Leo Yu Zhang
UnlearnShield: Shielding Forgotten Privacy against Unlearning Inversion
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Machine unlearning is an emerging technique that aims to remove the influence of specific data from trained models, thereby enhancing privacy protection. However, recent research has uncovered critical privacy vulnerabilities, showing that adversaries can exploit unlearning inversion to reconstruct data that was intended to be erased. Despite the severity of this threat, dedicated defenses remain lacking. To address this gap, we propose UnlearnShield, the first defense specifically tailored to counter unlearning inversion. UnlearnShield introduces directional perturbations in the cosine representation space and regulates them through a constraint module to jointly preserve model accuracy and forgetting efficacy, thereby reducing inversion risk while maintaining utility. Experiments demonstrate that it achieves a good trade-off among privacy protection, accuracy, and forgetting.
Erosion Attack for Adversarial Training to Enhance Semantic Segmentation Robustness
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Existing segmentation models exhibit significant vulnerability to adversarial attacks.To improve robustness, adversarial training incorporates adversarial examples into model training. However, existing attack methods consider only global semantic information and ignore contextual semantic relationships within the samples, limiting the effectiveness of adversarial training. To address this issue, we propose EroSeg-AT, a vulnerability-aware adversarial training framework that leverages EroSeg to generate adversarial examples. EroSeg first selects sensitive pixels based on pixel-level confidence and then progressively propagates perturbations to higher-confidence pixels, effectively disrupting the semantic consistency of the samples. Experimental results show that, compared to existing methods, our approach significantly improves attack effectiveness and enhances model robustness under adversarial training.
Beyond Denial-of-Service: The Puppeteer's Attack for Fine-Grained Control in Ranking-Based Federated Learning
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Federated Rank Learning (FRL) is a promising Federated Learning (FL) paradigm designed to be resilient against model poisoning attacks due to its discrete, ranking-based update mechanism. Unlike traditional FL methods that rely on model updates, FRL leverages discrete rankings as a communication parameter between clients and the server. This approach significantly reduces communication costs and limits an adversary's ability to scale or optimize malicious updates in the continuous space, thereby enhancing its robustness. This makes FRL particularly appealing for applications where system security and data privacy are crucial, such as web-based auction and bidding platforms. While FRL substantially reduces the attack surface, we demonstrate that it remains vulnerable to a new class of local model poisoning attack, i.e., fine-grained control attacks. We introduce the Edge Control Attack (ECA), the first fine-grained control attack tailored to ranking-based FL frameworks. Unlike conventional denial-of-service (DoS) attacks that cause conspicuous disruptions, ECA enables an adversary to precisely degrade a competitor's accuracy to any target level while maintaining a normal-looking convergence trajectory, thereby avoiding detection. ECA operates in two stages: (i) identifying and manipulating Ascending and Descending Edges to align the global model with the target model, and (ii) widening the selection boundary gap to stabilize the global model at the target accuracy. Extensive experiments across seven benchmark datasets and nine Byzantine-robust aggregation rules (AGRs) show that ECA achieves fine-grained accuracy control with an average error of only 0.224%, outperforming the baseline by up to 17x. Our findings highlight the need for stronger defenses against advanced poisoning attacks. Our code is available at: https://github.com/Chenzh0205/ECA
Gradient Structure Estimation under Label-Only Oracles via Spectral Sensitivity
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Hard-label black-box settings, where only top-1 predicted labels are observable, pose a fundamentally constrained yet practically important feedback model for understanding model behavior. A central challenge in this regime is whether meaningful gradient information can be recovered from such discrete responses. In this work, we develop a unified theoretical perspective showing that a wide range of existing sign-flipping hard-label attacks can be interpreted as implicitly approximating the sign of the true loss gradient. This observation reframes hard-label attacks from heuristic search procedures into instances of gradient sign recovery under extremely limited feedback. Motivated by this first-principles understanding, we propose a new attack framework that combines a zero-query frequency-domain initialization with a Pattern-Driven Optimization (PDO) strategy. We establish theoretical guarantees demonstrating that, under mild assumptions, our initialization achieves higher expected cosine similarity to the true gradient sign compared to random baselines, while the proposed PDO procedure attains substantially lower query complexity than existing structured search approaches. We empirically validate our framework through extensive experiments on CIFAR-10, ImageNet, and ObjectNet, covering standard and adversarially trained models, commercial APIs, and CLIP-based models. The results show that our method consistently surpasses SOTA hard-label attacks in both attack success rate and query efficiency, particularly in low-query regimes. Beyond image classification, our approach generalizes effectively to corrupted data, biomedical datasets, and dense prediction tasks. Notably, it also successfully circumvents Blacklight, a SOTA stateful defense, resulting in a $0\%$ detection rate. Our code will be released publicly soon at https://github.com/csjunjun/DPAttack.git.
Less Is More -- Until It Breaks: Security Pitfalls of Vision Token Compression in Large Vision-Language Models
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Visual token compression is widely adopted to improve the inference efficiency of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), enabling their deployment in latency-sensitive and resource-constrained scenarios. However, existing work has mainly focused on efficiency and performance, while the security implications of visual token compression remain largely unexplored. In this work, we first reveal that visual token compression substantially degrades the robustness of LVLMs: models that are robust under uncompressed inference become highly vulnerable once compression is enabled. These vulnerabilities are state-specific; failure modes emerge only in the compressed setting and completely disappear when compression is disabled, making them particularly hidden and difficult to diagnose. By analyzing the key stages of the compression process, we identify instability in token importance ranking as the primary cause of this robustness degradation. Small and imperceptible perturbations can significantly alter token rankings, leading the compression mechanism to mistakenly discard task-critical information and ultimately causing model failure. Motivated by this observation, we propose a Compression-Aware Attack to systematically study and exploit this vulnerability. CAA directly targets the token selection mechanism and induces failures exclusively under compressed inference. We further extend this approach to more realistic black-box settings and introduce Transfer CAA, where neither the target model nor the compression configuration is accessible. We further evaluate potential defenses and find that they provide only limited protection. Extensive experiments across models, datasets, and compression methods show that visual token compression significantly undermines robustness, revealing a previously overlooked efficiency-security trade-off.
Dual-View Inference Attack: Machine Unlearning Amplifies Privacy Exposure
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Machine unlearning is a newly popularized technique for removing specific training data from a trained model, enabling it to comply with data deletion requests. While it protects the rights of users requesting unlearning, it also introduces new privacy risks. Prior works have primarily focused on the privacy of data that has been unlearned, while the risks to retained data remain largely unexplored. To address this gap, we focus on the privacy risks of retained data and, for the first time, reveal the vulnerabilities introduced by machine unlearning under the dual-view setting, where an adversary can query both the original and the unlearned models. From an information-theoretic perspective, we introduce the concept of {privacy knowledge gain} and demonstrate that the dual-view setting allows adversaries to obtain more information than querying either model alone, thereby amplifying privacy leakage. To effectively demonstrate this threat, we propose DVIA, a Dual-View Inference Attack, which extracts membership information on retained data using black-box queries to both models. DVIA eliminates the need to train an attack model and employs a lightweight likelihood ratio inference module for efficient inference. Experiments across different datasets and model architectures validate the effectiveness of DVIA and highlight the privacy risks inherent in the dual-view setting.
Debiased Dual-Invariant Defense for Adversarially Robust Person Re-Identification
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Person re-identification (ReID) is a fundamental task in many real-world applications such as pedestrian trajectory tracking. However, advanced deep learning-based ReID models are highly susceptible to adversarial attacks, where imperceptible perturbations to pedestrian images can cause entirely incorrect predictions, posing significant security threats. Although numerous adversarial defense strategies have been proposed for classification tasks, their extension to metric learning tasks such as person ReID remains relatively unexplored. Moreover, the several existing defenses for person ReID fail to address the inherent unique challenges of adversarially robust ReID. In this paper, we systematically identify the challenges of adversarial defense in person ReID into two key issues: model bias and composite generalization requirements. To address them, we propose a debiased dual-invariant defense framework composed of two main phases. In the data balancing phase, we mitigate model bias using a diffusion-model-based data resampling strategy that promotes fairness and diversity in training data. In the bi-adversarial self-meta defense phase, we introduce a novel metric adversarial training approach incorporating farthest negative extension softening to overcome the robustness degradation caused by the absence of classifier. Additionally, we introduce an adversarially-enhanced self-meta mechanism to achieve dual-generalization for both unseen identities and unseen attack types. Experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art defenses.
TED++: Submanifold-Aware Backdoor Detection via Layerwise Tubular-Neighbourhood Screening
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:As deep neural networks power increasingly critical applications, stealthy backdoor attacks, where poisoned training inputs trigger malicious model behaviour while appearing benign, pose a severe security risk. Many existing defences are vulnerable when attackers exploit subtle distance-based anomalies or when clean examples are scarce. To meet this challenge, we introduce TED++, a submanifold-aware framework that effectively detects subtle backdoors that evade existing defences. TED++ begins by constructing a tubular neighbourhood around each class's hidden-feature manifold, estimating its local ``thickness'' from a handful of clean activations. It then applies Locally Adaptive Ranking (LAR) to detect any activation that drifts outside the admissible tube. By aggregating these LAR-adjusted ranks across all layers, TED++ captures how faithfully an input remains on the evolving class submanifolds. Based on such characteristic ``tube-constrained'' behaviour, TED++ flags inputs whose LAR-based ranking sequences deviate significantly. Extensive experiments are conducted on benchmark datasets and tasks, demonstrating that TED++ achieves state-of-the-art detection performance under both adaptive-attack and limited-data scenarios. Remarkably, even with only five held-out examples per class, TED++ still delivers near-perfect detection, achieving gains of up to 14\% in AUROC over the next-best method. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/namle-w/TEDpp.
Towards Real-World Deepfake Detection: A Diverse In-the-wild Dataset of Forgery Faces
Oct 09, 2025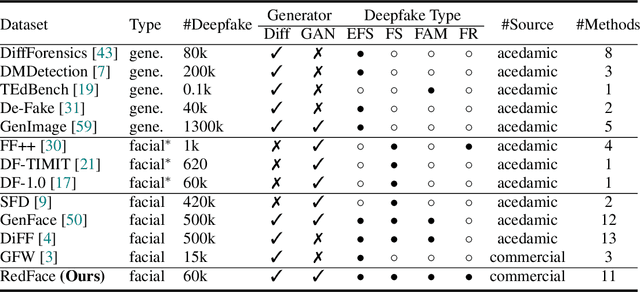

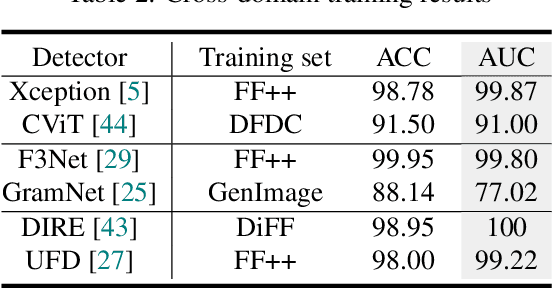
Abstract:Deepfakes, leveraging advanced AIGC (Artificial Intelligence-Generated Content) techniques, create hyper-realistic synthetic images and videos of human faces, posing a significant threat to the authenticity of social media. While this real-world threat is increasingly prevalent, existing academic evaluations and benchmarks for detecting deepfake forgery often fall short to achieve effective application for their lack of specificity, limited deepfake diversity, restricted manipulation techniques.To address these limitations, we introduce RedFace (Real-world-oriented Deepfake Face), a specialized facial deepfake dataset, comprising over 60,000 forged images and 1,000 manipulated videos derived from authentic facial features, to bridge the gap between academic evaluations and real-world necessity. Unlike prior benchmarks, which typically rely on academic methods to generate deepfakes, RedFace utilizes 9 commercial online platforms to integrate the latest deepfake technologies found "in the wild", effectively simulating real-world black-box scenarios.Moreover, RedFace's deepfakes are synthesized using bespoke algorithms, allowing it to capture diverse and evolving methods used by real-world deepfake creators. Extensive experimental results on RedFace (including cross-domain, intra-domain, and real-world social network dissemination simulations) verify the limited practicality of existing deepfake detection schemes against real-world applications. We further perform a detailed analysis of the RedFace dataset, elucidating the reason of its impact on detection performance compared to conventional datasets. Our dataset is available at: https://github.com/kikyou-220/RedFace.
Character-Level Perturbations Disrupt LLM Watermarks
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) watermarking embeds detectable signals into generated text for copyright protection, misuse prevention, and content detection. While prior studies evaluate robustness using watermark removal attacks, these methods are often suboptimal, creating the misconception that effective removal requires large perturbations or powerful adversaries. To bridge the gap, we first formalize the system model for LLM watermark, and characterize two realistic threat models constrained on limited access to the watermark detector. We then analyze how different types of perturbation vary in their attack range, i.e., the number of tokens they can affect with a single edit. We observe that character-level perturbations (e.g., typos, swaps, deletions, homoglyphs) can influence multiple tokens simultaneously by disrupting the tokenization process. We demonstrate that character-level perturbations are significantly more effective for watermark removal under the most restrictive threat model. We further propose guided removal attacks based on the Genetic Algorithm (GA) that uses a reference detector for optimization. Under a practical threat model with limited black-box queries to the watermark detector, our method demonstrates strong removal performance. Experiments confirm the superiority of character-level perturbations and the effectiveness of the GA in removing watermarks under realistic constraints. Additionally, we argue there is an adversarial dilemma when considering potential defenses: any fixed defense can be bypassed by a suitable perturbation strategy. Motivated by this principle, we propose an adaptive compound character-level attack. Experimental results show that this approach can effectively defeat the defenses. Our findings highlight significant vulnerabilities in existing LLM watermark schemes and underline the urgency for the development of new robust mechanisms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge