Jiuxin Lin
Focus on the Sound around You: Monaural Target Speaker Extraction via Distance and Speaker Information
Jun 28, 2023



Abstract:Previously, Target Speaker Extraction (TSE) has yielded outstanding performance in certain application scenarios for speech enhancement and source separation. However, obtaining auxiliary speaker-related information is still challenging in noisy environments with significant reverberation. inspired by the recently proposed distance-based sound separation, we propose the near sound (NS) extractor, which leverages distance information for TSE to reliably extract speaker information without requiring previous speaker enrolment, called speaker embedding self-enrollment (SESE). Full- & sub-band modeling is introduced to enhance our NS-Extractor's adaptability towards environments with significant reverberation. Experimental results on several cross-datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our improvements and the excellent performance of our proposed NS-Extractor in different application scenarios.
MC-SpEx: Towards Effective Speaker Extraction with Multi-Scale Interfusion and Conditional Speaker Modulation
Jun 28, 2023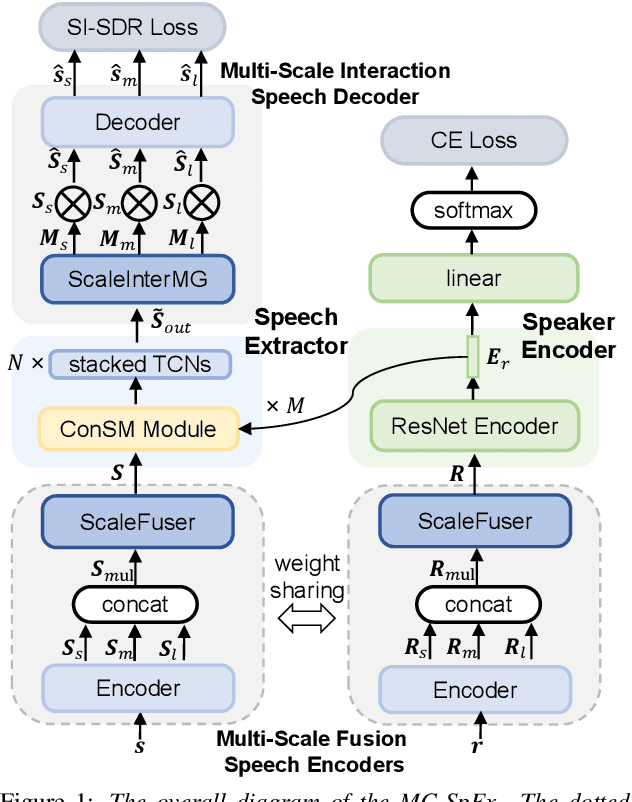

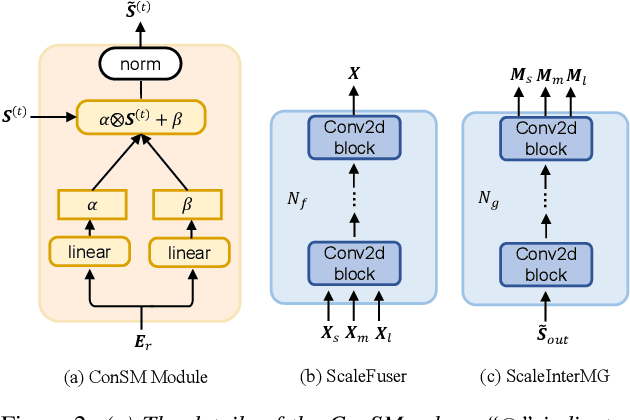

Abstract:The previous SpEx+ has yielded outstanding performance in speaker extraction and attracted much attention. However, it still encounters inadequate utilization of multi-scale information and speaker embedding. To this end, this paper proposes a new effective speaker extraction system with multi-scale interfusion and conditional speaker modulation (ConSM), which is called MC-SpEx. First of all, we design the weight-share multi-scale fusers (ScaleFusers) for efficiently leveraging multi-scale information as well as ensuring consistency of the model's feature space. Then, to consider different scale information while generating masks, the multi-scale interactive mask generator (ScaleInterMG) is presented. Moreover, we introduce ConSM module to fully exploit speaker embedding in the speech extractor. Experimental results on the Libri2Mix dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our improvements and the state-of-the-art performance of our proposed MC-SpEx.
AV-SepFormer: Cross-Attention SepFormer for Audio-Visual Target Speaker Extraction
Jun 25, 2023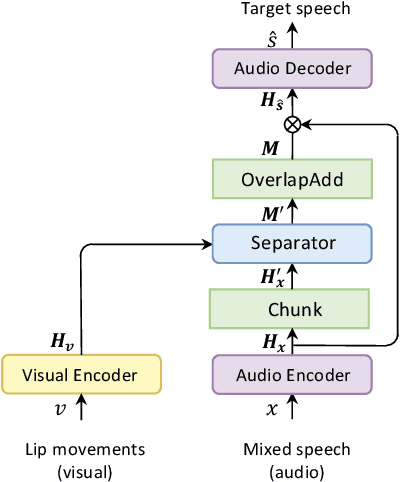



Abstract:Visual information can serve as an effective cue for target speaker extraction (TSE) and is vital to improving extraction performance. In this paper, we propose AV-SepFormer, a SepFormer-based attention dual-scale model that utilizes cross- and self-attention to fuse and model features from audio and visual. AV-SepFormer splits the audio feature into a number of chunks, equivalent to the length of the visual feature. Then self- and cross-attention are employed to model and fuse the multi-modal features. Furthermore, we use a novel 2D positional encoding, that introduces the positional information between and within chunks and provides significant gains over the traditional positional encoding. Our model has two key advantages: the time granularity of audio chunked feature is synchronized to the visual feature, which alleviates the harm caused by the inconsistency of audio and video sampling rate; by combining self- and cross-attention, feature fusion and speech extraction processes are unified within an attention paradigm. The experimental results show that AV-SepFormer significantly outperforms other existing methods.
Inter-SubNet: Speech Enhancement with Subband Interaction
May 09, 2023



Abstract:Subband-based approaches process subbands in parallel through the model with shared parameters to learn the commonality of local spectrums for noise reduction. In this way, they have achieved remarkable results with fewer parameters. However, in some complex environments, the lack of global spectral information has a negative impact on the performance of these subband-based approaches. To this end, this paper introduces the subband interaction as a new way to complement the subband model with the global spectral information such as cross-band dependencies and global spectral patterns, and proposes a new lightweight single-channel speech enhancement framework called Interactive Subband Network (Inter-SubNet). Experimental results on DNS Challenge - Interspeech 2021 dataset show that the proposed Inter-SubNet yields a significant improvement over the subband model and outperforms other state-of-the-art speech enhancement approaches, which demonstrate the effectiveness of subband interaction.
The ReprGesture entry to the GENEA Challenge 2022
Aug 25, 2022



Abstract:This paper describes the ReprGesture entry to the Generation and Evaluation of Non-verbal Behaviour for Embodied Agents (GENEA) challenge 2022. The GENEA challenge provides the processed datasets and performs crowdsourced evaluations to compare the performance of different gesture generation systems. In this paper, we explore an automatic gesture generation system based on multimodal representation learning. We use WavLM features for audio, FastText features for text and position and rotation matrix features for gesture. Each modality is projected to two distinct subspaces: modality-invariant and modality-specific. To learn inter-modality-invariant commonalities and capture the characters of modality-specific representations, gradient reversal layer based adversarial classifier and modality reconstruction decoders are used during training. The gesture decoder generates proper gestures using all representations and features related to the rhythm in the audio. Our code, pre-trained models and demo are available at https://github.com/YoungSeng/ReprGesture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge