Minghui Li
UnlearnShield: Shielding Forgotten Privacy against Unlearning Inversion
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Machine unlearning is an emerging technique that aims to remove the influence of specific data from trained models, thereby enhancing privacy protection. However, recent research has uncovered critical privacy vulnerabilities, showing that adversaries can exploit unlearning inversion to reconstruct data that was intended to be erased. Despite the severity of this threat, dedicated defenses remain lacking. To address this gap, we propose UnlearnShield, the first defense specifically tailored to counter unlearning inversion. UnlearnShield introduces directional perturbations in the cosine representation space and regulates them through a constraint module to jointly preserve model accuracy and forgetting efficacy, thereby reducing inversion risk while maintaining utility. Experiments demonstrate that it achieves a good trade-off among privacy protection, accuracy, and forgetting.
Erosion Attack for Adversarial Training to Enhance Semantic Segmentation Robustness
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Existing segmentation models exhibit significant vulnerability to adversarial attacks.To improve robustness, adversarial training incorporates adversarial examples into model training. However, existing attack methods consider only global semantic information and ignore contextual semantic relationships within the samples, limiting the effectiveness of adversarial training. To address this issue, we propose EroSeg-AT, a vulnerability-aware adversarial training framework that leverages EroSeg to generate adversarial examples. EroSeg first selects sensitive pixels based on pixel-level confidence and then progressively propagates perturbations to higher-confidence pixels, effectively disrupting the semantic consistency of the samples. Experimental results show that, compared to existing methods, our approach significantly improves attack effectiveness and enhances model robustness under adversarial training.
Dual-View Inference Attack: Machine Unlearning Amplifies Privacy Exposure
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Machine unlearning is a newly popularized technique for removing specific training data from a trained model, enabling it to comply with data deletion requests. While it protects the rights of users requesting unlearning, it also introduces new privacy risks. Prior works have primarily focused on the privacy of data that has been unlearned, while the risks to retained data remain largely unexplored. To address this gap, we focus on the privacy risks of retained data and, for the first time, reveal the vulnerabilities introduced by machine unlearning under the dual-view setting, where an adversary can query both the original and the unlearned models. From an information-theoretic perspective, we introduce the concept of {privacy knowledge gain} and demonstrate that the dual-view setting allows adversaries to obtain more information than querying either model alone, thereby amplifying privacy leakage. To effectively demonstrate this threat, we propose DVIA, a Dual-View Inference Attack, which extracts membership information on retained data using black-box queries to both models. DVIA eliminates the need to train an attack model and employs a lightweight likelihood ratio inference module for efficient inference. Experiments across different datasets and model architectures validate the effectiveness of DVIA and highlight the privacy risks inherent in the dual-view setting.
UFVideo: Towards Unified Fine-Grained Video Cooperative Understanding with Large Language Models
Dec 12, 2025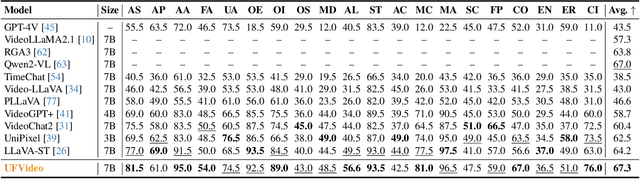
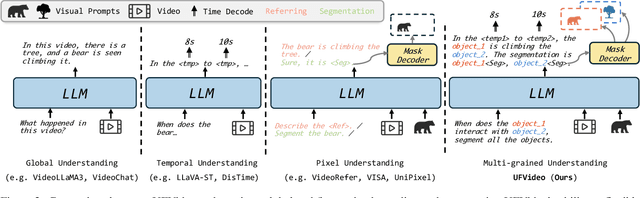
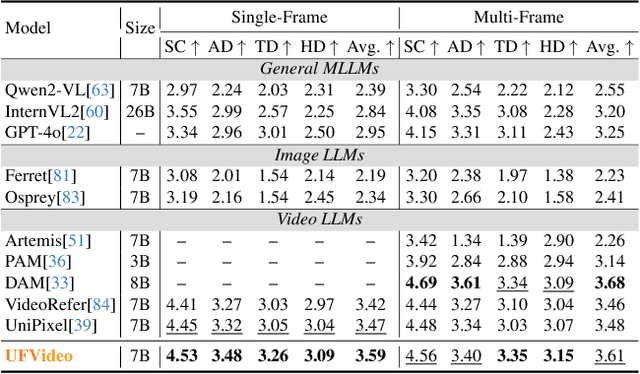
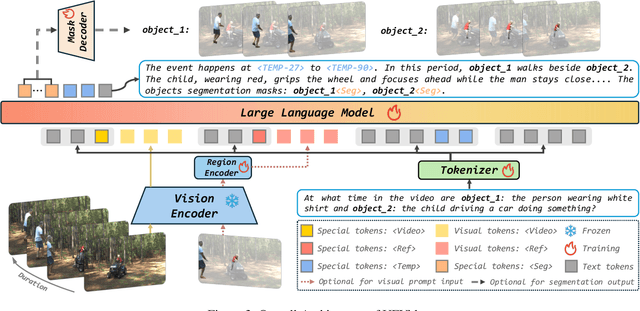
Abstract:With the advancement of multi-modal Large Language Models (LLMs), Video LLMs have been further developed to perform on holistic and specialized video understanding. However, existing works are limited to specialized video understanding tasks, failing to achieve a comprehensive and multi-grained video perception. To bridge this gap, we introduce UFVideo, the first Video LLM with unified multi-grained cooperative understanding capabilities. Specifically, we design unified visual-language guided alignment to flexibly handle video understanding across global, pixel and temporal scales within a single model. UFVideo dynamically encodes the visual and text inputs of different tasks and generates the textual response, temporal localization, or grounded mask. Additionally, to evaluate challenging multi-grained video understanding tasks, we construct the UFVideo-Bench consisting of three distinct collaborative tasks within the scales, which demonstrates UFVideo's flexibility and advantages over GPT-4o. Furthermore, we validate the effectiveness of our model across 9 public benchmarks covering various common video understanding tasks, providing valuable insights for future Video LLMs.
HiF-DTA: Hierarchical Feature Learning Network for Drug-Target Affinity Prediction
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Accurate prediction of Drug-Target Affinity (DTA) is crucial for reducing experimental costs and accelerating early screening in computational drug discovery. While sequence-based deep learning methods avoid reliance on costly 3D structures, they still overlook simultaneous modeling of global sequence semantic features and local topological structural features within drugs and proteins, and represent drugs as flat sequences without atomic-level, substructural-level, and molecular-level multi-scale features. We propose HiF-DTA, a hierarchical network that adopts a dual-pathway strategy to extract both global sequence semantic and local topological features from drug and protein sequences, and models drugs multi-scale to learn atomic, substructural, and molecular representations fused via a multi-scale bilinear attention module. Experiments on Davis, KIBA, and Metz datasets show HiF-DTA outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, with ablations confirming the importance of global-local extraction and multi-scale fusion.
Towards Real-World Deepfake Detection: A Diverse In-the-wild Dataset of Forgery Faces
Oct 09, 2025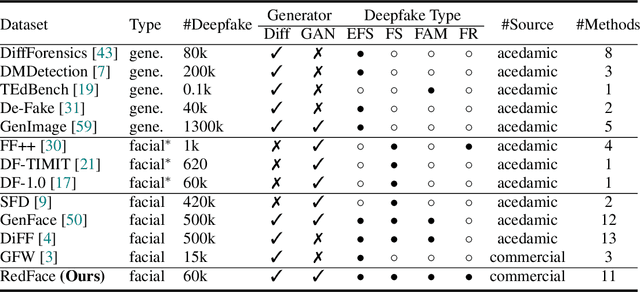

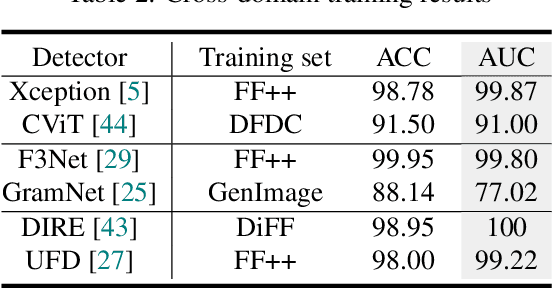
Abstract:Deepfakes, leveraging advanced AIGC (Artificial Intelligence-Generated Content) techniques, create hyper-realistic synthetic images and videos of human faces, posing a significant threat to the authenticity of social media. While this real-world threat is increasingly prevalent, existing academic evaluations and benchmarks for detecting deepfake forgery often fall short to achieve effective application for their lack of specificity, limited deepfake diversity, restricted manipulation techniques.To address these limitations, we introduce RedFace (Real-world-oriented Deepfake Face), a specialized facial deepfake dataset, comprising over 60,000 forged images and 1,000 manipulated videos derived from authentic facial features, to bridge the gap between academic evaluations and real-world necessity. Unlike prior benchmarks, which typically rely on academic methods to generate deepfakes, RedFace utilizes 9 commercial online platforms to integrate the latest deepfake technologies found "in the wild", effectively simulating real-world black-box scenarios.Moreover, RedFace's deepfakes are synthesized using bespoke algorithms, allowing it to capture diverse and evolving methods used by real-world deepfake creators. Extensive experimental results on RedFace (including cross-domain, intra-domain, and real-world social network dissemination simulations) verify the limited practicality of existing deepfake detection schemes against real-world applications. We further perform a detailed analysis of the RedFace dataset, elucidating the reason of its impact on detection performance compared to conventional datasets. Our dataset is available at: https://github.com/kikyou-220/RedFace.
Transferable Direct Prompt Injection via Activation-Guided MCMC Sampling
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Direct Prompt Injection (DPI) attacks pose a critical security threat to Large Language Models (LLMs) due to their low barrier of execution and high potential damage. To address the impracticality of existing white-box/gray-box methods and the poor transferability of black-box methods, we propose an activations-guided prompt injection attack framework. We first construct an Energy-based Model (EBM) using activations from a surrogate model to evaluate the quality of adversarial prompts. Guided by the trained EBM, we employ the token-level Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling to adaptively optimize adversarial prompts, thereby enabling gradient-free black-box attacks. Experimental results demonstrate our superior cross-model transferability, achieving 49.6% attack success rate (ASR) across five mainstream LLMs and 34.6% improvement over human-crafted prompts, and maintaining 36.6% ASR on unseen task scenarios. Interpretability analysis reveals a correlation between activations and attack effectiveness, highlighting the critical role of semantic patterns in transferable vulnerability exploitation.
Towards Reliable Forgetting: A Survey on Machine Unlearning Verification, Challenges, and Future Directions
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:With growing demands for privacy protection, security, and legal compliance (e.g., GDPR), machine unlearning has emerged as a critical technique for ensuring the controllability and regulatory alignment of machine learning models. However, a fundamental challenge in this field lies in effectively verifying whether unlearning operations have been successfully and thoroughly executed. Despite a growing body of work on unlearning techniques, verification methodologies remain comparatively underexplored and often fragmented. Existing approaches lack a unified taxonomy and a systematic framework for evaluation. To bridge this gap, this paper presents the first structured survey of machine unlearning verification methods. We propose a taxonomy that organizes current techniques into two principal categories -- behavioral verification and parametric verification -- based on the type of evidence used to assess unlearning fidelity. We examine representative methods within each category, analyze their underlying assumptions, strengths, and limitations, and identify potential vulnerabilities in practical deployment. In closing, we articulate a set of open problems in current verification research, aiming to provide a foundation for developing more robust, efficient, and theoretically grounded unlearning verification mechanisms.
Astra: Toward General-Purpose Mobile Robots via Hierarchical Multimodal Learning
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Modern robot navigation systems encounter difficulties in diverse and complex indoor environments. Traditional approaches rely on multiple modules with small models or rule-based systems and thus lack adaptability to new environments. To address this, we developed Astra, a comprehensive dual-model architecture, Astra-Global and Astra-Local, for mobile robot navigation. Astra-Global, a multimodal LLM, processes vision and language inputs to perform self and goal localization using a hybrid topological-semantic graph as the global map, and outperforms traditional visual place recognition methods. Astra-Local, a multitask network, handles local path planning and odometry estimation. Its 4D spatial-temporal encoder, trained through self-supervised learning, generates robust 4D features for downstream tasks. The planning head utilizes flow matching and a novel masked ESDF loss to minimize collision risks for generating local trajectories, and the odometry head integrates multi-sensor inputs via a transformer encoder to predict the relative pose of the robot. Deployed on real in-house mobile robots, Astra achieves high end-to-end mission success rate across diverse indoor environments.
Secure Transfer Learning: Training Clean Models Against Backdoor in (Both) Pre-trained Encoders and Downstream Datasets
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Transfer learning from pre-trained encoders has become essential in modern machine learning, enabling efficient model adaptation across diverse tasks. However, this combination of pre-training and downstream adaptation creates an expanded attack surface, exposing models to sophisticated backdoor embeddings at both the encoder and dataset levels--an area often overlooked in prior research. Additionally, the limited computational resources typically available to users of pre-trained encoders constrain the effectiveness of generic backdoor defenses compared to end-to-end training from scratch. In this work, we investigate how to mitigate potential backdoor risks in resource-constrained transfer learning scenarios. Specifically, we conduct an exhaustive analysis of existing defense strategies, revealing that many follow a reactive workflow based on assumptions that do not scale to unknown threats, novel attack types, or different training paradigms. In response, we introduce a proactive mindset focused on identifying clean elements and propose the Trusted Core (T-Core) Bootstrapping framework, which emphasizes the importance of pinpointing trustworthy data and neurons to enhance model security. Our empirical evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of T-Core, specifically assessing 5 encoder poisoning attacks, 7 dataset poisoning attacks, and 14 baseline defenses across five benchmark datasets, addressing four scenarios of 3 potential backdoor threats.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge