Yifan Jia
TeachPro: Multi-Label Qualitative Teaching Evaluation via Cross-View Graph Synergy and Semantic Anchored Evidence Encoding
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Standardized Student Evaluation of Teaching often suffer from low reliability, restricted response options, and response distortion. Existing machine learning methods that mine open-ended comments usually reduce feedback to binary sentiment, which overlooks concrete concerns such as content clarity, feedback timeliness, and instructor demeanor, and provides limited guidance for instructional improvement.We propose TeachPro, a multi-label learning framework that systematically assesses five key teaching dimensions: professional expertise, instructional behavior, pedagogical efficacy, classroom experience, and other performance metrics. We first propose a Dimension-Anchored Evidence Encoder, which integrates three core components: (i) a pre-trained text encoder that transforms qualitative feedback annotations into contextualized embeddings; (ii) a prompt module that represents five teaching dimensions as learnable semantic anchors; and (iii) a cross-attention mechanism that aligns evidence with pedagogical dimensions within a structured semantic space. We then propose a Cross-View Graph Synergy Network to represent student comments. This network comprises two components: (i) a Syntactic Branch that extracts explicit grammatical dependencies from parse trees, and (ii) a Semantic Branch that models latent conceptual relations derived from BERT-based similarity graphs. BiAffine fusion module aligns syntactic and semantic units, while a differential regularizer disentangles embeddings to encourage complementary representations. Finally, a cross-attention mechanism bridges the dimension-anchored evidence with the multi-view comment representations. We also contribute a novel benchmark dataset featuring expert qualitative annotations and multi-label scores. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TeachPro offers superior diagnostic granularity and robustness across diverse evaluation settings.
LMAE4Eth: Generalizable and Robust Ethereum Fraud Detection by Exploring Transaction Semantics and Masked Graph Embedding
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Current Ethereum fraud detection methods rely on context-independent, numerical transaction sequences, failing to capture semantic of account transactions. Furthermore, the pervasive homogeneity in Ethereum transaction records renders it challenging to learn discriminative account embeddings. Moreover, current self-supervised graph learning methods primarily learn node representations through graph reconstruction, resulting in suboptimal performance for node-level tasks like fraud account detection, while these methods also encounter scalability challenges. To tackle these challenges, we propose LMAE4Eth, a multi-view learning framework that fuses transaction semantics, masked graph embedding, and expert knowledge. We first propose a transaction-token contrastive language model (TxCLM) that transforms context-independent numerical transaction records into logically cohesive linguistic representations. To clearly characterize the semantic differences between accounts, we also use a token-aware contrastive learning pre-training objective together with the masked transaction model pre-training objective, learns high-expressive account representations. We then propose a masked account graph autoencoder (MAGAE) using generative self-supervised learning, which achieves superior node-level account detection by focusing on reconstructing account node features. To enable MAGAE to scale for large-scale training, we propose to integrate layer-neighbor sampling into the graph, which reduces the number of sampled vertices by several times without compromising training quality. Finally, using a cross-attention fusion network, we unify the embeddings of TxCLM and MAGAE to leverage the benefits of both. We evaluate our method against 21 baseline approaches on three datasets. Experimental results show that our method outperforms the best baseline by over 10% in F1-score on two of the datasets.
WebGuard++:Interpretable Malicious URL Detection via Bidirectional Fusion of HTML Subgraphs and Multi-Scale Convolutional BERT
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:URL+HTML feature fusion shows promise for robust malicious URL detection, since attacker artifacts persist in DOM structures. However, prior work suffers from four critical shortcomings: (1) incomplete URL modeling, failing to jointly capture lexical patterns and semantic context; (2) HTML graph sparsity, where threat-indicative nodes (e.g., obfuscated scripts) are isolated amid benign content, causing signal dilution during graph aggregation; (3) unidirectional analysis, ignoring URL-HTML feature bidirectional interaction; and (4) opaque decisions, lacking attribution to malicious DOM components. To address these challenges, we present WebGuard++, a detection framework with 4 novel components: 1) Cross-scale URL Encoder: Hierarchically learns local-to-global and coarse to fine URL features based on Transformer network with dynamic convolution. 2) Subgraph-aware HTML Encoder: Decomposes DOM graphs into interpretable substructures, amplifying sparse threat signals via Hierarchical feature fusion. 3) Bidirectional Coupling Module: Aligns URL and HTML embeddings through cross-modal contrastive learning, optimizing inter-modal consistency and intra-modal specificity. 4) Voting Module: Localizes malicious regions through consensus voting on malicious subgraph predictions. Experiments show WebGuard++ achieves significant improvements over state-of-the-art baselines, achieving 1.1x-7.9x higher TPR at fixed FPR of 0.001 and 0.0001 across both datasets.
Interpreting Social Bias in LVLMs via Information Flow Analysis and Multi-Round Dialogue Evaluation
May 27, 2025Abstract:Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in multimodal tasks, yet they also exhibit notable social biases. These biases often manifest as unintended associations between neutral concepts and sensitive human attributes, leading to disparate model behaviors across demographic groups. While existing studies primarily focus on detecting and quantifying such biases, they offer limited insight into the underlying mechanisms within the models. To address this gap, we propose an explanatory framework that combines information flow analysis with multi-round dialogue evaluation, aiming to understand the origin of social bias from the perspective of imbalanced internal information utilization. Specifically, we first identify high-contribution image tokens involved in the model's reasoning process for neutral questions via information flow analysis. Then, we design a multi-turn dialogue mechanism to evaluate the extent to which these key tokens encode sensitive information. Extensive experiments reveal that LVLMs exhibit systematic disparities in information usage when processing images of different demographic groups, suggesting that social bias is deeply rooted in the model's internal reasoning dynamics. Furthermore, we complement our findings from a textual modality perspective, showing that the model's semantic representations already display biased proximity patterns, thereby offering a cross-modal explanation of bias formation.
Benchmarking Multimodal Knowledge Conflict for Large Multimodal Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large Multimodal Models(LMMs) face notable challenges when encountering multimodal knowledge conflicts, particularly under retrieval-augmented generation(RAG) frameworks where the contextual information from external sources may contradict the model's internal parametric knowledge, leading to unreliable outputs. However, existing benchmarks fail to reflect such realistic conflict scenarios. Most focus solely on intra-memory conflicts, while context-memory and inter-context conflicts remain largely investigated. Furthermore, commonly used factual knowledge-based evaluations are often overlooked, and existing datasets lack a thorough investigation into conflict detection capabilities. To bridge this gap, we propose MMKC-Bench, a benchmark designed to evaluate factual knowledge conflicts in both context-memory and inter-context scenarios. MMKC-Bench encompasses three types of multimodal knowledge conflicts and includes 1,573 knowledge instances and 3,381 images across 23 broad types, collected through automated pipelines with human verification. We evaluate three representative series of LMMs on both model behavior analysis and conflict detection tasks. Our findings show that while current LMMs are capable of recognizing knowledge conflicts, they tend to favor internal parametric knowledge over external evidence. We hope MMKC-Bench will foster further research in multimodal knowledge conflict and enhance the development of multimodal RAG systems. The source code is available at https://github.com/MLLMKCBENCH/MLLMKC.
BioD2C: A Dual-level Semantic Consistency Constraint Framework for Biomedical VQA
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Biomedical visual question answering (VQA) has been widely studied and has demonstrated significant application value and potential in fields such as assistive medical diagnosis. Despite their success, current biomedical VQA models perform multimodal information interaction only at the model level within large language models (LLMs), leading to suboptimal multimodal semantic alignment when dealing with complex tasks. To address this issue, we propose BioD2C: a novel Dual-level Semantic Consistency Constraint Framework for Biomedical VQA, which achieves dual-level semantic interaction alignment at both the model and feature levels, enabling the model to adaptively learn visual features based on the question. Specifically, we firstly integrate textual features into visual features via an image-text fusion mechanism as feature-level semantic interaction, obtaining visual features conditioned on the given text; and then introduce a text-queue-based cross-modal soft semantic loss function to further align the image semantics with the question semantics. Specifically, in this work, we establish a new dataset, BioVGQ, to address inherent biases in prior datasets by filtering manually-altered images and aligning question-answer pairs with multimodal context, and train our model on this dataset. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that BioD2C achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance across multiple downstream datasets, showcasing its robustness, generalizability, and potential to advance biomedical VQA research.
Adaptive H&E-IHC information fusion staining framework based on feature extra
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining plays a significant role in the evaluation of diseases such as breast cancer. The H&E-to-IHC transformation based on generative models provides a simple and cost-effective method for obtaining IHC images. Although previous models can perform digital coloring well, they still suffer from (i) coloring only through the pixel features that are not prominent in HE, which is easy to cause information loss in the coloring process; (ii) The lack of pixel-perfect H&E-IHC groundtruth pairs poses a challenge to the classical L1 loss.To address the above challenges, we propose an adaptive information enhanced coloring framework based on feature extractors. We first propose the VMFE module to effectively extract the color information features using multi-scale feature extraction and wavelet transform convolution, while combining the shared decoder for feature fusion. The high-performance dual feature extractor of H&E-IHC is trained by contrastive learning, which can effectively perform feature alignment of HE-IHC in high latitude space. At the same time, the trained feature encoder is used to enhance the features and adaptively adjust the loss in the HE section staining process to solve the problems related to unclear and asymmetric information. We have tested on different datasets and achieved excellent performance.Our code is available at https://github.com/babyinsunshine/CEFF
Ethereum Fraud Detection via Joint Transaction Language Model and Graph Representation Learning
Sep 09, 2024Abstract:Ethereum faces growing fraud threats. Current fraud detection methods, whether employing graph neural networks or sequence models, fail to consider the semantic information and similarity patterns within transactions. Moreover, these approaches do not leverage the potential synergistic benefits of combining both types of models. To address these challenges, we propose TLMG4Eth that combines a transaction language model with graph-based methods to capture semantic, similarity, and structural features of transaction data in Ethereum. We first propose a transaction language model that converts numerical transaction data into meaningful transaction sentences, enabling the model to learn explicit transaction semantics. Then, we propose a transaction attribute similarity graph to learn transaction similarity information, enabling us to capture intuitive insights into transaction anomalies. Additionally, we construct an account interaction graph to capture the structural information of the account transaction network. We employ a deep multi-head attention network to fuse transaction semantic and similarity embeddings, and ultimately propose a joint training approach for the multi-head attention network and the account interaction graph to obtain the synergistic benefits of both.
Adversarial Attacks and Mitigation for Anomaly Detectors of Cyber-Physical Systems
May 22, 2021
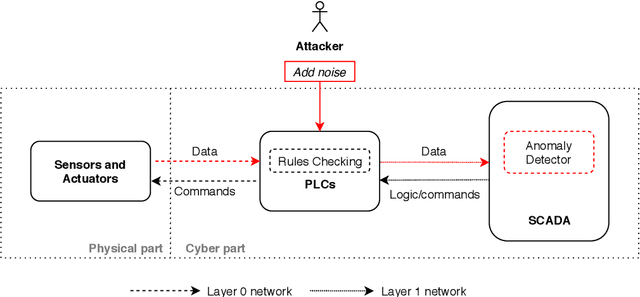
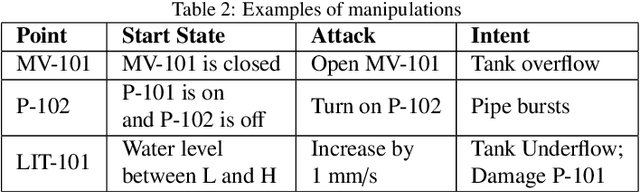
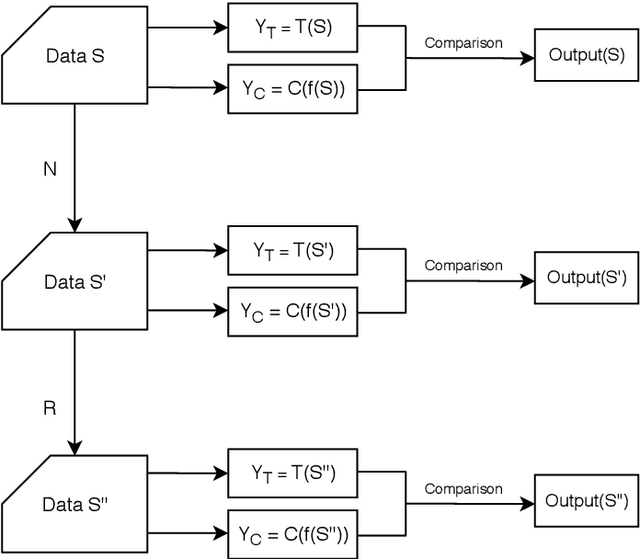
Abstract:The threats faced by cyber-physical systems (CPSs) in critical infrastructure have motivated research into a multitude of attack detection mechanisms, including anomaly detectors based on neural network models. The effectiveness of anomaly detectors can be assessed by subjecting them to test suites of attacks, but less consideration has been given to adversarial attackers that craft noise specifically designed to deceive them. While successfully applied in domains such as images and audio, adversarial attacks are much harder to implement in CPSs due to the presence of other built-in defence mechanisms such as rule checkers(or invariant checkers). In this work, we present an adversarial attack that simultaneously evades the anomaly detectors and rule checkers of a CPS. Inspired by existing gradient-based approaches, our adversarial attack crafts noise over the sensor and actuator values, then uses a genetic algorithm to optimise the latter, ensuring that the neural network and the rule checking system are both deceived.We implemented our approach for two real-world critical infrastructure testbeds, successfully reducing the classification accuracy of their detectors by over 50% on average, while simultaneously avoiding detection by rule checkers. Finally, we explore whether these attacks can be mitigated by training the detectors on adversarial samples.
Toward `verifying' a Water Treatment System
May 10, 2018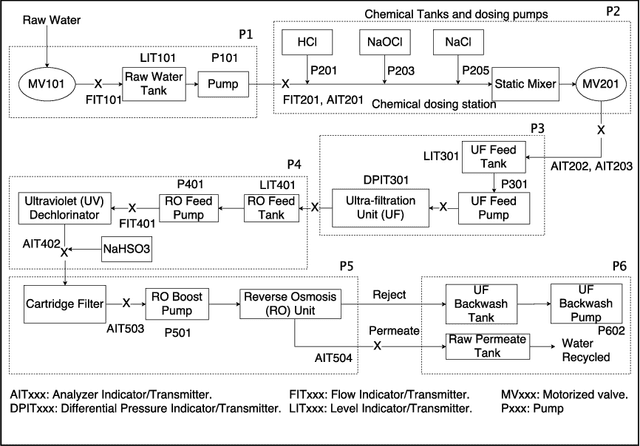
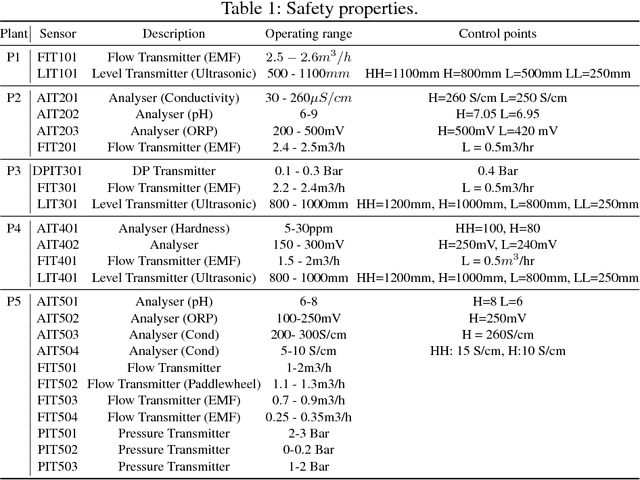
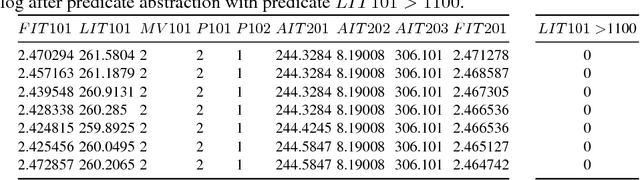
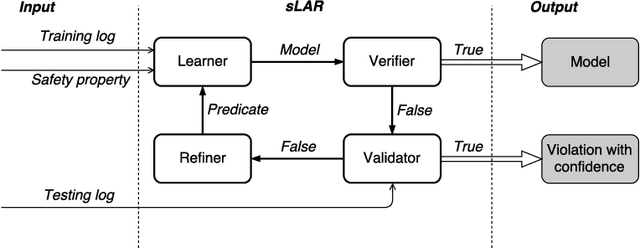
Abstract:Modeling and verifying real-world cyber-physical systems is challenging, which is especially so for complex systems where manually modeling is infeasible. In this work, we report our experience on combining model learning and abstraction refinement to analyze a challenging system, i.e., a real-world Secure Water Treatment system (SWaT). Given a set of safety requirements, the objective is to either show that the system is safe with a high probability (so that a system shutdown is rarely triggered due to safety violation) or not. As the system is too complicated to be manually modeled, we apply latest automatic model learning techniques to construct a set of Markov chains through abstraction and refinement, based on two long system execution logs (one for training and the other for testing). For each probabilistic safety property, we either report it does not hold with a certain level of probabilistic confidence, or report that it holds by showing the evidence in the form of an abstract Markov chain. The Markov chains can subsequently be implemented as runtime monitors in SWaT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge