Man Wang
Knowledge Distillation for Temporal Knowledge Graph Reasoning with Large Language Models
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Reasoning over temporal knowledge graphs (TKGs) is fundamental to improving the efficiency and reliability of intelligent decision-making systems and has become a key technological foundation for future artificial intelligence applications. Despite recent progress, existing TKG reasoning models typically rely on large parameter sizes and intensive computation, leading to high hardware costs and energy consumption. These constraints hinder their deployment on resource-constrained, low-power, and distributed platforms that require real-time inference. Moreover, most existing model compression and distillation techniques are designed for static knowledge graphs and fail to adequately capture the temporal dependencies inherent in TKGs, often resulting in degraded reasoning performance. To address these challenges, we propose a distillation framework specifically tailored for temporal knowledge graph reasoning. Our approach leverages large language models as teacher models to guide the distillation process, enabling effective transfer of both structural and temporal reasoning capabilities to lightweight student models. By integrating large-scale public knowledge with task-specific temporal information, the proposed framework enhances the student model's ability to model temporal dynamics while maintaining a compact and efficient architecture. Extensive experiments on multiple publicly available benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms strong baselines, achieving a favorable trade-off between reasoning accuracy, computational efficiency, and practical deployability.
Remote Sensing Temporal Vision-Language Models: A Comprehensive Survey
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Temporal image analysis in remote sensing has traditionally centered on change detection, which identifies regions of change between images captured at different times. However, change detection remains limited by its focus on visual-level interpretation, often lacking contextual or descriptive information. The rise of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) has introduced a new dimension to remote sensing temporal image analysis by integrating visual information with natural language, creating an avenue for advanced interpretation of temporal image changes. Remote Sensing Temporal VLMs (RSTVLMs) allow for dynamic interactions, generating descriptive captions, answering questions, and providing a richer semantic understanding of temporal images. This temporal vision-language capability is particularly valuable for complex remote sensing applications, where higher-level insights are crucial. This paper comprehensively reviews the progress of RSTVLM research, with a focus on the latest VLM applications for temporal image analysis. We categorize and discuss core methodologies, datasets, and metrics, highlight recent advances in temporal vision-language tasks, and outline key challenges and future directions for research in this emerging field. This survey fills a critical gap in the literature by providing an integrated overview of RSTVLM, offering a foundation for further advancements in remote sensing temporal image understanding. We will keep tracing related works at \url{https://github.com/Chen-Yang-Liu/Awesome-RS-Temporal-VLM}
Target Recognition Algorithm for Monitoring Images in Electric Power Construction Process
Feb 09, 2024



Abstract:To enhance precision and comprehensiveness in identifying targets in electric power construction monitoring video, a novel target recognition algorithm utilizing infrared imaging is explored. This algorithm employs a color processing technique based on a local linear mapping method to effectively recolor monitoring images. The process involves three key steps: color space conversion, color transfer, and pseudo-color encoding. It is designed to accentuate targets in the infrared imaging. For the refined identification of these targets, the algorithm leverages a support vector machine approach, utilizing an optimal hyperplane to accurately predict target types. We demonstrate the efficacy of the algorithm, which achieves high target recognition accuracy in both outdoor and indoor electric power construction monitoring scenarios. It maintains a false recognition rate below 3% across various environments.
Transmission Line Detection Based on Improved Hough Transform
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:To address the challenges of low detection accuracy and high false positive rates of transmission lines in UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) images, we explore the linear features and spatial distribution. We introduce an enhanced stochastic Hough transform technique tailored for detecting transmission lines in complex backgrounds. By employing the Hessian matrix for initial preprocessing of transmission lines, and utilizing boundary search and pixel row segmentation, our approach distinguishes transmission line areas from the background. We significantly reduce both false positives and missed detections, thereby improving the accuracy of transmission line identification. Experiments demonstrate that our method not only processes images more rapidly, but also yields superior detection results compared to conventional and random Hough transform methods.
CAT: Learning to Collaborate Channel and Spatial Attention from Multi-Information Fusion
Dec 13, 2022



Abstract:Channel and spatial attention mechanism has proven to provide an evident performance boost of deep convolution neural networks (CNNs). Most existing methods focus on one or run them parallel (series), neglecting the collaboration between the two attentions. In order to better establish the feature interaction between the two types of attention, we propose a plug-and-play attention module, which we term "CAT"-activating the Collaboration between spatial and channel Attentions based on learned Traits. Specifically, we represent traits as trainable coefficients (i.e., colla-factors) to adaptively combine contributions of different attention modules to fit different image hierarchies and tasks better. Moreover, we propose the global entropy pooling (GEP) apart from global average pooling (GAP) and global maximum pooling (GMP) operators, an effective component in suppressing noise signals by measuring the information disorder of feature maps. We introduce a three-way pooling operation into attention modules and apply the adaptive mechanism to fuse their outcomes. Extensive experiments on MS COCO, Pascal-VOC, Cifar-100, and ImageNet show that our CAT outperforms existing state-of-the-art attention mechanisms in object detection, instance segmentation, and image classification. The model and code will be released soon.
* 8 pages, 5 figures
Disentangling and Vectorization: A 3D Visual Perception Approach for Autonomous Driving Based on Surround-View Fisheye Cameras
Jul 19, 2021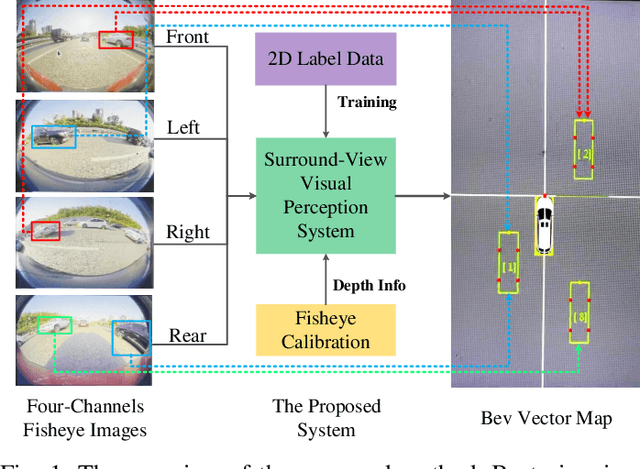
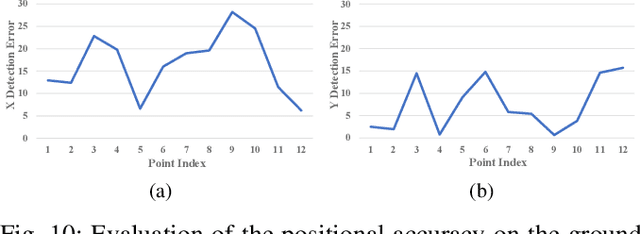

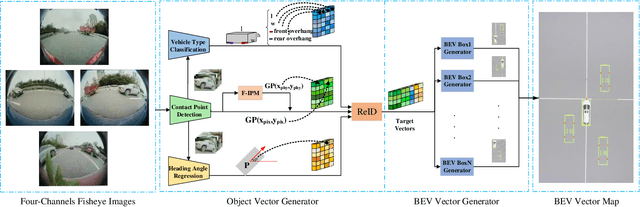
Abstract:The 3D visual perception for vehicles with the surround-view fisheye camera system is a critical and challenging task for low-cost urban autonomous driving. While existing monocular 3D object detection methods perform not well enough on the fisheye images for mass production, partly due to the lack of 3D datasets of such images. In this paper, we manage to overcome and avoid the difficulty of acquiring the large scale of accurate 3D labeled truth data, by breaking down the 3D object detection task into some sub-tasks, such as vehicle's contact point detection, type classification, re-identification and unit assembling, etc. Particularly, we propose the concept of Multidimensional Vector to include the utilizable information generated in different dimensions and stages, instead of the descriptive approach for the bird's eye view (BEV) or a cube of eight points. The experiments of real fisheye images demonstrate that our solution achieves state-of-the-art accuracy while being real-time in practice.
DeepWORD: A GCN-based Approach for Owner-Member Relationship Detection in Autonomous Driving
Apr 20, 2021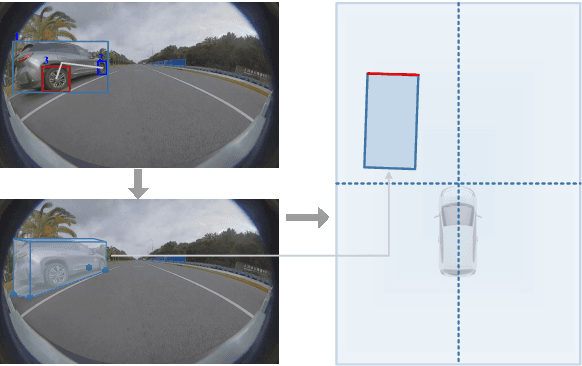
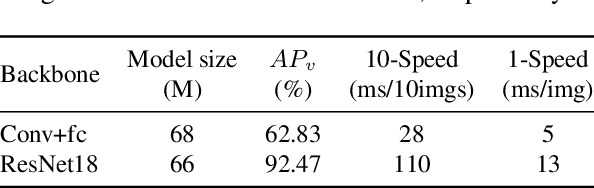
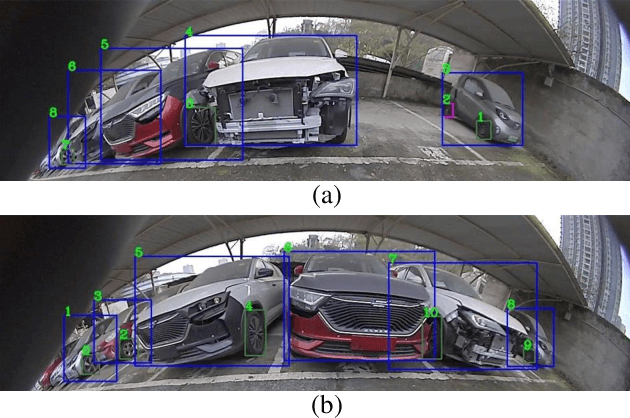
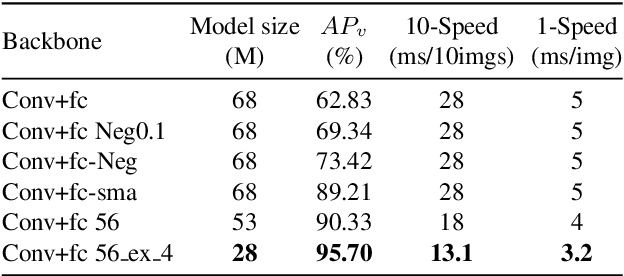
Abstract:It's worth noting that the owner-member relationship between wheels and vehicles has an significant contribution to the 3D perception of vehicles, especially in the embedded environment. However, there are currently two main challenges about the above relationship prediction: i) The traditional heuristic methods based on IoU can hardly deal with the traffic jam scenarios for the occlusion. ii) It is difficult to establish an efficient applicable solution for the vehicle-mounted system. To address these issues, we propose an innovative relationship prediction method, namely DeepWORD, by designing a graph convolution network (GCN). Specifically, we utilize the feature maps with local correlation as the input of nodes to improve the information richness. Besides, we introduce the graph attention network (GAT) to dynamically amend the prior estimation deviation. Furthermore, we establish an annotated owner-member relationship dataset called WORD as a large-scale benchmark, which will be available soon. The experiments demonstrate that our solution achieves state-of-the-art accuracy and real-time in practice.
Vehicle Re-ID for Surround-view Camera System
Jun 30, 2020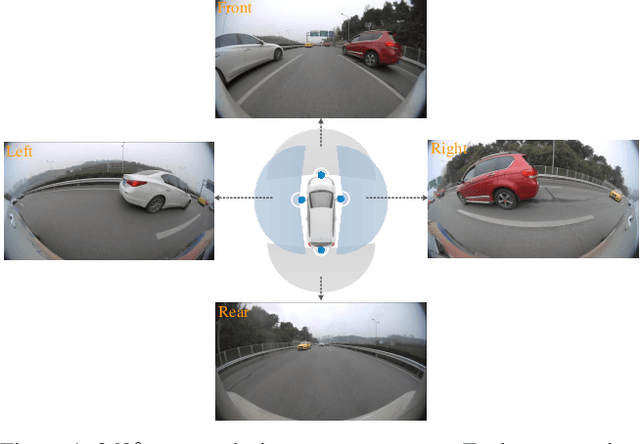
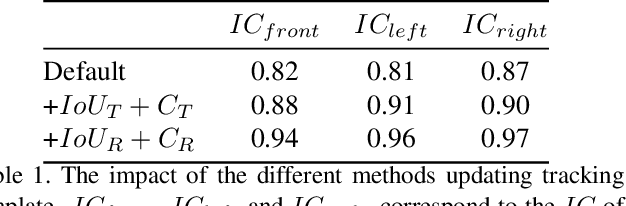
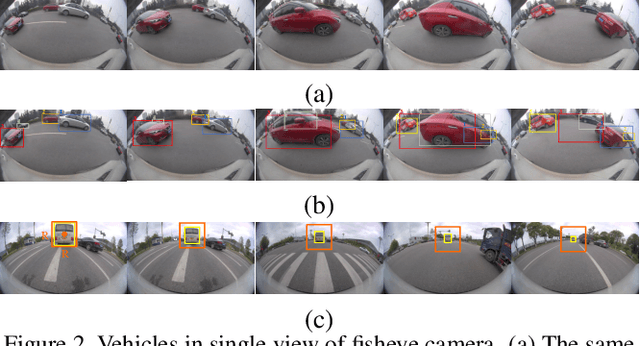
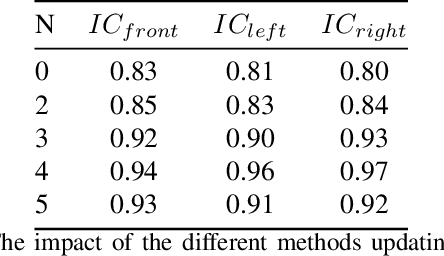
Abstract:The vehicle re-identification (ReID) plays a critical role in the perception system of autonomous driving, which attracts more and more attention in recent years. However, to our best knowledge, there is no existing complete solution for the surround-view system mounted on the vehicle. In this paper, we argue two main challenges in above scenario: i) In single camera view, it is difficult to recognize the same vehicle from the past image frames due to the fisheye distortion, occlusion, truncation, etc. ii) In multi-camera view, the appearance of the same vehicle varies greatly from different camera's viewpoints. Thus, we present an integral vehicle Re-ID solution to address these problems. Specifically, we propose a novel quality evaluation mechanism to balance the effect of tracking box's drift and target's consistency. Besides, we take advantage of the Re-ID network based on attention mechanism, then combined with a spatial constraint strategy to further boost the performance between different cameras. The experiments demonstrate that our solution achieves state-of-the-art accuracy while being real-time in practice. Besides, we will release the code and annotated fisheye dataset for the benefit of community.
PSDet: Efficient and Universal Parking Slot Detection
May 12, 2020



Abstract:While real-time parking slot detection plays a critical role in valet parking systems, existing methods have limited success in real-world applications. We argue two reasons accounting for the unsatisfactory performance: \romannumeral1, The available datasets have limited diversity, which causes the low generalization ability. \romannumeral2, Expert knowledge for parking slot detection is under-estimated. Thus, we annotate a large-scale benchmark for training the network and release it for the benefit of community. Driven by the observation of various parking lots in our benchmark, we propose the circular descriptor to regress the coordinates of parking slot vertexes and accordingly localize slots accurately. To further boost the performance, we develop a two-stage deep architecture to localize vertexes in the coarse-to-fine manner. In our benchmark and other datasets, it achieves the state-of-the-art accuracy while being real-time in practice. Benchmark is available at: https://github.com/wuzzh/Parking-slot-dataset
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge