Wenkai Zhang
A Resource-Efficient Training Framework for Remote Sensing Text--Image Retrieval
Jan 18, 2025



Abstract:Remote sensing text--image retrieval (RSTIR) aims to retrieve the matched remote sensing (RS) images from the database according to the descriptive text. Recently, the rapid development of large visual-language pre-training models provides new insights for RSTIR. Nevertheless, as the complexity of models grows in RSTIR, the previous studies suffer from suboptimal resource efficiency during transfer learning. To address this issue, we propose a computation and memory-efficient retrieval (CMER) framework for RSTIR. To reduce the training memory consumption, we propose the Focus-Adapter module, which adopts a side branch structure. Its focus layer suppresses the interference of background pixels for small targets. Simultaneously, to enhance data efficacy, we regard the RS scene category as the metadata and design a concise augmentation technique. The scene label augmentation leverages the prior knowledge from land cover categories and shrinks the search space. We propose the negative sample recycling strategy to make the negative sample pool decoupled from the mini-batch size. It improves the generalization performance without introducing additional encoders. We have conducted quantitative and qualitative experiments on public datasets and expanded the benchmark with some advanced approaches, which demonstrates the competitiveness of the proposed CMER. Compared with the recent advanced methods, the overall retrieval performance of CMER is 2%--5% higher on RSITMD. Moreover, our proposed method reduces memory consumption by 49% and has a 1.4x data throughput during training. The code of the CMER and the dataset will be released at https://github.com/ZhangWeihang99/CMER.
Learning to Evaluate Performance of Multi-modal Semantic Localization
Sep 19, 2022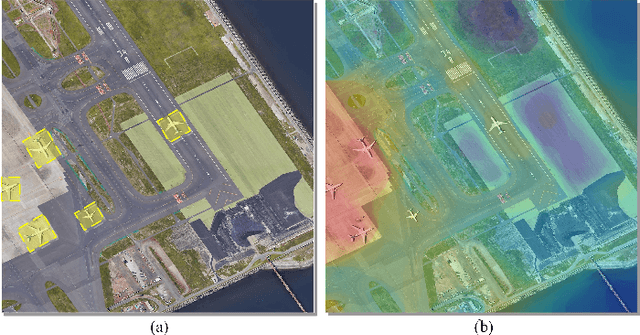
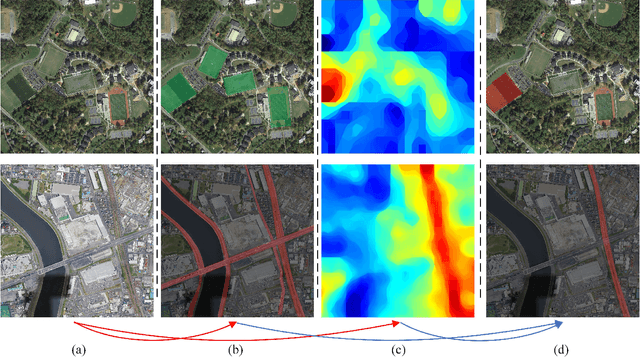
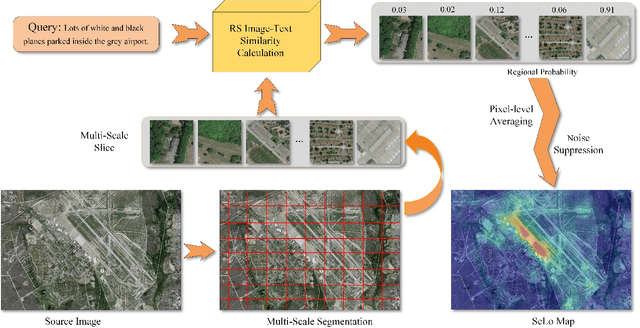
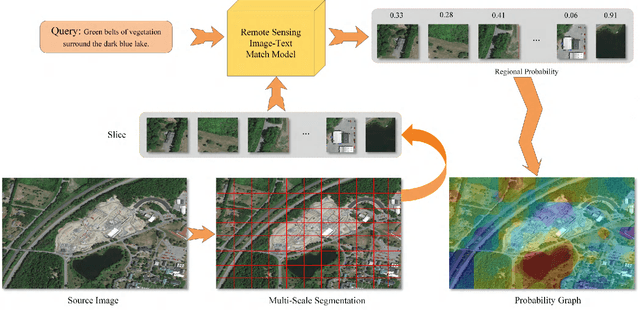
Abstract:Semantic localization (SeLo) refers to the task of obtaining the most relevant locations in large-scale remote sensing (RS) images using semantic information such as text. As an emerging task based on cross-modal retrieval, SeLo achieves semantic-level retrieval with only caption-level annotation, which demonstrates its great potential in unifying downstream tasks. Although SeLo has been carried out successively, but there is currently no work has systematically explores and analyzes this urgent direction. In this paper, we thoroughly study this field and provide a complete benchmark in terms of metrics and testdata to advance the SeLo task. Firstly, based on the characteristics of this task, we propose multiple discriminative evaluation metrics to quantify the performance of the SeLo task. The devised significant area proportion, attention shift distance, and discrete attention distance are utilized to evaluate the generated SeLo map from pixel-level and region-level. Next, to provide standard evaluation data for the SeLo task, we contribute a diverse, multi-semantic, multi-objective Semantic Localization Testset (AIR-SLT). AIR-SLT consists of 22 large-scale RS images and 59 test cases with different semantics, which aims to provide a comprehensive evaluations for retrieval models. Finally, we analyze the SeLo performance of RS cross-modal retrieval models in detail, explore the impact of different variables on this task, and provide a complete benchmark for the SeLo task. We have also established a new paradigm for RS referring expression comprehension, and demonstrated the great advantage of SeLo in semantics through combining it with tasks such as detection and road extraction. The proposed evaluation metrics, semantic localization testsets, and corresponding scripts have been open to access at github.com/xiaoyuan1996/SemanticLocalizationMetrics .
Open-domain Dialogue Generation Grounded with Dynamic Multi-form Knowledge Fusion
Apr 24, 2022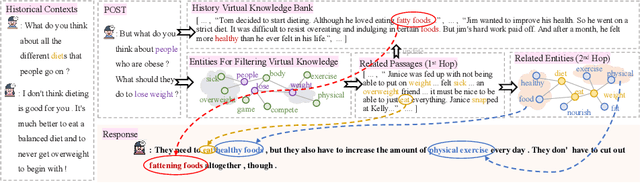

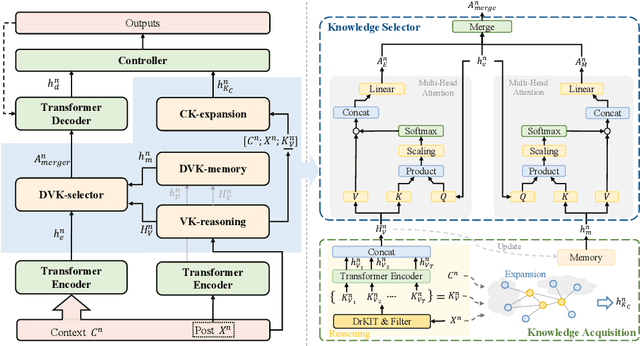
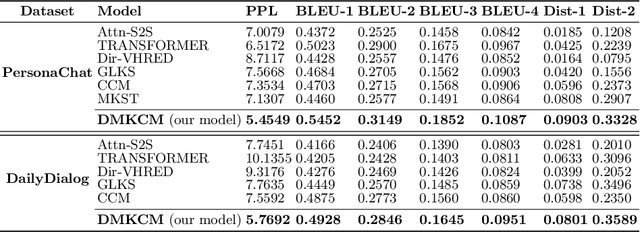
Abstract:Open-domain multi-turn conversations normally face the challenges of how to enrich and expand the content of the conversation. Recently, many approaches based on external knowledge are proposed to generate rich semantic and information conversation. Two types of knowledge have been studied for knowledge-aware open-domain dialogue generation: structured triples from knowledge graphs and unstructured texts from documents. To take both advantages of abundant unstructured latent knowledge in the documents and the information expansion capabilities of the structured knowledge graph, this paper presents a new dialogue generation model, Dynamic Multi-form Knowledge Fusion based Open-domain Chatt-ing Machine (DMKCM).In particular, DMKCM applies an indexed text (a virtual Knowledge Base) to locate relevant documents as 1st hop and then expands the content of the dialogue and its 1st hop using a commonsense knowledge graph to get apposite triples as 2nd hop. To merge these two forms of knowledge into the dialogue effectively, we design a dynamic virtual knowledge selector and a controller that help to enrich and expand knowledge space. Moreover, DMKCM adopts a novel dynamic knowledge memory module that effectively uses historical reasoning knowledge to generate better responses. Experimental results indicate the effectiveness of our method in terms of dialogue coherence and informativeness.
Exploring a Fine-Grained Multiscale Method for Cross-Modal Remote Sensing Image Retrieval
Apr 21, 2022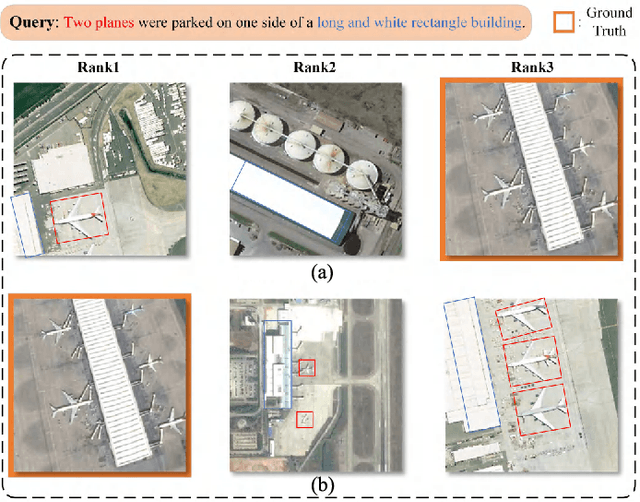
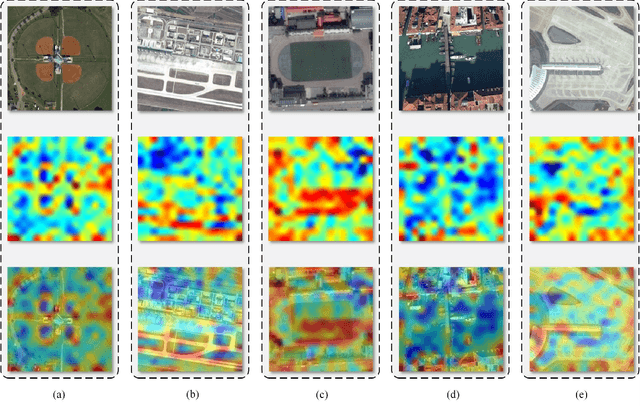
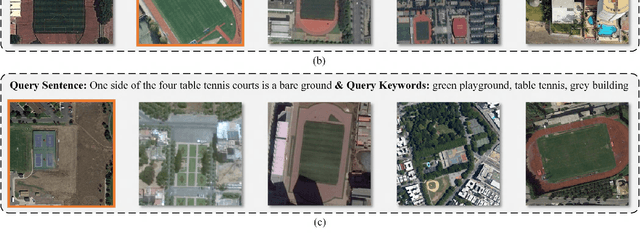
Abstract:Remote sensing (RS) cross-modal text-image retrieval has attracted extensive attention for its advantages of flexible input and efficient query. However, traditional methods ignore the characteristics of multi-scale and redundant targets in RS image, leading to the degradation of retrieval accuracy. To cope with the problem of multi-scale scarcity and target redundancy in RS multimodal retrieval task, we come up with a novel asymmetric multimodal feature matching network (AMFMN). Our model adapts to multi-scale feature inputs, favors multi-source retrieval methods, and can dynamically filter redundant features. AMFMN employs the multi-scale visual self-attention (MVSA) module to extract the salient features of RS image and utilizes visual features to guide the text representation. Furthermore, to alleviate the positive samples ambiguity caused by the strong intraclass similarity in RS image, we propose a triplet loss function with dynamic variable margin based on prior similarity of sample pairs. Finally, unlike the traditional RS image-text dataset with coarse text and higher intraclass similarity, we construct a fine-grained and more challenging Remote sensing Image-Text Match dataset (RSITMD), which supports RS image retrieval through keywords and sentence separately and jointly. Experiments on four RS text-image datasets demonstrate that the proposed model can achieve state-of-the-art performance in cross-modal RS text-image retrieval task.
Remote Sensing Cross-Modal Text-Image Retrieval Based on Global and Local Information
Apr 21, 2022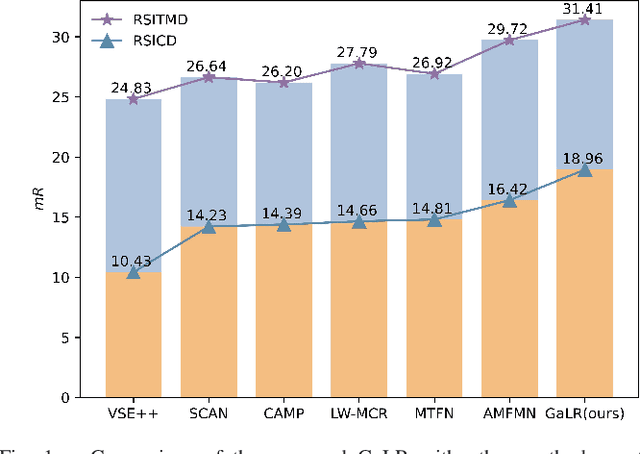
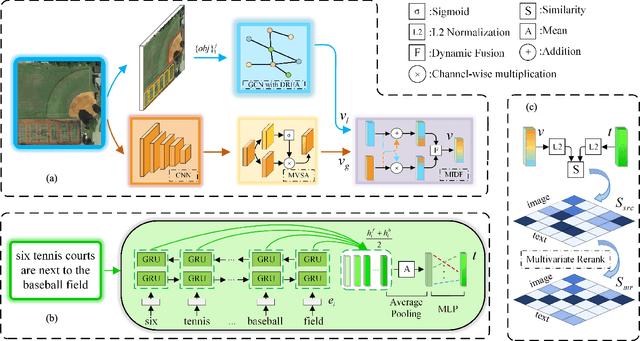
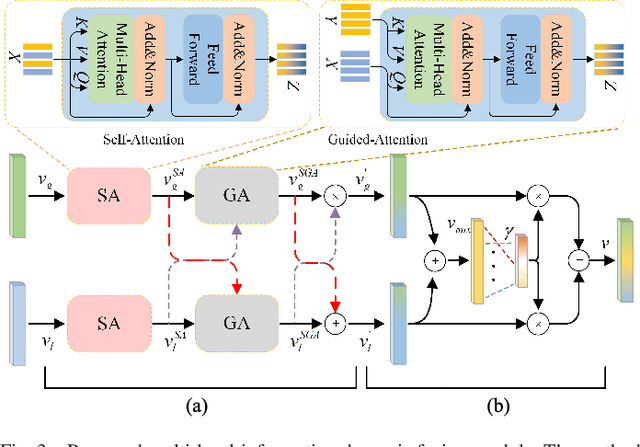
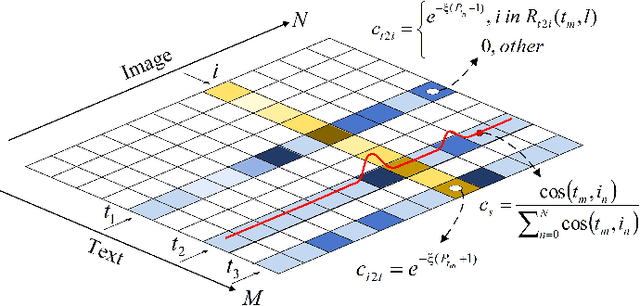
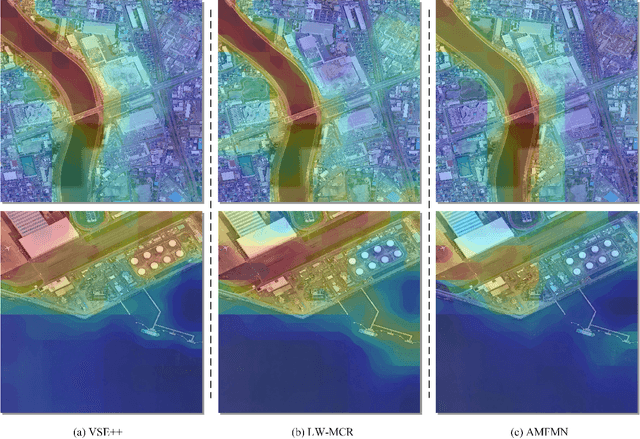
Abstract:Cross-modal remote sensing text-image retrieval (RSCTIR) has recently become an urgent research hotspot due to its ability of enabling fast and flexible information extraction on remote sensing (RS) images. However, current RSCTIR methods mainly focus on global features of RS images, which leads to the neglect of local features that reflect target relationships and saliency. In this article, we first propose a novel RSCTIR framework based on global and local information (GaLR), and design a multi-level information dynamic fusion (MIDF) module to efficaciously integrate features of different levels. MIDF leverages local information to correct global information, utilizes global information to supplement local information, and uses the dynamic addition of the two to generate prominent visual representation. To alleviate the pressure of the redundant targets on the graph convolution network (GCN) and to improve the model s attention on salient instances during modeling local features, the de-noised representation matrix and the enhanced adjacency matrix (DREA) are devised to assist GCN in producing superior local representations. DREA not only filters out redundant features with high similarity, but also obtains more powerful local features by enhancing the features of prominent objects. Finally, to make full use of the information in the similarity matrix during inference, we come up with a plug-and-play multivariate rerank (MR) algorithm. The algorithm utilizes the k nearest neighbors of the retrieval results to perform a reverse search, and improves the performance by combining multiple components of bidirectional retrieval. Extensive experiments on public datasets strongly demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of GaLR methods on the RSCTIR task. The code of GaLR method, MR algorithm, and corresponding files have been made available at https://github.com/xiaoyuan1996/GaLR .
Disentangling and Vectorization: A 3D Visual Perception Approach for Autonomous Driving Based on Surround-View Fisheye Cameras
Jul 19, 2021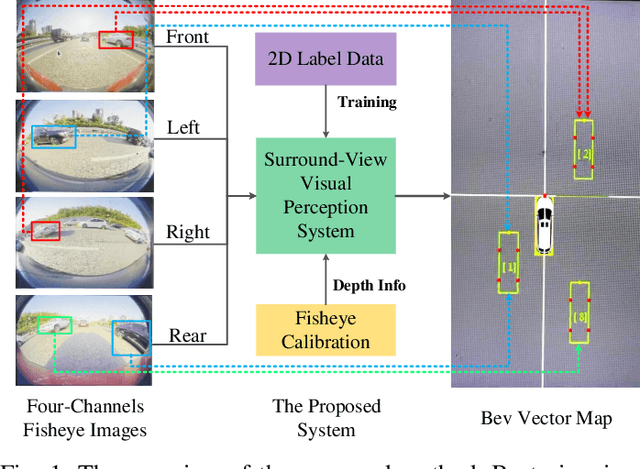
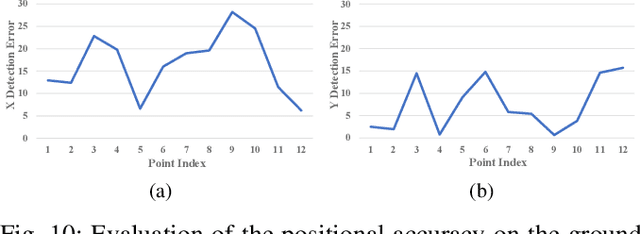

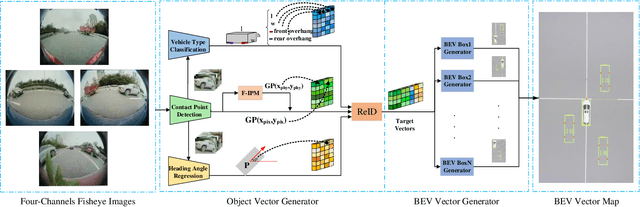
Abstract:The 3D visual perception for vehicles with the surround-view fisheye camera system is a critical and challenging task for low-cost urban autonomous driving. While existing monocular 3D object detection methods perform not well enough on the fisheye images for mass production, partly due to the lack of 3D datasets of such images. In this paper, we manage to overcome and avoid the difficulty of acquiring the large scale of accurate 3D labeled truth data, by breaking down the 3D object detection task into some sub-tasks, such as vehicle's contact point detection, type classification, re-identification and unit assembling, etc. Particularly, we propose the concept of Multidimensional Vector to include the utilizable information generated in different dimensions and stages, instead of the descriptive approach for the bird's eye view (BEV) or a cube of eight points. The experiments of real fisheye images demonstrate that our solution achieves state-of-the-art accuracy while being real-time in practice.
Denoising Distantly Supervised Named Entity Recognition via a Hypergeometric Probabilistic Model
Jun 17, 2021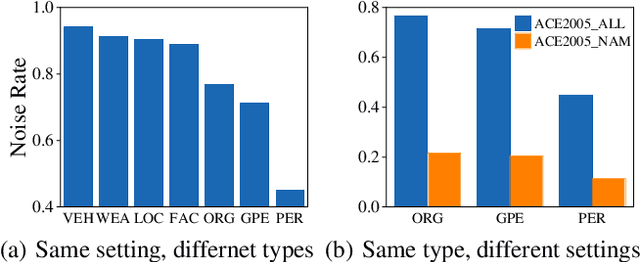
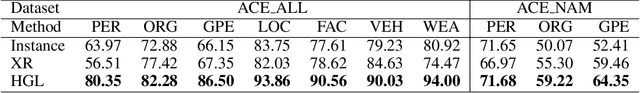
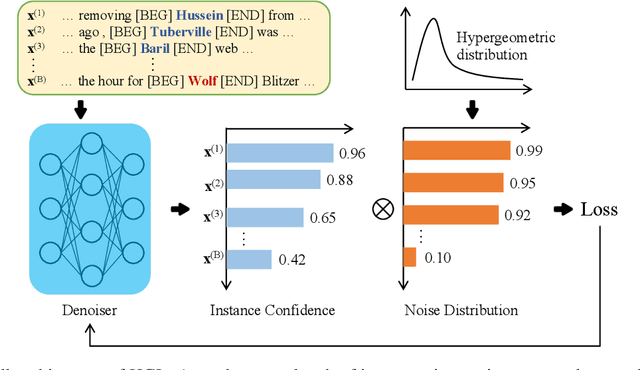
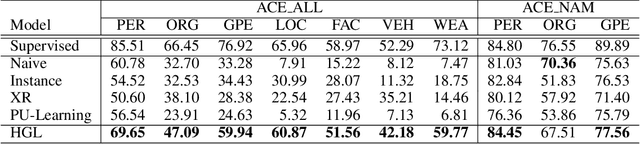
Abstract:Denoising is the essential step for distant supervision based named entity recognition. Previous denoising methods are mostly based on instance-level confidence statistics, which ignore the variety of the underlying noise distribution on different datasets and entity types. This makes them difficult to be adapted to high noise rate settings. In this paper, we propose Hypergeometric Learning (HGL), a denoising algorithm for distantly supervised NER that takes both noise distribution and instance-level confidence into consideration. Specifically, during neural network training, we naturally model the noise samples in each batch following a hypergeometric distribution parameterized by the noise-rate. Then each instance in the batch is regarded as either correct or noisy one according to its label confidence derived from previous training step, as well as the noise distribution in this sampled batch. Experiments show that HGL can effectively denoise the weakly-labeled data retrieved from distant supervision, and therefore results in significant improvements on the trained models.
De-biasing Distantly Supervised Named Entity Recognition via Causal Intervention
Jun 17, 2021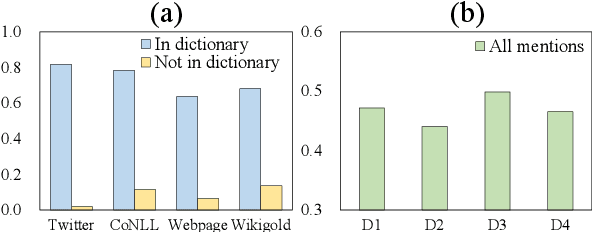
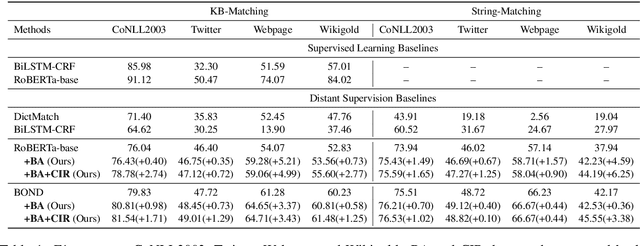
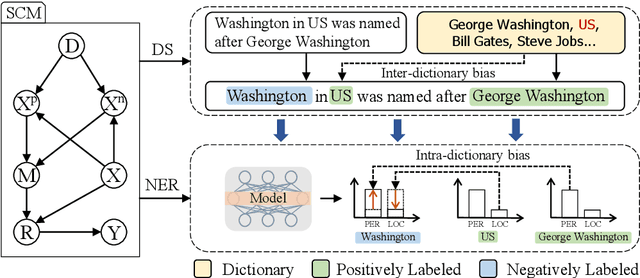
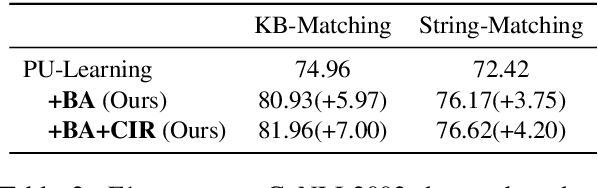
Abstract:Distant supervision tackles the data bottleneck in NER by automatically generating training instances via dictionary matching. Unfortunately, the learning of DS-NER is severely dictionary-biased, which suffers from spurious correlations and therefore undermines the effectiveness and the robustness of the learned models. In this paper, we fundamentally explain the dictionary bias via a Structural Causal Model (SCM), categorize the bias into intra-dictionary and inter-dictionary biases, and identify their causes. Based on the SCM, we learn de-biased DS-NER via causal interventions. For intra-dictionary bias, we conduct backdoor adjustment to remove the spurious correlations introduced by the dictionary confounder. For inter-dictionary bias, we propose a causal invariance regularizer which will make DS-NER models more robust to the perturbation of dictionaries. Experiments on four datasets and three DS-NER models show that our method can significantly improve the performance of DS-NER.
DeepWORD: A GCN-based Approach for Owner-Member Relationship Detection in Autonomous Driving
Apr 20, 2021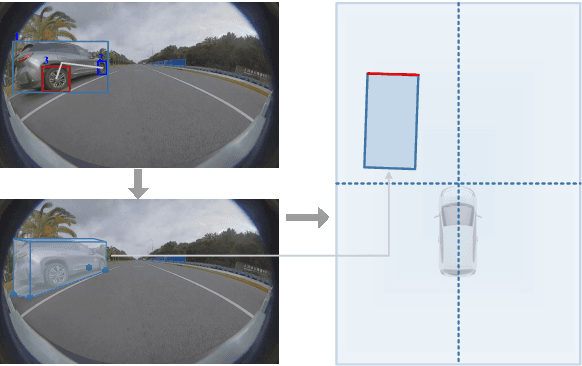
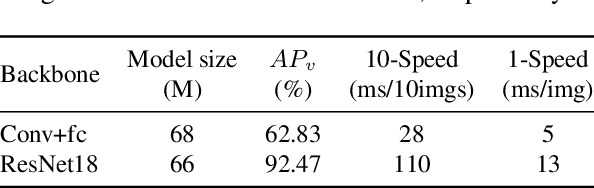
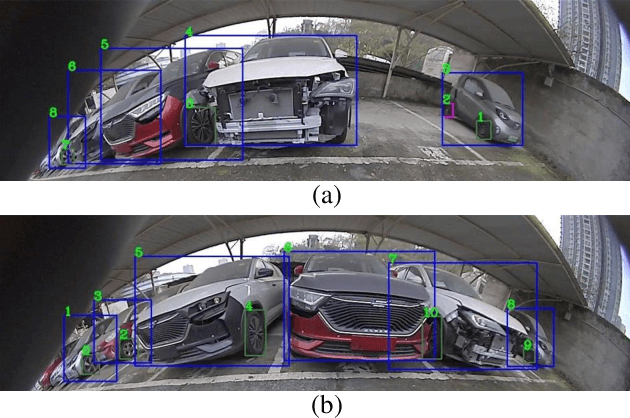
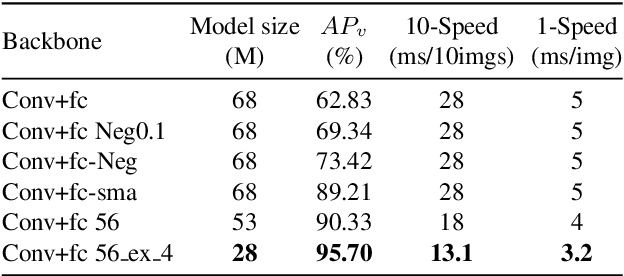
Abstract:It's worth noting that the owner-member relationship between wheels and vehicles has an significant contribution to the 3D perception of vehicles, especially in the embedded environment. However, there are currently two main challenges about the above relationship prediction: i) The traditional heuristic methods based on IoU can hardly deal with the traffic jam scenarios for the occlusion. ii) It is difficult to establish an efficient applicable solution for the vehicle-mounted system. To address these issues, we propose an innovative relationship prediction method, namely DeepWORD, by designing a graph convolution network (GCN). Specifically, we utilize the feature maps with local correlation as the input of nodes to improve the information richness. Besides, we introduce the graph attention network (GAT) to dynamically amend the prior estimation deviation. Furthermore, we establish an annotated owner-member relationship dataset called WORD as a large-scale benchmark, which will be available soon. The experiments demonstrate that our solution achieves state-of-the-art accuracy and real-time in practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge