Zhening Liu
Mon3tr: Monocular 3D Telepresence with Pre-built Gaussian Avatars as Amortization
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Immersive telepresence aims to transform human interaction in AR/VR applications by enabling lifelike full-body holographic representations for enhanced remote collaboration. However, existing systems rely on hardware-intensive multi-camera setups and demand high bandwidth for volumetric streaming, limiting their real-time performance on mobile devices. To overcome these challenges, we propose Mon3tr, a novel Monocular 3D telepresence framework that integrates 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) based parametric human modeling into telepresence for the first time. Mon3tr adopts an amortized computation strategy, dividing the process into a one-time offline multi-view reconstruction phase to build a user-specific avatar and a monocular online inference phase during live telepresence sessions. A single monocular RGB camera is used to capture body motions and facial expressions in real time to drive the 3DGS-based parametric human model, significantly reducing system complexity and cost. The extracted motion and appearance features are transmitted at < 0.2 Mbps over WebRTC's data channel, allowing robust adaptation to network fluctuations. On the receiver side, e.g., Meta Quest 3, we develop a lightweight 3DGS attribute deformation network to dynamically generate corrective 3DGS attribute adjustments on the pre-built avatar, synthesizing photorealistic motion and appearance at ~ 60 FPS. Extensive experiments demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of our method, achieving a PSNR of > 28 dB for novel poses, an end-to-end latency of ~ 80 ms, and > 1000x bandwidth reduction compared to point-cloud streaming, while supporting real-time operation from monocular inputs across diverse scenarios. Our demos can be found at https://mon3tr3d.github.io.
Spatia: Video Generation with Updatable Spatial Memory
Dec 17, 2025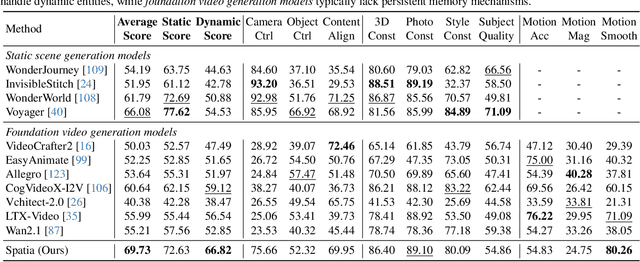
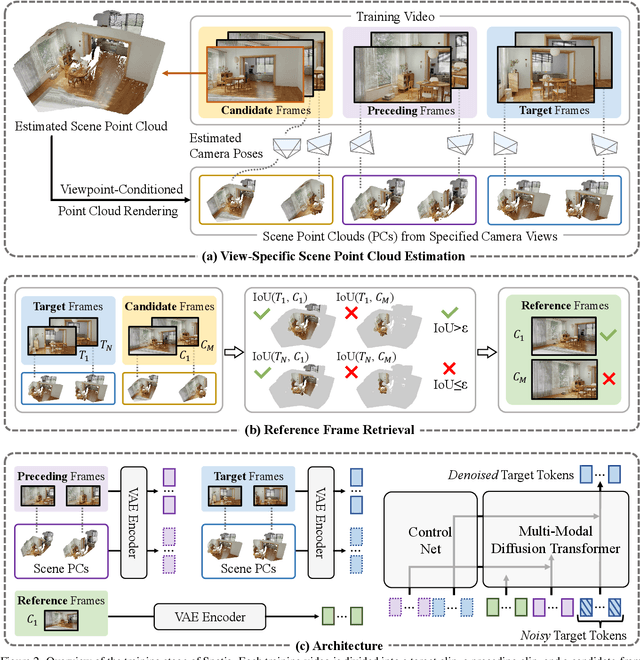

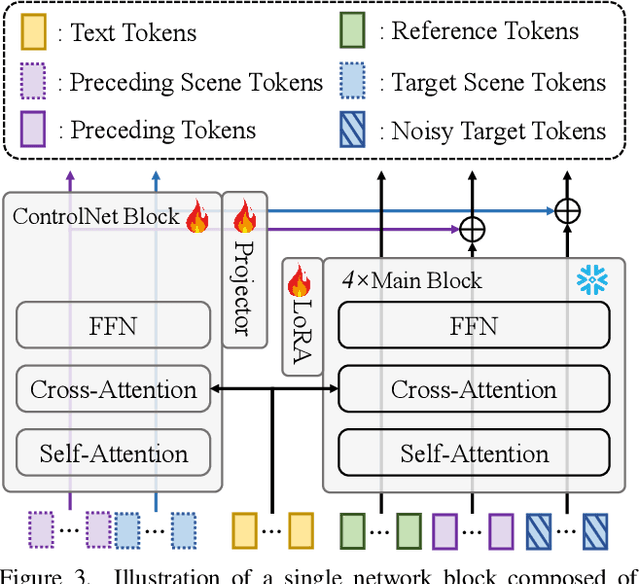
Abstract:Existing video generation models struggle to maintain long-term spatial and temporal consistency due to the dense, high-dimensional nature of video signals. To overcome this limitation, we propose Spatia, a spatial memory-aware video generation framework that explicitly preserves a 3D scene point cloud as persistent spatial memory. Spatia iteratively generates video clips conditioned on this spatial memory and continuously updates it through visual SLAM. This dynamic-static disentanglement design enhances spatial consistency throughout the generation process while preserving the model's ability to produce realistic dynamic entities. Furthermore, Spatia enables applications such as explicit camera control and 3D-aware interactive editing, providing a geometrically grounded framework for scalable, memory-driven video generation.
Task-Oriented Feature Compression for Multimodal Understanding via Device-Edge Co-Inference
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:With the rapid development of large multimodal models (LMMs), multimodal understanding applications are emerging. As most LMM inference requests originate from edge devices with limited computational capabilities, the predominant inference pipeline involves directly forwarding the input data to an edge server which handles all computations. However, this approach introduces high transmission latency due to limited uplink bandwidth of edge devices and significant computation latency caused by the prohibitive number of visual tokens, thus hindering delay-sensitive tasks and degrading user experience. To address this challenge, we propose a task-oriented feature compression (TOFC) method for multimodal understanding in a device-edge co-inference framework, where visual features are merged by clustering and encoded by a learnable and selective entropy model before feature projection. Specifically, we employ density peaks clustering based on K nearest neighbors to reduce the number of visual features, thereby minimizing both data transmission and computational complexity. Subsequently, a learnable entropy model with hyperprior is utilized to encode and decode merged features, further reducing transmission overhead. To enhance compression efficiency, multiple entropy models are adaptively selected based on the characteristics of the visual features, enabling a more accurate estimation of the probability distribution. Comprehensive experiments on seven visual question answering benchmarks validate the effectiveness of the proposed TOFC method. Results show that TOFC achieves up to 60% reduction in data transmission overhead and 50% reduction in system latency while maintaining identical task performance, compared with traditional image compression methods.
Dynamics-Aware Gaussian Splatting Streaming Towards Fast On-the-Fly Training for 4D Reconstruction
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:The recent development of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has led to great interest in 4D dynamic spatial reconstruction from multi-view visual inputs. While existing approaches mainly rely on processing full-length multi-view videos for 4D reconstruction, there has been limited exploration of iterative online reconstruction methods that enable on-the-fly training and per-frame streaming. Current 3DGS-based streaming methods treat the Gaussian primitives uniformly and constantly renew the densified Gaussians, thereby overlooking the difference between dynamic and static features and also neglecting the temporal continuity in the scene. To address these limitations, we propose a novel three-stage pipeline for iterative streamable 4D dynamic spatial reconstruction. Our pipeline comprises a selective inheritance stage to preserve temporal continuity, a dynamics-aware shift stage for distinguishing dynamic and static primitives and optimizing their movements, and an error-guided densification stage to accommodate emerging objects. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in online 4D reconstruction, demonstrating a 20% improvement in on-the-fly training speed, superior representation quality, and real-time rendering capability. Project page: https://www.liuzhening.top/DASS
MEGA: Memory-Efficient 4D Gaussian Splatting for Dynamic Scenes
Oct 17, 2024Abstract:4D Gaussian Splatting (4DGS) has recently emerged as a promising technique for capturing complex dynamic 3D scenes with high fidelity. It utilizes a 4D Gaussian representation and a GPU-friendly rasterizer, enabling rapid rendering speeds. Despite its advantages, 4DGS faces significant challenges, notably the requirement of millions of 4D Gaussians, each with extensive associated attributes, leading to substantial memory and storage cost. This paper introduces a memory-efficient framework for 4DGS. We streamline the color attribute by decomposing it into a per-Gaussian direct color component with only 3 parameters and a shared lightweight alternating current color predictor. This approach eliminates the need for spherical harmonics coefficients, which typically involve up to 144 parameters in classic 4DGS, thereby creating a memory-efficient 4D Gaussian representation. Furthermore, we introduce an entropy-constrained Gaussian deformation technique that uses a deformation field to expand the action range of each Gaussian and integrates an opacity-based entropy loss to limit the number of Gaussians, thus forcing our model to use as few Gaussians as possible to fit a dynamic scene well. With simple half-precision storage and zip compression, our framework achieves a storage reduction by approximately 190$\times$ and 125$\times$ on the Technicolor and Neural 3D Video datasets, respectively, compared to the original 4DGS. Meanwhile, it maintains comparable rendering speeds and scene representation quality, setting a new standard in the field.
EVA-Gaussian: 3D Gaussian-based Real-time Human Novel View Synthesis under Diverse Camera Settings
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:The feed-forward based 3D Gaussian Splatting method has demonstrated exceptional capability in real-time human novel view synthesis. However, existing approaches are restricted to dense viewpoint settings, which limits their flexibility in free-viewpoint rendering across a wide range of camera view angle discrepancies. To address this limitation, we propose a real-time pipeline named EVA-Gaussian for 3D human novel view synthesis across diverse camera settings. Specifically, we first introduce an Efficient cross-View Attention (EVA) module to accurately estimate the position of each 3D Gaussian from the source images. Then, we integrate the source images with the estimated Gaussian position map to predict the attributes and feature embeddings of the 3D Gaussians. Moreover, we employ a recurrent feature refiner to correct artifacts caused by geometric errors in position estimation and enhance visual fidelity.To further improve synthesis quality, we incorporate a powerful anchor loss function for both 3D Gaussian attributes and human face landmarks. Experimental results on the THuman2.0 and THumansit datasets showcase the superiority of our EVA-Gaussian approach in rendering quality across diverse camera settings. Project page: https://zhenliuzju.github.io/huyingdong/EVA-Gaussian.
Bidirectional Stereo Image Compression with Cross-Dimensional Entropy Model
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:With the rapid advancement of stereo vision technologies, stereo image compression has emerged as a crucial field that continues to draw significant attention. Previous approaches have primarily employed a unidirectional paradigm, where the compression of one view is dependent on the other, resulting in imbalanced compression. To address this issue, we introduce a symmetric bidirectional stereo image compression architecture, named BiSIC. Specifically, we propose a 3D convolution based codec backbone to capture local features and incorporate bidirectional attention blocks to exploit global features. Moreover, we design a novel cross-dimensional entropy model that integrates various conditioning factors, including the spatial context, channel context, and stereo dependency, to effectively estimate the distribution of latent representations for entropy coding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed BiSIC outperforms conventional image/video compression standards, as well as state-of-the-art learning-based methods, in terms of both PSNR and MS-SSIM.
Content-aware Masked Image Modeling Transformer for Stereo Image Compression
Mar 20, 2024Abstract:Existing learning-based stereo image codec adopt sophisticated transformation with simple entropy models derived from single image codecs to encode latent representations. However, those entropy models struggle to effectively capture the spatial-disparity characteristics inherent in stereo images, which leads to suboptimal rate-distortion results. In this paper, we propose a stereo image compression framework, named CAMSIC. CAMSIC independently transforms each image to latent representation and employs a powerful decoder-free Transformer entropy model to capture both spatial and disparity dependencies, by introducing a novel content-aware masked image modeling (MIM) technique. Our content-aware MIM facilitates efficient bidirectional interaction between prior information and estimated tokens, which naturally obviates the need for an extra Transformer decoder. Experiments show that our stereo image codec achieves state-of-the-art rate-distortion performance on two stereo image datasets Cityscapes and InStereo2K with fast encoding and decoding speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge