Xinpeng Wang
Tongji University
NAMeGEn: Creative Name Generation via A Novel Agent-based Multiple Personalized Goal Enhancement Framework
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Trained on diverse human-authored texts, Large Language Models (LLMs) unlocked the potential for Creative Natural Language Generation (CNLG), benefiting various applications like advertising and storytelling. Nevertheless, CNLG still remains difficult due to two main challenges. (1) Multi-objective flexibility: user requirements are often personalized, fine-grained, and pluralistic, which LLMs struggle to satisfy simultaneously; (2) Interpretive complexity: beyond generation, creativity also involves understanding and interpreting implicit meaning to enhance users' perception. These challenges significantly limit current methods, especially in short-form text generation, in generating creative and insightful content. To address this, we focus on Chinese baby naming, a representative short-form CNLG task requiring adherence to explicit user constraints (e.g., length, semantics, anthroponymy) while offering meaningful aesthetic explanations. We propose NAMeGEn, a novel multi-agent optimization framework that iteratively alternates between objective extraction, name generation, and evaluation to meet diverse requirements and generate accurate explanations. To support this task, we further construct a classical Chinese poetry corpus with 17k+ poems to enhance aesthetics, and introduce CBNames, a new benchmark with tailored metrics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that NAMeGEn effectively generates creative names that meet diverse, personalized requirements while providing meaningful explanations, outperforming six baseline methods spanning various LLM backbones without any training.
Is It Thinking or Cheating? Detecting Implicit Reward Hacking by Measuring Reasoning Effort
Oct 01, 2025



Abstract:Reward hacking, where a reasoning model exploits loopholes in a reward function to achieve high rewards without solving the intended task, poses a significant threat. This behavior may be explicit, i.e. verbalized in the model's chain-of-thought (CoT), or implicit, where the CoT appears benign thus bypasses CoT monitors. To detect implicit reward hacking, we propose TRACE (Truncated Reasoning AUC Evaluation). Our key observation is that hacking occurs when exploiting the loophole is easier than solving the actual task. This means that the model is using less `effort' than required to achieve high reward. TRACE quantifies effort by measuring how early a model's reasoning becomes sufficient to pass a verifier. We progressively truncate a model's CoT at various lengths, force the model to answer, and measure the verifier-passing rate at each cutoff. A hacking model, which takes a shortcut, will achieve a high passing rate with only a small fraction of its CoT, yielding a large area under the accuracy-vs-length curve. TRACE achieves over 65% gains over our strongest 72B CoT monitor in math reasoning, and over 30% gains over a 32B monitor in coding. We further show that TRACE can discover unknown loopholes during training. Overall, TRACE offers a scalable unsupervised approach for oversight where current monitoring methods prove ineffective.
Refusal Direction is Universal Across Safety-Aligned Languages
May 22, 2025Abstract:Refusal mechanisms in large language models (LLMs) are essential for ensuring safety. Recent research has revealed that refusal behavior can be mediated by a single direction in activation space, enabling targeted interventions to bypass refusals. While this is primarily demonstrated in an English-centric context, appropriate refusal behavior is important for any language, but poorly understood. In this paper, we investigate the refusal behavior in LLMs across 14 languages using PolyRefuse, a multilingual safety dataset created by translating malicious and benign English prompts into these languages. We uncover the surprising cross-lingual universality of the refusal direction: a vector extracted from English can bypass refusals in other languages with near-perfect effectiveness, without any additional fine-tuning. Even more remarkably, refusal directions derived from any safety-aligned language transfer seamlessly to others. We attribute this transferability to the parallelism of refusal vectors across languages in the embedding space and identify the underlying mechanism behind cross-lingual jailbreaks. These findings provide actionable insights for building more robust multilingual safety defenses and pave the way for a deeper mechanistic understanding of cross-lingual vulnerabilities in LLMs.
Algorithmic Fidelity of Large Language Models in Generating Synthetic German Public Opinions: A Case Study
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:In recent research, large language models (LLMs) have been increasingly used to investigate public opinions. This study investigates the algorithmic fidelity of LLMs, i.e., the ability to replicate the socio-cultural context and nuanced opinions of human participants. Using open-ended survey data from the German Longitudinal Election Studies (GLES), we prompt different LLMs to generate synthetic public opinions reflective of German subpopulations by incorporating demographic features into the persona prompts. Our results show that Llama performs better than other LLMs at representing subpopulations, particularly when there is lower opinion diversity within those groups. Our findings further reveal that the LLM performs better for supporters of left-leaning parties like The Greens and The Left compared to other parties, and matches the least with the right-party AfD. Additionally, the inclusion or exclusion of specific variables in the prompts can significantly impact the models' predictions. These findings underscore the importance of aligning LLMs to more effectively model diverse public opinions while minimizing political biases and enhancing robustness in representativeness.
Understanding When Tree of Thoughts Succeeds: Larger Models Excel in Generation, Not Discrimination
Oct 24, 2024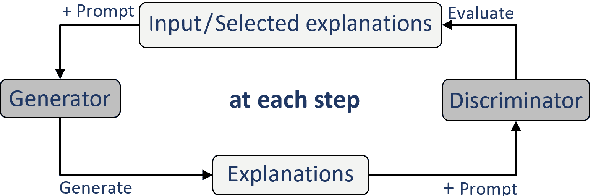
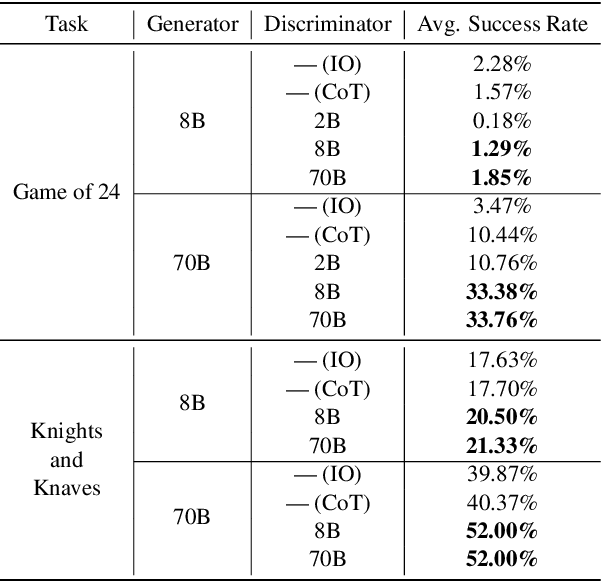

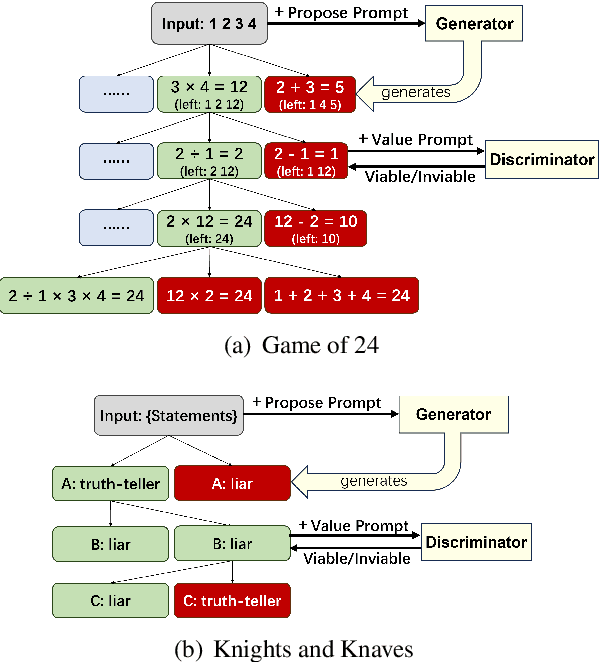
Abstract:Tree of Thoughts (ToT) is a reasoning strategy for Large Language Models (LLMs) that employs a generator to suggest reasoning steps and a discriminator to decide which steps to implement. ToT demonstrates strong performance on reasoning tasks, often surpassing simple methods such as Input-Output (IO) prompting and Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning. However, ToT does not consistently outperform such simpler methods across all models, leaving large knowledge gaps on the conditions under which ToT is most beneficial. In this paper, we analyze the roles of the generator and discriminator separately to better understand the conditions when ToT is beneficial. We find that the generator plays a more critical role than the discriminator in driving the success of ToT. Scaling the generator leads to notable improvements in ToT performance, even when using a smaller model as the discriminator, whereas scaling the discriminator with a fixed generator yields only marginal gains. Our results show that models across different scales exhibit comparable discrimination capabilities, yet differ significantly in their generative performance for ToT.
FedCCRL: Federated Domain Generalization with Cross-Client Representation Learning
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Domain Generalization (DG) aims to train models that can effectively generalize to unseen domains. However, in the context of Federated Learning (FL), where clients collaboratively train a model without directly sharing their data, most existing DG algorithms are not directly applicable to the FL setting due to privacy constraints, as well as the limited data quantity and domain diversity at each client. To tackle these challenges, we propose FedCCRL, a novel federated domain generalization method that significantly improves the model's ability to generalize to unseen domains without compromising privacy or incurring excessive computational and communication costs. Specifically, we adapt MixStyle to the federated setting to transfer domain-specific features while AugMix is employed to perturb domain-invariant features. Furthermore, we leverage supervised contrastive loss for representation alignment and utilize Jensen-Shannon divergence to ensure consistent predictions between original and augmented samples. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that FedCCRL achieves the state-of-the-art performances on the PACS, OfficeHome and miniDomainNet datasets across varying numbers of clients. Code is available at https://github.com/SanphouWang/FedCCRL.
DAMRO: Dive into the Attention Mechanism of LVLM to Reduce Object Hallucination
Oct 06, 2024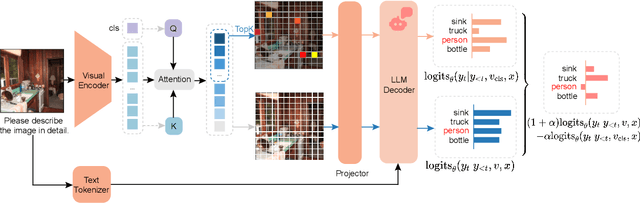
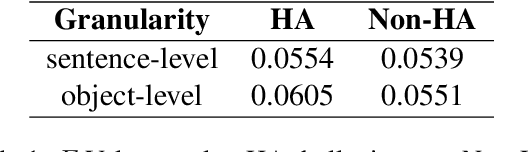

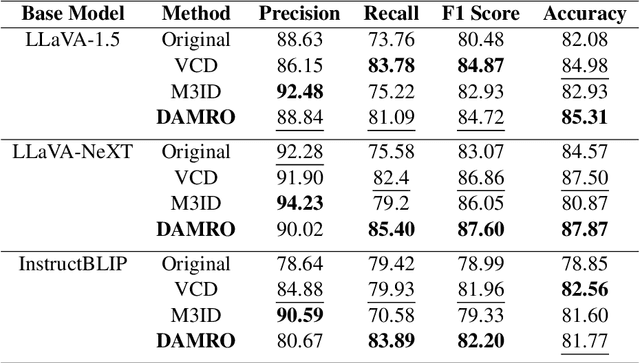
Abstract:Despite the great success of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), they inevitably suffer from hallucination. As we know, both the visual encoder and the Large Language Model (LLM) decoder in LVLMs are Transformer-based, allowing the model to extract visual information and generate text outputs via attention mechanisms. We find that the attention distribution of LLM decoder on image tokens is highly consistent with the visual encoder and both distributions tend to focus on particular background tokens rather than the referred objects in the image. We attribute to the unexpected attention distribution to an inherent flaw in the visual encoder itself, which misguides LLMs to over emphasize the redundant information and generate object hallucination. To address the issue, we propose DAMRO, a novel training-free strategy that $D$ive into $A$ttention $M$echanism of LVLM to $R$educe $O$bject Hallucination. Specifically, our approach employs classification token (CLS) of ViT to filter out high-attention outlier tokens scattered in the background and then eliminate their influence during decoding stage. We evaluate our method on LVLMs including LLaVA-1.5, LLaVA-NeXT and InstructBLIP, using various benchmarks such as POPE, CHAIR, MME and GPT-4V Aided Evaluation. The results demonstrate that our approach significantly reduces the impact of these outlier tokens, thus effectively alleviating the hallucination of LVLMs. The code of our method will be released soon.
Surgical, Cheap, and Flexible: Mitigating False Refusal in Language Models via Single Vector Ablation
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:Training a language model to be both helpful and harmless requires careful calibration of refusal behaviours: Models should refuse to follow malicious instructions or give harmful advice (e.g. "how do I kill someone?"), but they should not refuse safe requests, even if they superficially resemble unsafe ones (e.g. "how do I kill a Python process?"). Avoiding such false refusal, as prior work has shown, is challenging even for highly-capable language models. In this paper, we propose a simple and surgical method for mitigating false refusal in language models via single vector ablation. For a given model, we extract a false refusal vector and show that ablating this vector reduces false refusal rate without negatively impacting model safety and general model capabilities. We also show that our approach can be used for fine-grained calibration of model safety. Our approach is training-free and model-agnostic, making it useful for mitigating the problem of false refusal in current and future language models.
"Seeing the Big through the Small": Can LLMs Approximate Human Judgment Distributions on NLI from a Few Explanations?
Jun 25, 2024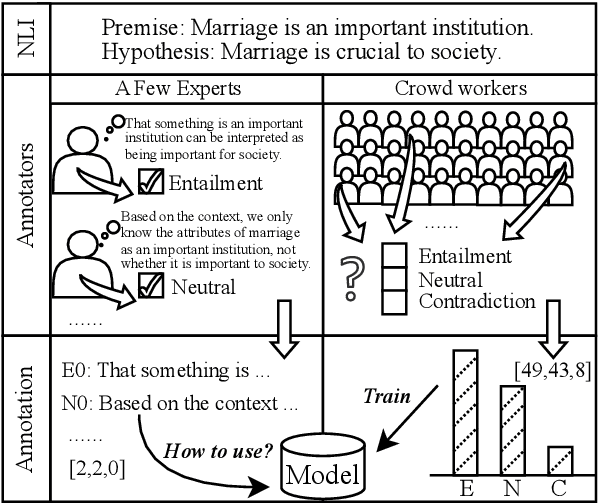
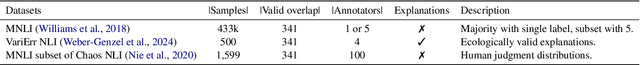
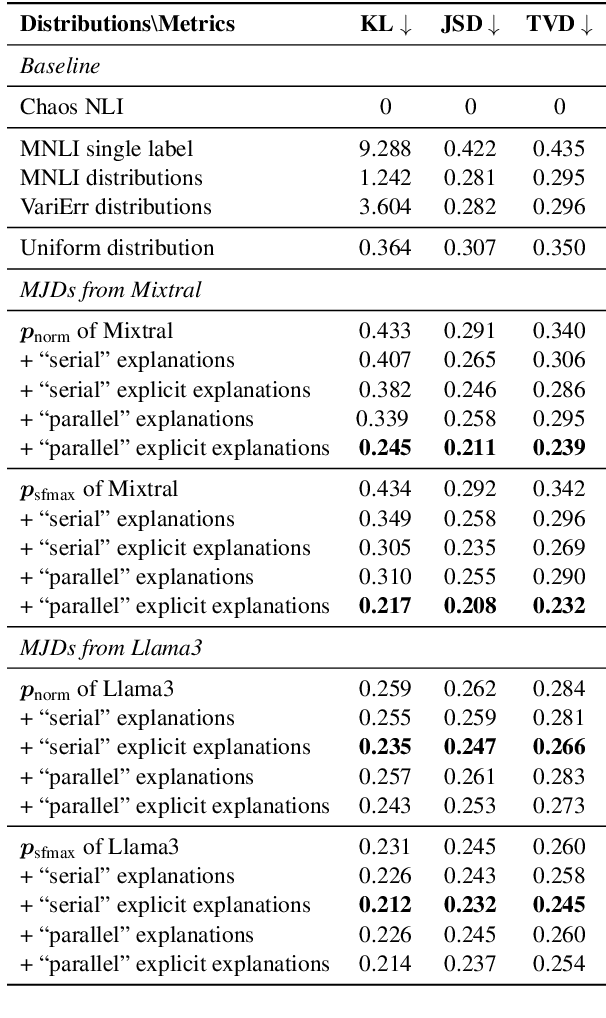
Abstract:Human label variation (HLV) is a valuable source of information that arises when multiple human annotators provide different labels for valid reasons. In Natural Language Inference (NLI) earlier approaches to capturing HLV involve either collecting annotations from many crowd workers to represent human judgment distribution (HJD) or use expert linguists to provide detailed explanations for their chosen labels. While the former method provides denser HJD information, obtaining it is resource-intensive. In contrast, the latter offers richer textual information but it is challenging to scale up to many human judges. Besides, large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used as evaluators (``LLM judges'') but with mixed results, and few works aim to study HJDs. This study proposes to exploit LLMs to approximate HJDs using a small number of expert labels and explanations. Our experiments show that a few explanations significantly improve LLMs' ability to approximate HJDs with and without explicit labels, thereby providing a solution to scale up annotations for HJD. However, fine-tuning smaller soft-label aware models with the LLM-generated model judgment distributions (MJDs) presents partially inconsistent results: while similar in distance, their resulting fine-tuned models and visualized distributions differ substantially. We show the importance of complementing instance-level distance measures with a global-level shape metric and visualization to more effectively evaluate MJDs against human judgment distributions.
The Potential and Challenges of Evaluating Attitudes, Opinions, and Values in Large Language Models
Jun 16, 2024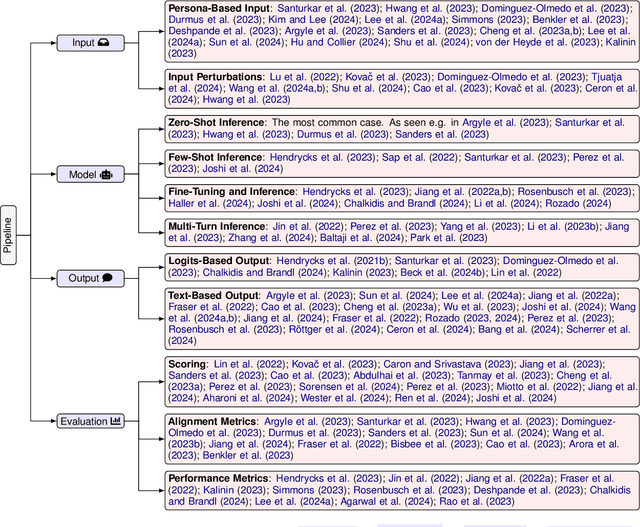
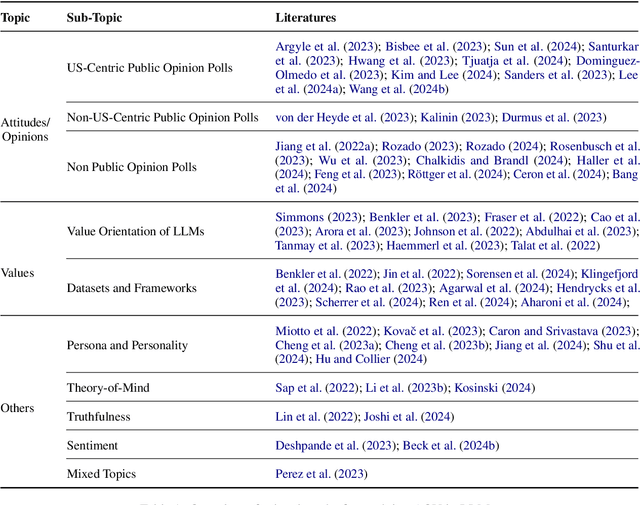
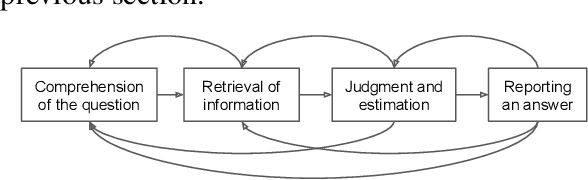
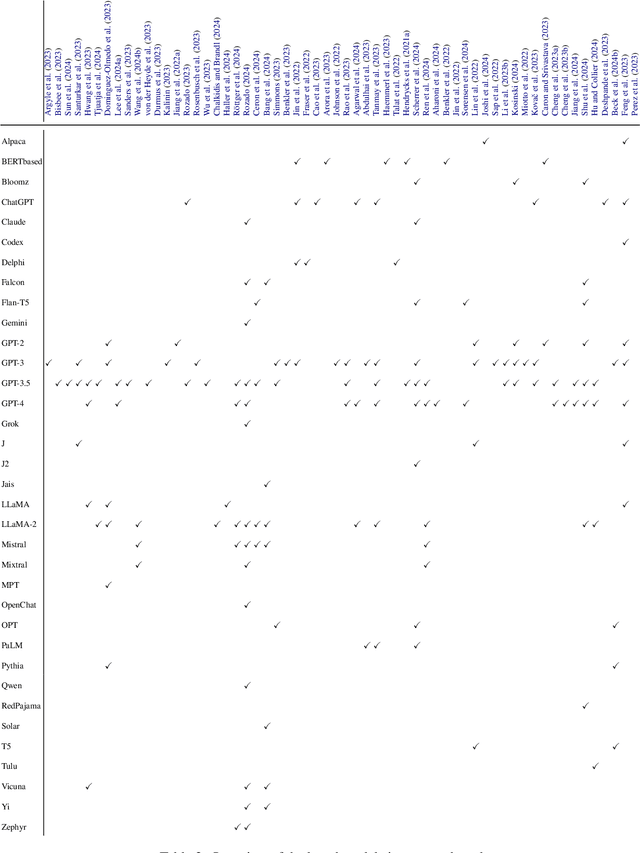
Abstract:Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have sparked wide interest in validating and comprehending the human-like cognitive-behavioral traits LLMs may have. These cognitive-behavioral traits include typically Attitudes, Opinions, Values (AOV). However, measuring AOV embedded within LLMs remains opaque, and different evaluation methods may yield different results. This has led to a lack of clarity on how different studies are related to each other and how they can be interpreted. This paper aims to bridge this gap by providing an overview of recent works on the evaluation of AOV in LLMs. Moreover, we survey related approaches in different stages of the evaluation pipeline in these works. By doing so, we address the potential and challenges with respect to understanding the model, human-AI alignment, and downstream application in social sciences. Finally, we provide practical insights into evaluation methods, model enhancement, and interdisciplinary collaboration, thereby contributing to the evolving landscape of evaluating AOV in LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge