Chenyang Liu
Adaptive Confidence Gating in Multi-Agent Collaboration for Efficient and Optimized Code Generation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have catalyzed breakthroughs in automated code generation, Small Language Models (SLMs) often encounter reasoning bottlenecks and failure loops when addressing complex logical requirements. To overcome these challenges, we propose DebateCoder, a multi-agent collaborative framework designed to improve the reasoning ability of SLMs (e.g., Pangu-1B) in resource-constrained environments. DebateCoder uses a structured role-playing protocol with three agents: User Agent (A_UA), Technical Agent (A_TA), and Quality Assurance Agent (A_QA). It also includes an Adaptive Confidence Gating mechanism with a 95% threshold to balance accuracy and inference efficiency. In addition, we introduce a multi-turn deliberation module and a reviewer-guided analytical debugging loop for orthogonal pre-generation debate and post-generation refinement. Experiments on HumanEval and MBPP show that DebateCoder achieves 70.12% Pass@1 on HumanEval, outperforming MapCoder while reducing API overhead by about 35%. These results indicate that collaborative protocols can mitigate limitations of small-parameter models and provide a scalable, efficient approach to high-quality automated software engineering.
Dual Information Speech Language Models for Emotional Conversations
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Conversational systems relying on text-based large language models (LLMs) often overlook paralinguistic cues, essential for understanding emotions and intentions. Speech-language models (SLMs), which use speech as input, are emerging as a promising solution. However, SLMs built by extending frozen LLMs struggle to capture paralinguistic information and exhibit reduced context understanding. We identify entangled information and improper training strategies as key issues. To address these issues, we propose two heterogeneous adapters and suggest a weakly supervised training strategy. Our approach disentangles paralinguistic and linguistic information, enabling SLMs to interpret speech through structured representations. It also preserves contextual understanding by avoiding the generation of task-specific vectors through controlled randomness. This approach trains only the adapters on common datasets, ensuring parameter and data efficiency. Experiments demonstrate competitive performance in emotional conversation tasks, showcasing the model's ability to effectively integrate both paralinguistic and linguistic information within contextual settings.
RSRefSeg 2: Decoupling Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation with Foundation Models
Jul 08, 2025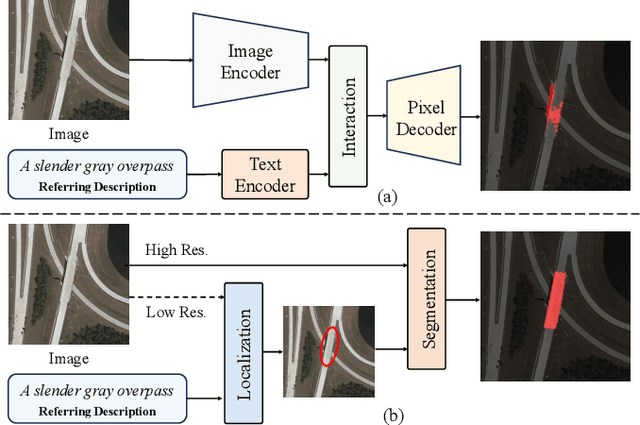
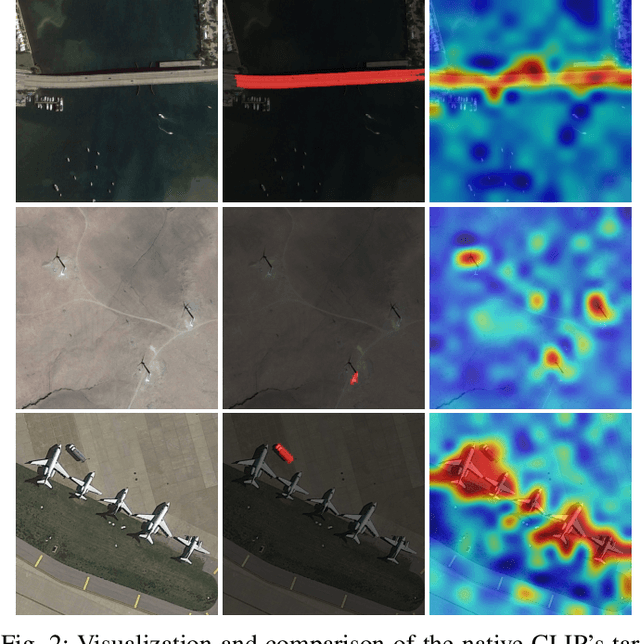
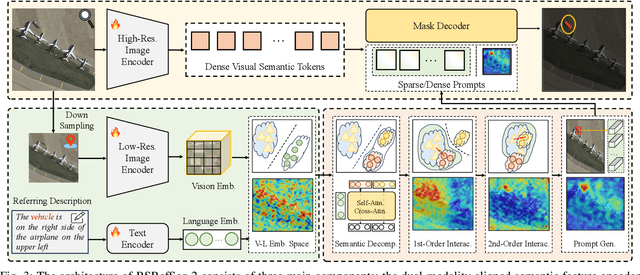
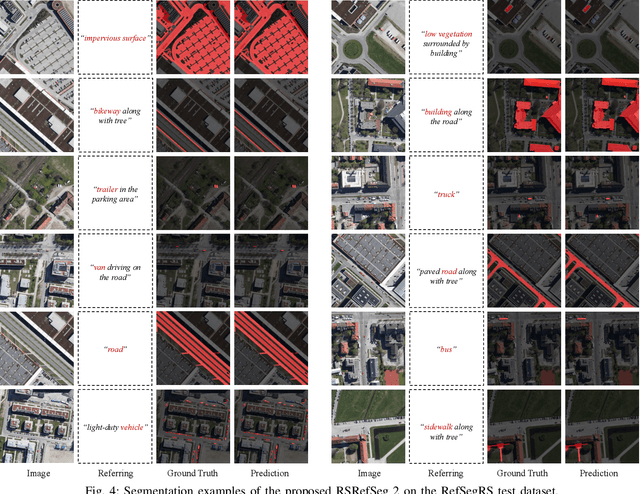
Abstract:Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation provides a flexible and fine-grained framework for remote sensing scene analysis via vision-language collaborative interpretation. Current approaches predominantly utilize a three-stage pipeline encompassing dual-modal encoding, cross-modal interaction, and pixel decoding. These methods demonstrate significant limitations in managing complex semantic relationships and achieving precise cross-modal alignment, largely due to their coupled processing mechanism that conflates target localization with boundary delineation. This architectural coupling amplifies error propagation under semantic ambiguity while restricting model generalizability and interpretability. To address these issues, we propose RSRefSeg 2, a decoupling paradigm that reformulates the conventional workflow into a collaborative dual-stage framework: coarse localization followed by fine segmentation. RSRefSeg 2 integrates CLIP's cross-modal alignment strength with SAM's segmentation generalizability through strategic foundation model collaboration. Specifically, CLIP is employed as the dual-modal encoder to activate target features within its pre-aligned semantic space and generate localization prompts. To mitigate CLIP's misactivation challenges in multi-entity scenarios described by referring texts, a cascaded second-order prompter is devised, which enhances precision through implicit reasoning via decomposition of text embeddings into complementary semantic subspaces. These optimized semantic prompts subsequently direct the SAM to generate pixel-level refined masks, thereby completing the semantic transmission pipeline. Extensive experiments (RefSegRS, RRSIS-D, and RISBench) demonstrate that RSRefSeg 2 surpasses contemporary methods in segmentation accuracy (+~3% gIoU) and complex semantic interpretation. Code is available at: https://github.com/KyanChen/RSRefSeg2.
DynamicVis: An Efficient and General Visual Foundation Model for Remote Sensing Image Understanding
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:The advancement of remote sensing technology has improved the spatial resolution of satellite imagery, facilitating more detailed visual representations for diverse interpretations. However, existing methods exhibit limited generalization capabilities across varied applications. While some contemporary foundation models demonstrate potential, they are hindered by insufficient cross-task adaptability and primarily process low-resolution imagery of restricted sizes, thus failing to fully exploit high-resolution data or leverage comprehensive large-scene semantics. Crucially, remote sensing imagery differs fundamentally from natural images, as key foreground targets (eg., maritime objects, artificial structures) often occupy minimal spatial proportions (~1%) and exhibit sparse distributions. Efficiently modeling cross-task generalizable knowledge from lengthy 2D tokens (~100,000) poses a significant challenge yet remains critical for remote sensing image understanding. Motivated by the selective attention mechanisms inherent to the human visual system, we propose DynamicVis, a dynamic visual perception foundation model for remote sensing imagery. The framework integrates a novel dynamic region perception backbone based on the selective state space model, which strategically balances localized detail extraction with global contextual integration, enabling computationally efficient encoding of large-scale data while maintaining architectural scalability. To enhance cross-task knowledge transferring, we introduce a multi-instance learning paradigm utilizing meta-embedding representations, trained on million-scale region-level annotations. Evaluations across nine downstream tasks demonstrate the model's versatility. DynamicVis achieves multi-level feature modeling with exceptional efficiency, processing (2048x2048) pixels with 97 ms latency (6% of ViT's) and 833 MB GPU memory (3% of ViT's).
Molecule Generation for Target Protein Binding with Hierarchical Consistency Diffusion Model
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:Effective generation of molecular structures, or new chemical entities, that bind to target proteins is crucial for lead identification and optimization in drug discovery. Despite advancements in atom- and motif-wise deep learning models for 3D molecular generation, current methods often struggle with validity and reliability. To address these issues, we develop the Atom-Motif Consistency Diffusion Model (AMDiff), utilizing a joint-training paradigm for multi-view learning. This model features a hierarchical diffusion architecture that integrates both atom- and motif-level views of molecules, allowing for comprehensive exploration of complementary information. By leveraging classifier-free guidance and incorporating binding site features as conditional inputs, AMDiff ensures robust molecule generation across diverse targets. Compared to existing approaches, AMDiff exhibits superior validity and novelty in generating molecules tailored to fit various protein pockets. Case studies targeting protein kinases, including Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) and Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), demonstrate the model's capability in structure-based de novo drug design. Overall, AMDiff bridges the gap between atom-view and motif-view drug discovery and speeds up the process of target-aware molecular generation.
RSRefSeg: Referring Remote Sensing Image Segmentation with Foundation Models
Jan 12, 2025


Abstract:Referring remote sensing image segmentation is crucial for achieving fine-grained visual understanding through free-format textual input, enabling enhanced scene and object extraction in remote sensing applications. Current research primarily utilizes pre-trained language models to encode textual descriptions and align them with visual modalities, thereby facilitating the expression of relevant visual features. However, these approaches often struggle to establish robust alignments between fine-grained semantic concepts, leading to inconsistent representations across textual and visual information. To address these limitations, we introduce a referring remote sensing image segmentation foundational model, RSRefSeg. RSRefSeg leverages CLIP for visual and textual encoding, employing both global and local textual semantics as filters to generate referring-related visual activation features in the latent space. These activated features then serve as input prompts for SAM, which refines the segmentation masks through its robust visual generalization capabilities. Experimental results on the RRSIS-D dataset demonstrate that RSRefSeg outperforms existing methods, underscoring the effectiveness of foundational models in enhancing multimodal task comprehension. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/KyanChen/RSRefSeg}.
Semantic-CD: Remote Sensing Image Semantic Change Detection towards Open-vocabulary Setting
Jan 12, 2025Abstract:Remote sensing image semantic change detection is a method used to analyze remote sensing images, aiming to identify areas of change as well as categorize these changes within images of the same location taken at different times. Traditional change detection methods often face challenges in generalizing across semantic categories in practical scenarios. To address this issue, we introduce a novel approach called Semantic-CD, specifically designed for semantic change detection in remote sensing images. This method incorporates the open vocabulary semantics from the vision-language foundation model, CLIP. By utilizing CLIP's extensive vocabulary knowledge, our model enhances its ability to generalize across categories and improves segmentation through fully decoupled multi-task learning, which includes both binary change detection and semantic change detection tasks. Semantic-CD consists of four main components: a bi-temporal CLIP visual encoder for extracting features from bi-temporal images, an open semantic prompter for creating semantic cost volume maps with open vocabulary, a binary change detection decoder for generating binary change detection masks, and a semantic change detection decoder for producing semantic labels. Experimental results on the SECOND dataset demonstrate that Semantic-CD achieves more accurate masks and reduces semantic classification errors, illustrating its effectiveness in applying semantic priors from vision-language foundation models to SCD tasks.
Text2Earth: Unlocking Text-driven Remote Sensing Image Generation with a Global-Scale Dataset and a Foundation Model
Jan 01, 2025



Abstract:Generative foundation models have advanced large-scale text-driven natural image generation, becoming a prominent research trend across various vertical domains. However, in the remote sensing field, there is still a lack of research on large-scale text-to-image (text2image) generation technology. Existing remote sensing image-text datasets are small in scale and confined to specific geographic areas and scene types. Besides, existing text2image methods have struggled to achieve global-scale, multi-resolution controllable, and unbounded image generation. To address these challenges, this paper presents two key contributions: the Git-10M dataset and the Text2Earth foundation model. Git-10M is a global-scale image-text dataset comprising 10 million image-text pairs, 5 times larger than the previous largest one. The dataset covers a wide range of geographic scenes and contains resolution information, significantly surpassing existing datasets in both size and diversity. Building on Git-10M, we propose Text2Earth, a 1.3 billion parameter generative foundation model based on the diffusion framework to model global-scale remote sensing scenes. Text2Earth integrates a resolution guidance mechanism, enabling users to specify image resolutions. A dynamic condition adaptation strategy is proposed for training and inference to improve image quality. Text2Earth excels in zero-shot text2image generation and demonstrates robust generalization and flexibility across multiple tasks, including unbounded scene construction, image editing, and cross-modal image generation. This robust capability surpasses previous models restricted to the basic fixed size and limited scene types. On the previous benchmark dataset, Text2Earth outperforms previous models with an improvement of +26.23 FID and +20.95% Zero-shot Cls-OA metric.Our project page is \url{https://chen-yang-liu.github.io/Text2Earth}
Remote Sensing Temporal Vision-Language Models: A Comprehensive Survey
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Temporal image analysis in remote sensing has traditionally centered on change detection, which identifies regions of change between images captured at different times. However, change detection remains limited by its focus on visual-level interpretation, often lacking contextual or descriptive information. The rise of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) has introduced a new dimension to remote sensing temporal image analysis by integrating visual information with natural language, creating an avenue for advanced interpretation of temporal image changes. Remote Sensing Temporal VLMs (RSTVLMs) allow for dynamic interactions, generating descriptive captions, answering questions, and providing a richer semantic understanding of temporal images. This temporal vision-language capability is particularly valuable for complex remote sensing applications, where higher-level insights are crucial. This paper comprehensively reviews the progress of RSTVLM research, with a focus on the latest VLM applications for temporal image analysis. We categorize and discuss core methodologies, datasets, and metrics, highlight recent advances in temporal vision-language tasks, and outline key challenges and future directions for research in this emerging field. This survey fills a critical gap in the literature by providing an integrated overview of RSTVLM, offering a foundation for further advancements in remote sensing temporal image understanding. We will keep tracing related works at \url{https://github.com/Chen-Yang-Liu/Awesome-RS-Temporal-VLM}
Semantic-CC: Boosting Remote Sensing Image Change Captioning via Foundational Knowledge and Semantic Guidance
Jul 19, 2024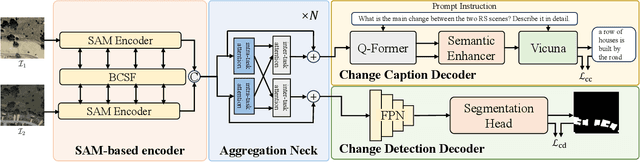


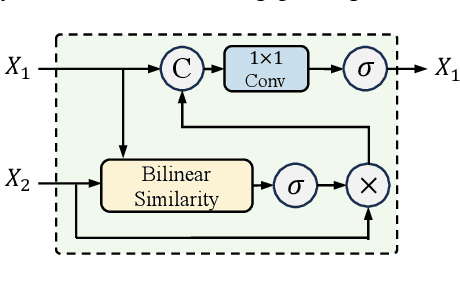
Abstract:Remote sensing image change captioning (RSICC) aims to articulate the changes in objects of interest within bi-temporal remote sensing images using natural language. Given the limitations of current RSICC methods in expressing general features across multi-temporal and spatial scenarios, and their deficiency in providing granular, robust, and precise change descriptions, we introduce a novel change captioning (CC) method based on the foundational knowledge and semantic guidance, which we term Semantic-CC. Semantic-CC alleviates the dependency of high-generalization algorithms on extensive annotations by harnessing the latent knowledge of foundation models, and it generates more comprehensive and accurate change descriptions guided by pixel-level semantics from change detection (CD). Specifically, we propose a bi-temporal SAM-based encoder for dual-image feature extraction; a multi-task semantic aggregation neck for facilitating information interaction between heterogeneous tasks; a straightforward multi-scale change detection decoder to provide pixel-level semantic guidance; and a change caption decoder based on the large language model (LLM) to generate change description sentences. Moreover, to ensure the stability of the joint training of CD and CC, we propose a three-stage training strategy that supervises different tasks at various stages. We validate the proposed method on the LEVIR-CC and LEVIR-CD datasets. The experimental results corroborate the complementarity of CD and CC, demonstrating that Semantic-CC can generate more accurate change descriptions and achieve optimal performance across both tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge