Zhang Sheng
Dynamic Feature Fusion: Combining Global Graph Structures and Local Semantics for Blockchain Fraud Detection
Jan 03, 2025Abstract:The advent of blockchain technology has facilitated the widespread adoption of smart contracts in the financial sector. However, current fraud detection methodologies exhibit limitations in capturing both global structural patterns within transaction networks and local semantic relationships embedded in transaction data. Most existing models focus on either structural information or semantic features individually, leading to suboptimal performance in detecting complex fraud patterns.In this paper, we propose a dynamic feature fusion model that combines graph-based representation learning and semantic feature extraction for blockchain fraud detection. Specifically, we construct global graph representations to model account relationships and extract local contextual features from transaction data. A dynamic multimodal fusion mechanism is introduced to adaptively integrate these features, enabling the model to capture both structural and semantic fraud patterns effectively. We further develop a comprehensive data processing pipeline, including graph construction, temporal feature enhancement, and text preprocessing. Experimental results on large-scale real-world blockchain datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing benchmarks across accuracy, F1 score, and recall metrics. This work highlights the importance of integrating structural relationships and semantic similarities for robust fraud detection and offers a scalable solution for securing blockchain systems.
Ethereum Fraud Detection via Joint Transaction Language Model and Graph Representation Learning
Sep 09, 2024Abstract:Ethereum faces growing fraud threats. Current fraud detection methods, whether employing graph neural networks or sequence models, fail to consider the semantic information and similarity patterns within transactions. Moreover, these approaches do not leverage the potential synergistic benefits of combining both types of models. To address these challenges, we propose TLMG4Eth that combines a transaction language model with graph-based methods to capture semantic, similarity, and structural features of transaction data in Ethereum. We first propose a transaction language model that converts numerical transaction data into meaningful transaction sentences, enabling the model to learn explicit transaction semantics. Then, we propose a transaction attribute similarity graph to learn transaction similarity information, enabling us to capture intuitive insights into transaction anomalies. Additionally, we construct an account interaction graph to capture the structural information of the account transaction network. We employ a deep multi-head attention network to fuse transaction semantic and similarity embeddings, and ultimately propose a joint training approach for the multi-head attention network and the account interaction graph to obtain the synergistic benefits of both.
Detecting Curve Text in the Wild: New Dataset and New Solution
Dec 06, 2017

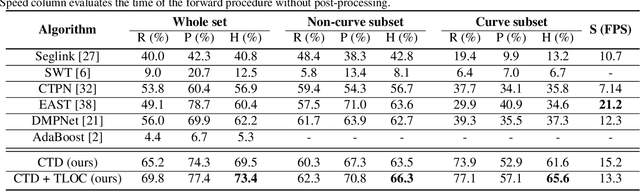
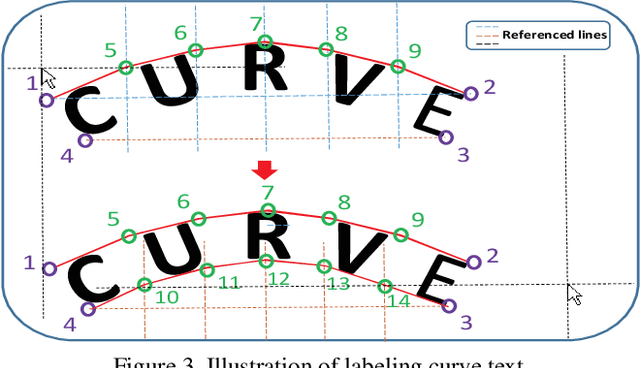
Abstract:Scene text detection has been made great progress in recent years. The detection manners are evolving from axis-aligned rectangle to rotated rectangle and further to quadrangle. However, current datasets contain very little curve text, which can be widely observed in scene images such as signboard, product name and so on. To raise the concerns of reading curve text in the wild, in this paper, we construct a curve text dataset named CTW1500, which includes over 10k text annotations in 1,500 images (1000 for training and 500 for testing). Based on this dataset, we pioneering propose a polygon based curve text detector (CTD) which can directly detect curve text without empirical combination. Moreover, by seamlessly integrating the recurrent transverse and longitudinal offset connection (TLOC), the proposed method can be end-to-end trainable to learn the inherent connection among the position offsets. This allows the CTD to explore context information instead of predicting points independently, resulting in more smooth and accurate detection. We also propose two simple but effective post-processing methods named non-polygon suppress (NPS) and polygonal non-maximum suppression (PNMS) to further improve the detection accuracy. Furthermore, the proposed approach in this paper is designed in an universal manner, which can also be trained with rectangular or quadrilateral bounding boxes without extra efforts. Experimental results on CTW-1500 demonstrate our method with only a light backbone can outperform state-of-the-art methods with a large margin. By evaluating only in the curve or non-curve subset, the CTD + TLOC can still achieve the best results. Code is available at https://github.com/Yuliang-Liu/Curve-Text-Detector.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge