Shulin He
Room Impulse Response as a Prompt for Acoustic Echo Cancellation
May 26, 2025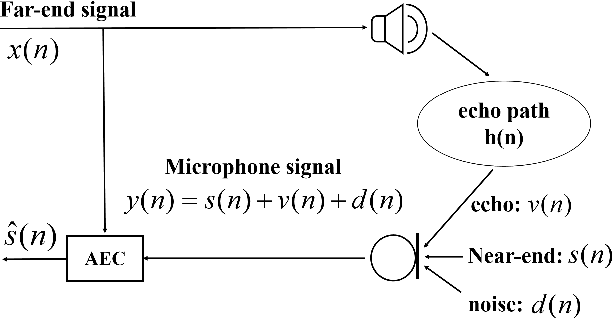
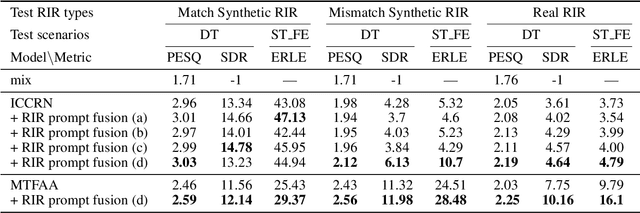
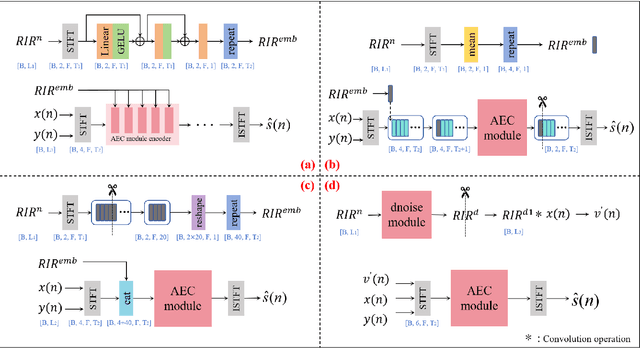
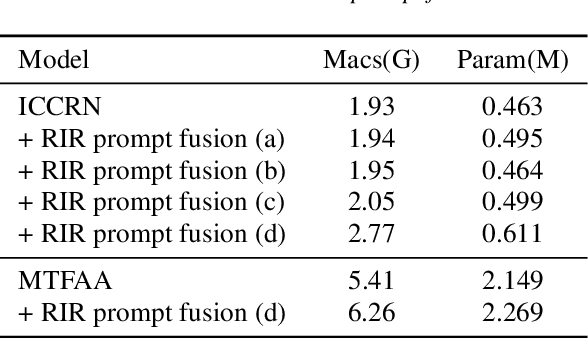
Abstract:Data-driven acoustic echo cancellation (AEC) methods, predominantly trained on synthetic or constrained real-world datasets, encounter performance declines in unseen echo scenarios, especially in real environments where echo paths are not directly observable. Our proposed method counters this limitation by integrating room impulse response (RIR) as a pivotal training prompt, aiming to improve the generalization of AEC models in such unforeseen conditions. We also explore four RIR prompt fusion methods. Comprehensive evaluations, including both simulated RIR under unknown conditions and recorded RIR in real, demonstrate that the proposed approach significantly improves performance compared to baseline models. These results substantiate the effectiveness of our RIR-guided approach in strengthening the model's generalization capabilities.
Listen to Extract: Onset-Prompted Target Speaker Extraction
May 08, 2025



Abstract:We propose $\textit{listen to extract}$ (LExt), a highly-effective while extremely-simple algorithm for monaural target speaker extraction (TSE). Given an enrollment utterance of a target speaker, LExt aims at extracting the target speaker from the speaker's mixed speech with other speakers. For each mixture, LExt concatenates an enrollment utterance of the target speaker to the mixture signal at the waveform level, and trains deep neural networks (DNN) to extract the target speech based on the concatenated mixture signal. The rationale is that, this way, an artificial speech onset is created for the target speaker and it could prompt the DNN (a) which speaker is the target to extract; and (b) spectral-temporal patterns of the target speaker that could help extraction. This simple approach produces strong TSE performance on multiple public TSE datasets including WSJ0-2mix, WHAM! and WHAMR!.
Robust Target Speaker Direction of Arrival Estimation
Dec 25, 2024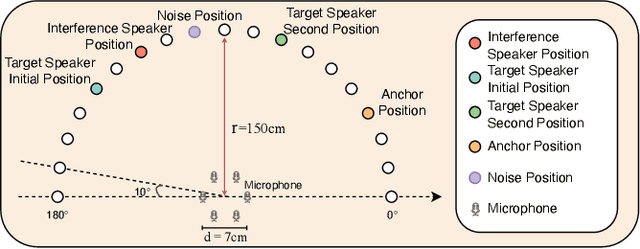
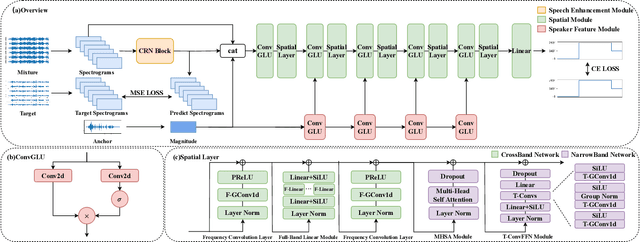
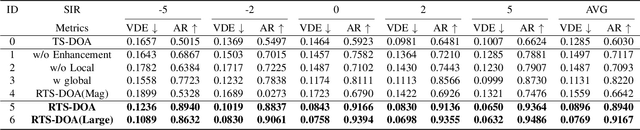
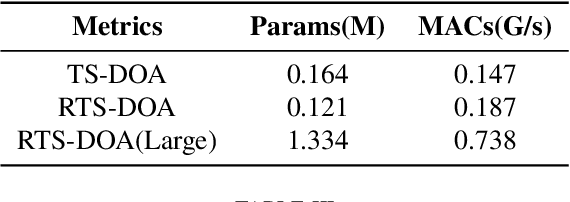
Abstract:In multi-speaker environments the direction of arrival (DOA) of a target speaker is key for improving speech clarity and extracting target speaker's voice. However, traditional DOA estimation methods often struggle in the presence of noise, reverberation, and particularly when competing speakers are present. To address these challenges, we propose RTS-DOA, a robust real-time DOA estimation system. This system innovatively uses the registered speech of the target speaker as a reference and leverages full-band and sub-band spectral information from a microphone array to estimate the DOA of the target speaker's voice. Specifically, the system comprises a speech enhancement module for initially improving speech quality, a spatial module for learning spatial information, and a speaker module for extracting voiceprint features. Experimental results on the LibriSpeech dataset demonstrate that our RTS-DOA system effectively tackles multi-speaker scenarios and established new optimal benchmarks.
FlashSpeech: Efficient Zero-Shot Speech Synthesis
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:Recent progress in large-scale zero-shot speech synthesis has been significantly advanced by language models and diffusion models. However, the generation process of both methods is slow and computationally intensive. Efficient speech synthesis using a lower computing budget to achieve quality on par with previous work remains a significant challenge. In this paper, we present FlashSpeech, a large-scale zero-shot speech synthesis system with approximately 5\% of the inference time compared with previous work. FlashSpeech is built on the latent consistency model and applies a novel adversarial consistency training approach that can train from scratch without the need for a pre-trained diffusion model as the teacher. Furthermore, a new prosody generator module enhances the diversity of prosody, making the rhythm of the speech sound more natural. The generation processes of FlashSpeech can be achieved efficiently with one or two sampling steps while maintaining high audio quality and high similarity to the audio prompt for zero-shot speech generation. Our experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of FlashSpeech. Notably, FlashSpeech can be about 20 times faster than other zero-shot speech synthesis systems while maintaining comparable performance in terms of voice quality and similarity. Furthermore, FlashSpeech demonstrates its versatility by efficiently performing tasks like voice conversion, speech editing, and diverse speech sampling. Audio samples can be found in https://flashspeech.github.io/.
SICRN: Advancing Speech Enhancement through State Space Model and Inplace Convolution Techniques
Feb 22, 2024Abstract:Speech enhancement aims to improve speech quality and intelligibility, especially in noisy environments where background noise degrades speech signals. Currently, deep learning methods achieve great success in speech enhancement, e.g. the representative convolutional recurrent neural network (CRN) and its variants. However, CRN typically employs consecutive downsampling and upsampling convolution for frequency modeling, which destroys the inherent structure of the signal over frequency. Additionally, convolutional layers lacks of temporal modelling abilities. To address these issues, we propose an innovative module combing a State space model and Inplace Convolution (SIC), and to replace the conventional convolution in CRN, called SICRN. Specifically, a dual-path multidimensional State space model captures the global frequencies dependency and long-term temporal dependencies. Meanwhile, the 2D-inplace convolution is used to capture the local structure, which abandons the downsampling and upsampling. Systematic evaluations on the public INTERSPEECH 2020 DNS challenge dataset demonstrate SICRN's efficacy. Compared to strong baselines, SICRN achieves performance close to state-of-the-art while having advantages in model parameters, computations, and algorithmic delay. The proposed SICRN shows great promise for improved speech enhancement.
3S-TSE: Efficient Three-Stage Target Speaker Extraction for Real-Time and Low-Resource Applications
Dec 18, 2023



Abstract:Target speaker extraction (TSE) aims to isolate a specific voice from multiple mixed speakers relying on a registerd sample. Since voiceprint features usually vary greatly, current end-to-end neural networks require large model parameters which are computational intensive and impractical for real-time applications, espetially on resource-constrained platforms. In this paper, we address the TSE task using microphone array and introduce a novel three-stage solution that systematically decouples the process: First, a neural network is trained to estimate the direction of the target speaker. Second, with the direction determined, the Generalized Sidelobe Canceller (GSC) is used to extract the target speech. Third, an Inplace Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network (ICRN) acts as a denoising post-processor, refining the GSC output to yield the final separated speech. Our approach delivers superior performance while drastically reducing computational load, setting a new standard for efficient real-time target speaker extraction.
Hierarchical Modeling of Spatial Cues via Spherical Harmonics for Multi-Channel Speech Enhancement
Sep 19, 2023



Abstract:Multi-channel speech enhancement utilizes spatial information from multiple microphones to extract the target speech. However, most existing methods do not explicitly model spatial cues, instead relying on implicit learning from multi-channel spectra. To better leverage spatial information, we propose explicitly incorporating spatial modeling by applying spherical harmonic transforms (SHT) to the multi-channel input. In detail, a hierarchical framework is introduced whereby lower order harmonics capturing broader spatial patterns are estimated first, then combined with higher orders to recursively predict finer spatial details. Experiments on TIMIT demonstrate the proposed method can effectively recover target spatial patterns and achieve improved performance over baseline models, using fewer parameters and computations. Explicitly modeling spatial information hierarchically enables more effective multi-channel speech enhancement.
PDPCRN: Parallel Dual-Path CRN with Bi-directional Inter-Branch Interactions for Multi-Channel Speech Enhancement
Sep 19, 2023



Abstract:Multi-channel speech enhancement seeks to utilize spatial information to distinguish target speech from interfering signals. While deep learning approaches like the dual-path convolutional recurrent network (DPCRN) have made strides, challenges persist in effectively modeling inter-channel correlations and amalgamating multi-level information. In response, we introduce the Parallel Dual-Path Convolutional Recurrent Network (PDPCRN). This acoustic modeling architecture has two key innovations. First, a parallel design with separate branches extracts complementary features. Second, bi-directional modules enable cross-branch communication. Together, these facilitate diverse representation fusion and enhanced modeling. Experimental validation on TIMIT datasets underscores the prowess of PDPCRN. Notably, against baseline models like the standard DPCRN, PDPCRN not only outperforms in PESQ and STOI metrics but also boasts a leaner computational footprint with reduced parameters.
MC-SpEx: Towards Effective Speaker Extraction with Multi-Scale Interfusion and Conditional Speaker Modulation
Jun 28, 2023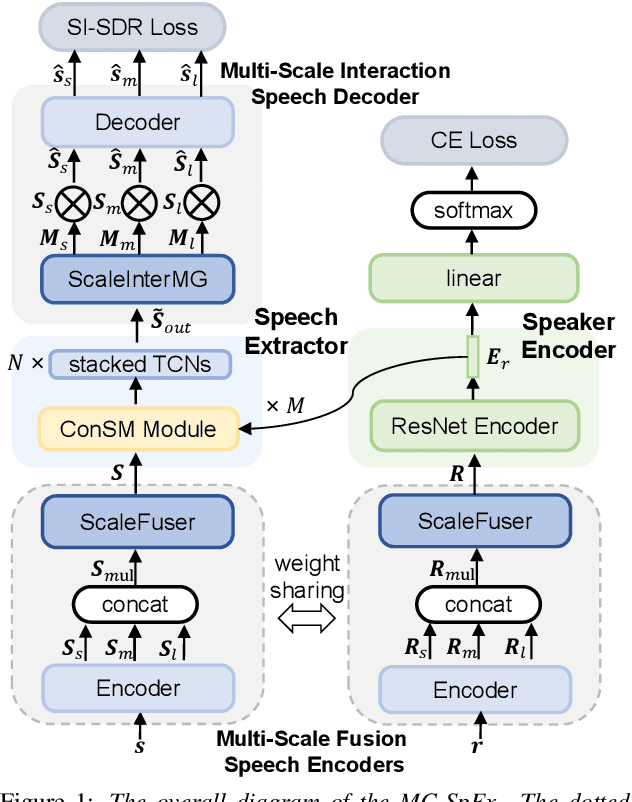

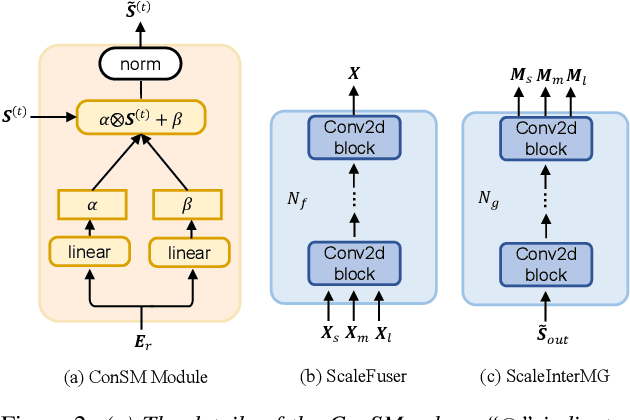

Abstract:The previous SpEx+ has yielded outstanding performance in speaker extraction and attracted much attention. However, it still encounters inadequate utilization of multi-scale information and speaker embedding. To this end, this paper proposes a new effective speaker extraction system with multi-scale interfusion and conditional speaker modulation (ConSM), which is called MC-SpEx. First of all, we design the weight-share multi-scale fusers (ScaleFusers) for efficiently leveraging multi-scale information as well as ensuring consistency of the model's feature space. Then, to consider different scale information while generating masks, the multi-scale interactive mask generator (ScaleInterMG) is presented. Moreover, we introduce ConSM module to fully exploit speaker embedding in the speech extractor. Experimental results on the Libri2Mix dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our improvements and the state-of-the-art performance of our proposed MC-SpEx.
Gesper: A Restoration-Enhancement Framework for General Speech Reconstruction
Jun 14, 2023Abstract:This paper describes a real-time General Speech Reconstruction (Gesper) system submitted to the ICASSP 2023 Speech Signal Improvement (SSI) Challenge. This novel proposed system is a two-stage architecture, in which the speech restoration is performed, and then cascaded by speech enhancement. We propose a complex spectral mapping-based generative adversarial network (CSM-GAN) as the speech restoration module for the first time. For noise suppression and dereverberation, the enhancement module is performed with fullband-wideband parallel processing. On the blind test set of ICASSP 2023 SSI Challenge, the proposed Gesper system, which satisfies the real-time condition, achieves 3.27 P.804 overall mean opinion score (MOS) and 3.35 P.835 overall MOS, ranked 1st in both track 1 and track 2.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge