Shang Gao
DichroGAN: Towards Restoration of in-air Colours of Seafloor from Satellite Imagery
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Recovering the in-air colours of seafloor from satellite imagery is a challenging task due to the exponential attenuation of light with depth in the water column. In this study, we present DichroGAN, a conditional generative adversarial network (cGAN) designed for this purpose. DichroGAN employs a two-steps simultaneous training: first, two generators utilise a hyperspectral image cube to estimate diffuse and specular reflections, thereby obtaining atmospheric scene radiance. Next, a third generator receives as input the generated scene radiance containing the features of each spectral band, while a fourth generator estimates the underwater light transmission. These generators work together to remove the effects of light absorption and scattering, restoring the in-air colours of seafloor based on the underwater image formation equation. DichroGAN is trained on a compact dataset derived from PRISMA satellite imagery, comprising RGB images paired with their corresponding spectral bands and masks. Extensive experiments on both satellite and underwater datasets demonstrate that DichroGAN achieves competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art underwater restoration techniques.
GCA-ResUNet: Medical Image Segmentation Using Grouped Coordinate Attention
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Accurate segmentation of heterogeneous anatomical structures is pivotal for computer-aided diagnosis and subsequent clinical decision-making. Although U-Net based convolutional neural networks have achieved remarkable progress, their intrinsic locality and largely homogeneous attention formulations often limit the modeling of long-range contextual dependencies, especially in multi-organ scenarios and low-contrast regions. Transformer-based architectures mitigate this issue by leveraging global self-attention, but they usually require higher computational resources and larger training data, which may impede deployment in resource-constrained clinical environments.In this paper, we propose GCA-ResUNet, an efficient medical image segmentation framework equipped with a lightweight and plug-and-play Grouped Coordinate Attention (GCA) module. The proposed GCA decouples channel-wise context modeling into multiple groups to explicitly account for semantic heterogeneity across channels, and integrates direction-aware coordinate encoding to capture structured spatial dependencies along horizontal and vertical axes. This design enhances global representation capability while preserving the efficiency advantages of CNN backbones. Extensive experiments on two widely used benchmarks, Synapse and ACDC, demonstrate that GCA-ResUNet achieves Dice scores of 86.11% and 92.64%, respectively, outperforming a range of representative CNN and Transformer-based methods, including Swin-UNet and TransUNet. In particular, GCA-ResUNet yields consistent improvements in delineating small anatomical structures with complex boundaries. These results indicate that the proposed approach provides a favorable trade-off between segmentation accuracy and computational efficiency, offering a practical and scalable solution for clinical deployment.
GCA-ResUNet:Image segmentation in medical images using grouped coordinate attention
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Medical image segmentation underpins computer-aided diagnosis and therapy by supporting clinical diagnosis, preoperative planning, and disease monitoring. While U-Net style convolutional neural networks perform well due to their encoder-decoder structures with skip connections, they struggle to capture long-range dependencies. Transformer-based variants address global context but often require heavy computation and large training datasets. This paper proposes GCA-ResUNet, an efficient segmentation network that integrates Grouped Coordinate Attention (GCA) into ResNet-50 residual blocks. GCA uses grouped coordinate modeling to jointly encode global dependencies across channels and spatial locations, strengthening feature representation and boundary delineation while adding minimal parameter and FLOP overhead compared with self-attention. On the Synapse dataset, GCA-ResUNet achieves a Dice score of 86.11%, and on the ACDC dataset, it reaches 92.64%, surpassing several state-of-the-art baselines while maintaining fast inference and favorable computational efficiency. These results indicate that GCA offers a practical way to enhance convolutional architectures with global modeling capability, enabling high-accuracy and resource-efficient medical image segmentation.
Regularizing Subspace Redundancy of Low-Rank Adaptation
Jul 28, 2025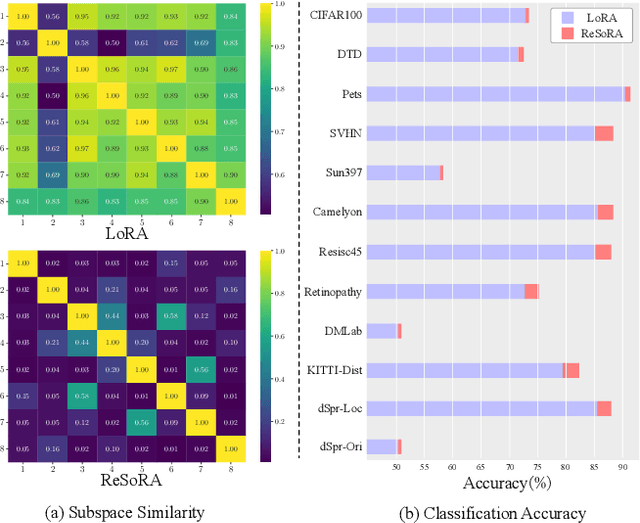
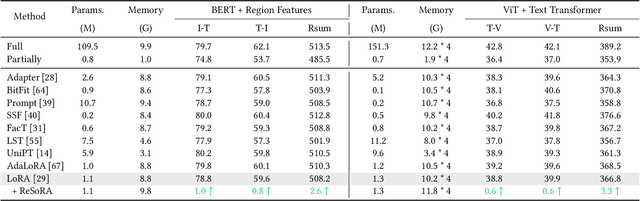
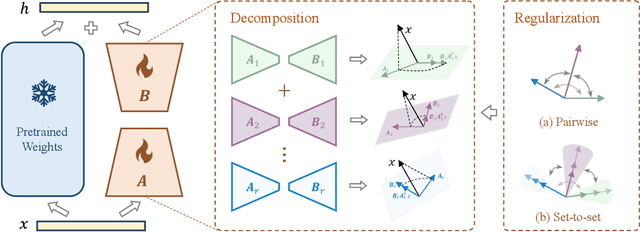
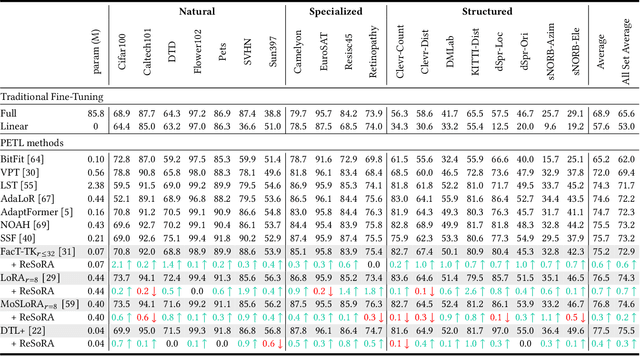
Abstract:Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and its variants have delivered strong capability in Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning (PETL) by minimizing trainable parameters and benefiting from reparameterization. However, their projection matrices remain unrestricted during training, causing high representation redundancy and diminishing the effectiveness of feature adaptation in the resulting subspaces. While existing methods mitigate this by manually adjusting the rank or implicitly applying channel-wise masks, they lack flexibility and generalize poorly across various datasets and architectures. Hence, we propose ReSoRA, a method that explicitly models redundancy between mapping subspaces and adaptively Regularizes Subspace redundancy of Low-Rank Adaptation. Specifically, it theoretically decomposes the low-rank submatrices into multiple equivalent subspaces and systematically applies de-redundancy constraints to the feature distributions across different projections. Extensive experiments validate that our proposed method consistently facilitates existing state-of-the-art PETL methods across various backbones and datasets in vision-language retrieval and standard visual classification benchmarks. Besides, as a training supervision, ReSoRA can be seamlessly integrated into existing approaches in a plug-and-play manner, with no additional inference costs. Code is publicly available at: https://github.com/Lucenova/ReSoRA.
Dual Semantic-Aware Network for Noise Suppressed Ultrasound Video Segmentation
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Ultrasound imaging is a prevalent diagnostic tool known for its simplicity and non-invasiveness. However, its inherent characteristics often introduce substantial noise, posing considerable challenges for automated lesion or organ segmentation in ultrasound video sequences. To address these limitations, we propose the Dual Semantic-Aware Network (DSANet), a novel framework designed to enhance noise robustness in ultrasound video segmentation by fostering mutual semantic awareness between local and global features. Specifically, we introduce an Adjacent-Frame Semantic-Aware (AFSA) module, which constructs a channel-wise similarity matrix to guide feature fusion across adjacent frames, effectively mitigating the impact of random noise without relying on pixel-level relationships. Additionally, we propose a Local-and-Global Semantic-Aware (LGSA) module that reorganizes and fuses temporal unconditional local features, which capture spatial details independently at each frame, with conditional global features that incorporate temporal context from adjacent frames. This integration facilitates multi-level semantic representation, significantly improving the model's resilience to noise interference. Extensive evaluations on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that DSANet substantially outperforms state-of-the-art methods in segmentation accuracy. Moreover, since our model avoids pixel-level feature dependencies, it achieves significantly higher inference FPS than video-based methods, and even surpasses some image-based models. Code can be found in \href{https://github.com/ZhouL2001/DSANet}{DSANet}
Da Yu: Towards USV-Based Image Captioning for Waterway Surveillance and Scene Understanding
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Automated waterway environment perception is crucial for enabling unmanned surface vessels (USVs) to understand their surroundings and make informed decisions. Most existing waterway perception models primarily focus on instance-level object perception paradigms (e.g., detection, segmentation). However, due to the complexity of waterway environments, current perception datasets and models fail to achieve global semantic understanding of waterways, limiting large-scale monitoring and structured log generation. With the advancement of vision-language models (VLMs), we leverage image captioning to introduce WaterCaption, the first captioning dataset specifically designed for waterway environments. WaterCaption focuses on fine-grained, multi-region long-text descriptions, providing a new research direction for visual geo-understanding and spatial scene cognition. Exactly, it includes 20.2k image-text pair data with 1.8 million vocabulary size. Additionally, we propose Da Yu, an edge-deployable multi-modal large language model for USVs, where we propose a novel vision-to-language projector called Nano Transformer Adaptor (NTA). NTA effectively balances computational efficiency with the capacity for both global and fine-grained local modeling of visual features, thereby significantly enhancing the model's ability to generate long-form textual outputs. Da Yu achieves an optimal balance between performance and efficiency, surpassing state-of-the-art models on WaterCaption and several other captioning benchmarks.
TED-LaST: Towards Robust Backdoor Defense Against Adaptive Attacks
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are vulnerable to backdoor attacks, where attackers implant hidden triggers during training to maliciously control model behavior. Topological Evolution Dynamics (TED) has recently emerged as a powerful tool for detecting backdoor attacks in DNNs. However, TED can be vulnerable to backdoor attacks that adaptively distort topological representation distributions across network layers. To address this limitation, we propose TED-LaST (Topological Evolution Dynamics against Laundry, Slow release, and Target mapping attack strategies), a novel defense strategy that enhances TED's robustness against adaptive attacks. TED-LaST introduces two key innovations: label-supervised dynamics tracking and adaptive layer emphasis. These enhancements enable the identification of stealthy threats that evade traditional TED-based defenses, even in cases of inseparability in topological space and subtle topological perturbations. We review and classify data poisoning tricks in state-of-the-art adaptive attacks and propose enhanced adaptive attack with target mapping, which can dynamically shift malicious tasks and fully leverage the stealthiness that adaptive attacks possess. Our comprehensive experiments on multiple datasets (CIFAR-10, GTSRB, and ImageNet100) and model architectures (ResNet20, ResNet101) show that TED-LaST effectively counteracts sophisticated backdoors like Adap-Blend, Adapt-Patch, and the proposed enhanced adaptive attack. TED-LaST sets a new benchmark for robust backdoor detection, substantially enhancing DNN security against evolving threats.
Interpreting Social Bias in LVLMs via Information Flow Analysis and Multi-Round Dialogue Evaluation
May 27, 2025Abstract:Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in multimodal tasks, yet they also exhibit notable social biases. These biases often manifest as unintended associations between neutral concepts and sensitive human attributes, leading to disparate model behaviors across demographic groups. While existing studies primarily focus on detecting and quantifying such biases, they offer limited insight into the underlying mechanisms within the models. To address this gap, we propose an explanatory framework that combines information flow analysis with multi-round dialogue evaluation, aiming to understand the origin of social bias from the perspective of imbalanced internal information utilization. Specifically, we first identify high-contribution image tokens involved in the model's reasoning process for neutral questions via information flow analysis. Then, we design a multi-turn dialogue mechanism to evaluate the extent to which these key tokens encode sensitive information. Extensive experiments reveal that LVLMs exhibit systematic disparities in information usage when processing images of different demographic groups, suggesting that social bias is deeply rooted in the model's internal reasoning dynamics. Furthermore, we complement our findings from a textual modality perspective, showing that the model's semantic representations already display biased proximity patterns, thereby offering a cross-modal explanation of bias formation.
Likert or Not: LLM Absolute Relevance Judgments on Fine-Grained Ordinal Scales
May 25, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) obtain state of the art zero shot relevance ranking performance on a variety of information retrieval tasks. The two most common prompts to elicit LLM relevance judgments are pointwise scoring (a.k.a. relevance generation), where the LLM sees a single query-document pair and outputs a single relevance score, and listwise ranking (a.k.a. permutation generation), where the LLM sees a query and a list of documents and outputs a permutation, sorting the documents in decreasing order of relevance. The current research community consensus is that listwise ranking yields superior performance, and significant research effort has been devoted to crafting LLM listwise ranking algorithms. The underlying hypothesis is that LLMs are better at making relative relevance judgments than absolute ones. In tension with this hypothesis, we find that the gap between pointwise scoring and listwise ranking shrinks when pointwise scoring is implemented using a sufficiently large ordinal relevance label space, becoming statistically insignificant for many LLM-benchmark dataset combinations (where ``significant'' means ``95\% confidence that listwise ranking improves NDCG@10''). Our evaluations span four LLMs, eight benchmark datasets from the BEIR and TREC-DL suites, and two proprietary datasets with relevance labels collected after the training cut-off of all LLMs evaluated.
BioD2C: A Dual-level Semantic Consistency Constraint Framework for Biomedical VQA
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Biomedical visual question answering (VQA) has been widely studied and has demonstrated significant application value and potential in fields such as assistive medical diagnosis. Despite their success, current biomedical VQA models perform multimodal information interaction only at the model level within large language models (LLMs), leading to suboptimal multimodal semantic alignment when dealing with complex tasks. To address this issue, we propose BioD2C: a novel Dual-level Semantic Consistency Constraint Framework for Biomedical VQA, which achieves dual-level semantic interaction alignment at both the model and feature levels, enabling the model to adaptively learn visual features based on the question. Specifically, we firstly integrate textual features into visual features via an image-text fusion mechanism as feature-level semantic interaction, obtaining visual features conditioned on the given text; and then introduce a text-queue-based cross-modal soft semantic loss function to further align the image semantics with the question semantics. Specifically, in this work, we establish a new dataset, BioVGQ, to address inherent biases in prior datasets by filtering manually-altered images and aligning question-answer pairs with multimodal context, and train our model on this dataset. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that BioD2C achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance across multiple downstream datasets, showcasing its robustness, generalizability, and potential to advance biomedical VQA research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge