code analysis tasks, such as abstract syntax tree generation, which indicates the potential of using ChatGPT to comprehend code syntax and static behaviors. However, it is unclear whether ChatGPT can complete more complicated real-world vulnerability management tasks, such as the prediction of security relevance and patch correctness, which require an all-encompassing understanding of various aspects, including code syntax, program semantics, and related manual comments. In this paper, we explore ChatGPT's capabilities on 6 tasks involving the complete vulnerability management process with a large-scale dataset containing 78,445 samples. For each task, we compare ChatGPT against SOTA approaches, investigate the impact of different prompts, and explore the difficulties. The results suggest promising potential in leveraging ChatGPT to assist vulnerability management. One notable example is ChatGPT's proficiency in tasks like generating titles for software bug reports. Furthermore, our findings reveal the difficulties encountered by ChatGPT and shed light on promising future directions. For instance, directly providing random demonstration examples in the prompt cannot consistently guarantee good performance in vulnerability management. By contrast, leveraging ChatGPT in a self-heuristic way -- extracting expertise from demonstration examples itself and integrating the extracted expertise in the prompt is a promising research direction. Besides, ChatGPT may misunderstand and misuse the information in the prompt. Consequently, effectively guiding ChatGPT to focus on helpful information rather than the irrelevant content is still an open problem.
Job2Vec: Job Title Benchmarking with Collective Multi-View Representation Learning
Sep 16, 2020
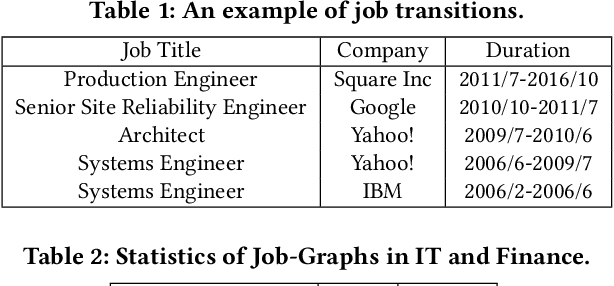
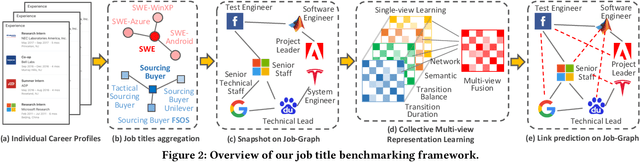
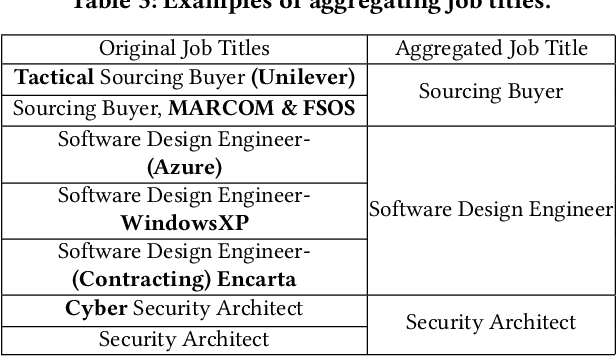
Abstract:Job Title Benchmarking (JTB) aims at matching job titles with similar expertise levels across various companies. JTB could provide precise guidance and considerable convenience for both talent recruitment and job seekers for position and salary calibration/prediction. Traditional JTB approaches mainly rely on manual market surveys, which is expensive and labor-intensive. Recently, the rapid development of Online Professional Graph has accumulated a large number of talent career records, which provides a promising trend for data-driven solutions. However, it is still a challenging task since (1) the job title and job transition (job-hopping) data is messy which contains a lot of subjective and non-standard naming conventions for the same position (e.g., Programmer, Software Development Engineer, SDE, Implementation Engineer), (2) there is a large amount of missing title/transition information, and (3) one talent only seeks limited numbers of jobs which brings the incompleteness and randomness modeling job transition patterns. To overcome these challenges, we aggregate all the records to construct a large-scale Job Title Benchmarking Graph (Job-Graph), where nodes denote job titles affiliated with specific companies and links denote the correlations between jobs. We reformulate the JTB as the task of link prediction over the Job-Graph that matched job titles should have links. Along this line, we propose a collective multi-view representation learning method (Job2Vec) by examining the Job-Graph jointly in (1) graph topology view, (2)semantic view, (3) job transition balance view, and (4) job transition duration view. We fuse the multi-view representations in the encode-decode paradigm to obtain a unified optimal representation for the task of link prediction. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments to validate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge