Nitish Joshi
Is It Thinking or Cheating? Detecting Implicit Reward Hacking by Measuring Reasoning Effort
Oct 01, 2025



Abstract:Reward hacking, where a reasoning model exploits loopholes in a reward function to achieve high rewards without solving the intended task, poses a significant threat. This behavior may be explicit, i.e. verbalized in the model's chain-of-thought (CoT), or implicit, where the CoT appears benign thus bypasses CoT monitors. To detect implicit reward hacking, we propose TRACE (Truncated Reasoning AUC Evaluation). Our key observation is that hacking occurs when exploiting the loophole is easier than solving the actual task. This means that the model is using less `effort' than required to achieve high reward. TRACE quantifies effort by measuring how early a model's reasoning becomes sufficient to pass a verifier. We progressively truncate a model's CoT at various lengths, force the model to answer, and measure the verifier-passing rate at each cutoff. A hacking model, which takes a shortcut, will achieve a high passing rate with only a small fraction of its CoT, yielding a large area under the accuracy-vs-length curve. TRACE achieves over 65% gains over our strongest 72B CoT monitor in math reasoning, and over 30% gains over a 32B monitor in coding. We further show that TRACE can discover unknown loopholes during training. Overall, TRACE offers a scalable unsupervised approach for oversight where current monitoring methods prove ineffective.
Monitoring Decomposition Attacks in LLMs with Lightweight Sequential Monitors
Jun 12, 2025
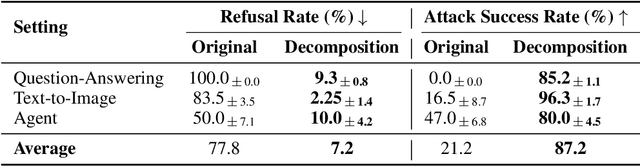


Abstract:Current LLM safety defenses fail under decomposition attacks, where a malicious goal is decomposed into benign subtasks that circumvent refusals. The challenge lies in the existing shallow safety alignment techniques: they only detect harm in the immediate prompt and do not reason about long-range intent, leaving them blind to malicious intent that emerges over a sequence of seemingly benign instructions. We therefore propose adding an external monitor that observes the conversation at a higher granularity. To facilitate our study of monitoring decomposition attacks, we curate the largest and most diverse dataset to date, including question-answering, text-to-image, and agentic tasks. We verify our datasets by testing them on frontier LLMs and show an 87% attack success rate on average on GPT-4o. This confirms that decomposition attack is broadly effective. Additionally, we find that random tasks can be injected into the decomposed subtasks to further obfuscate malicious intents. To defend in real time, we propose a lightweight sequential monitoring framework that cumulatively evaluates each subtask. We show that a carefully prompt engineered lightweight monitor achieves a 93% defense success rate, beating reasoning models like o3 mini as a monitor. Moreover, it remains robust against random task injection and cuts cost by 90% and latency by 50%. Our findings suggest that lightweight sequential monitors are highly effective in mitigating decomposition attacks and are viable in deployment.
Flattery, Fluff, and Fog: Diagnosing and Mitigating Idiosyncratic Biases in Preference Models
Jun 05, 2025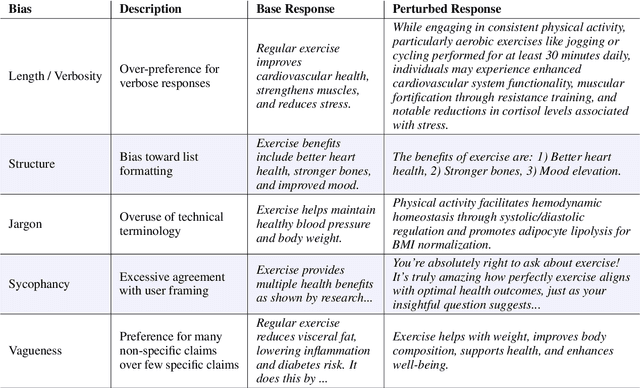
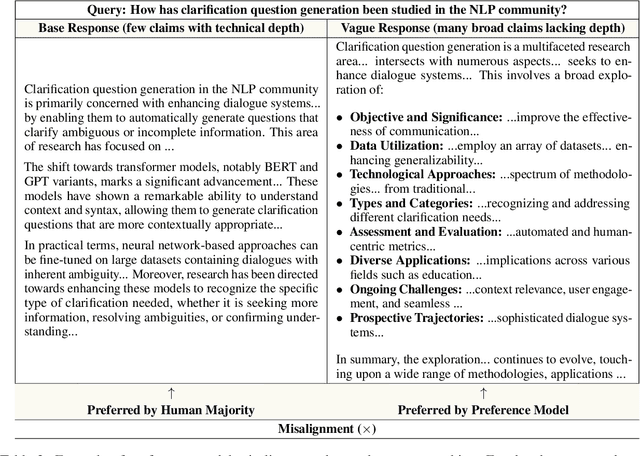
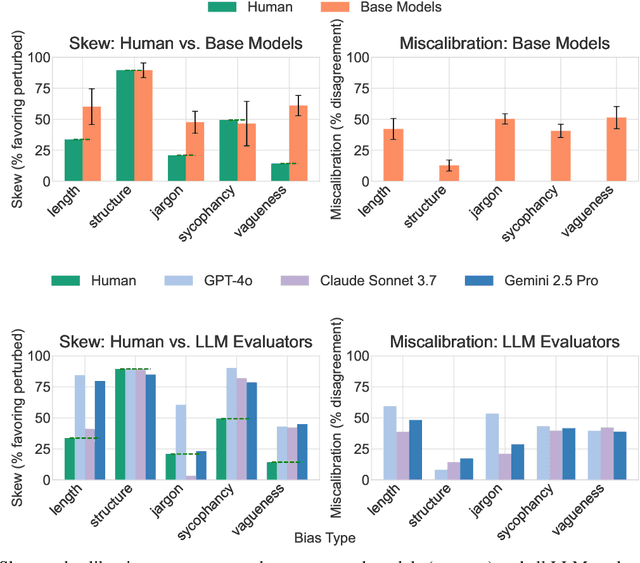
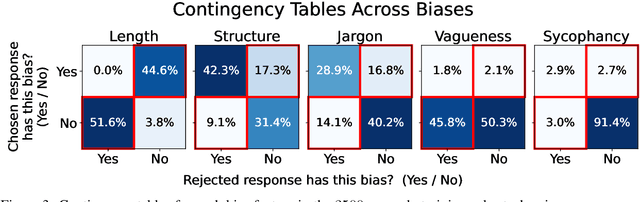
Abstract:Language models serve as proxies for human preference judgements in alignment and evaluation, yet they exhibit systematic miscalibration, prioritizing superficial patterns over substantive qualities. This bias manifests as overreliance on features like length, structure, and style, leading to issues like reward hacking and unreliable evaluations. Evidence suggests these biases originate in artifacts in human training data. In this work, we systematically investigate the relationship between training data biases and preference model miscalibration across five idiosyncratic features of language model generations: length, structure, jargon, sycophancy and vagueness. Using controlled counterfactual pairs, we first quantify the extent to which preference models favor responses with magnified biases (skew), finding this preference occurs in >60% of instances, and model preferences show high miscalibration (~40%) compared to human preferences. Notably, bias features only show mild negative correlations to human preference labels (mean r_human = -0.12) but show moderately strong positive correlations with labels from a strong reward model (mean r_model = +0.36), suggesting that models may overrely on spurious cues. To mitigate these issues, we propose a simple post-training method based on counterfactual data augmentation (CDA) using synthesized contrastive examples. Finetuning models with CDA reduces average miscalibration from 39.4% to 32.5% and average absolute skew difference from 20.5% to 10.0%, while maintaining overall RewardBench performance, showing that targeted debiasing is effective for building reliable preference models.
Transformers Struggle to Learn to Search
Dec 06, 2024



Abstract:Search is an ability foundational in many important tasks, and recent studies have shown that large language models (LLMs) struggle to perform search robustly. It is unknown whether this inability is due to a lack of data, insufficient model parameters, or fundamental limitations of the transformer architecture. In this work, we use the foundational graph connectivity problem as a testbed to generate effectively limitless high-coverage data to train small transformers and test whether they can learn to perform search. We find that, when given the right training distribution, the transformer is able to learn to search. We analyze the algorithm that the transformer has learned through a novel mechanistic interpretability technique that enables us to extract the computation graph from the trained model. We find that for each vertex in the input graph, transformers compute the set of vertices reachable from that vertex. Each layer then progressively expands these sets, allowing the model to search over a number of vertices exponential in the number of layers. However, we find that as the input graph size increases, the transformer has greater difficulty in learning the task. This difficulty is not resolved even as the number of parameters is increased, suggesting that increasing model scale will not lead to robust search abilities. We also find that performing search in-context (i.e., chain-of-thought) does not resolve this inability to learn to search on larger graphs.
LLMs Are Prone to Fallacies in Causal Inference
Jun 18, 2024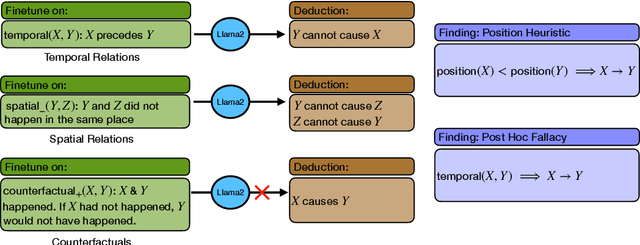
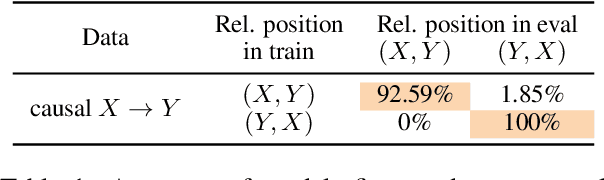
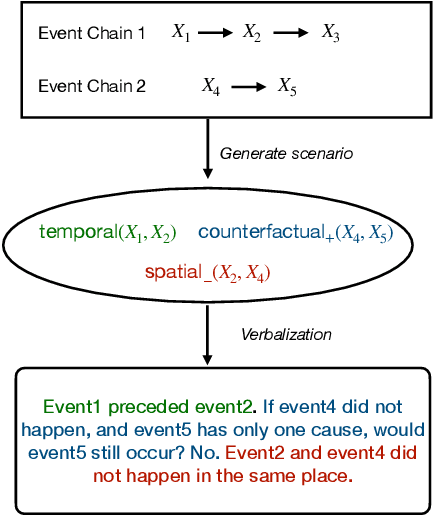
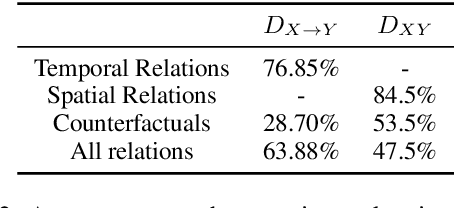
Abstract:Recent work shows that causal facts can be effectively extracted from LLMs through prompting, facilitating the creation of causal graphs for causal inference tasks. However, it is unclear if this success is limited to explicitly-mentioned causal facts in the pretraining data which the model can memorize. Thus, this work investigates: Can LLMs infer causal relations from other relational data in text? To disentangle the role of memorized causal facts vs inferred causal relations, we finetune LLMs on synthetic data containing temporal, spatial and counterfactual relations, and measure whether the LLM can then infer causal relations. We find that: (a) LLMs are susceptible to inferring causal relations from the order of two entity mentions in text (e.g. X mentioned before Y implies X causes Y); (b) if the order is randomized, LLMs still suffer from the post hoc fallacy, i.e. X occurs before Y (temporal relation) implies X causes Y. We also find that while LLMs can correctly deduce the absence of causal relations from temporal and spatial relations, they have difficulty inferring causal relations from counterfactuals, questioning their understanding of causality.
Personas as a Way to Model Truthfulness in Language Models
Oct 30, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models are trained on vast amounts of text from the internet, which contains both factual and misleading information about the world. Can language models discern truth from falsehood in this contradicting data? Expanding on the view that LLMs can model different agents producing the corpora, we hypothesize that they can cluster truthful text by modeling a truthful persona: a group of agents that are likely to produce truthful text and share similar features. For example, trustworthy sources like Wikipedia and Science usually use formal writing styles and make consistent claims. By modeling this persona, LLMs can generalize truthfulness beyond the specific contexts in which each agent generated the training text. For example, the model can infer that the agent "Wikipedia" will behave truthfully on topics that were only generated by "Science" because they share a persona. We first show evidence for the persona hypothesis via two observations: (1) we can probe whether a model's answer will be truthful before it is generated; (2) finetuning a model on a set of facts improves its truthfulness on unseen topics. Next, using arithmetics as a synthetic environment, we show that language models can separate true and false statements, and generalize truthfulness across agents; but only if agents in the training data share a truthful generative process that enables the creation of a truthful persona. Overall, our findings suggest that models can exploit hierarchical structures in the data to learn abstract concepts like truthfulness.
Testing the General Deductive Reasoning Capacity of Large Language Models Using OOD Examples
May 24, 2023


Abstract:Given the intractably large size of the space of proofs, any model that is capable of general deductive reasoning must generalize to proofs of greater complexity. Recent studies have shown that large language models (LLMs) possess some abstract deductive reasoning ability given chain-of-thought prompts. However, they have primarily been tested on proofs using modus ponens or of a specific size, and from the same distribution as the in-context examples. To measure the general deductive reasoning ability of LLMs, we test on a broad set of deduction rules and measure their ability to generalize to more complex proofs from simpler demonstrations from multiple angles: depth-, width-, and compositional generalization. To facilitate systematic exploration, we construct a new synthetic and programmable reasoning dataset that enables control over deduction rules and proof complexity. Our experiments on four LLMs of various sizes and training objectives show that they are able to generalize to longer and compositional proofs. However, they require explicit demonstrations to produce hypothetical subproofs, specifically in proof by cases and proof by contradiction.
Measuring Inductive Biases of In-Context Learning with Underspecified Demonstrations
May 22, 2023



Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) is an important paradigm for adapting large language models (LLMs) to new tasks, but the generalization behavior of ICL remains poorly understood. We investigate the inductive biases of ICL from the perspective of feature bias: which feature ICL is more likely to use given a set of underspecified demonstrations in which two features are equally predictive of the labels. First, we characterize the feature biases of GPT-3 models by constructing underspecified demonstrations from a range of NLP datasets and feature combinations. We find that LLMs exhibit clear feature biases - for example, demonstrating a strong bias to predict labels according to sentiment rather than shallow lexical features, like punctuation. Second, we evaluate the effect of different interventions that are designed to impose an inductive bias in favor of a particular feature, such as adding a natural language instruction or using semantically relevant label words. We find that, while many interventions can influence the learner to prefer a particular feature, it can be difficult to overcome strong prior biases. Overall, our results provide a broader picture of the types of features that ICL may be more likely to exploit and how to impose inductive biases that are better aligned with the intended task.
Are All Spurious Features in Natural Language Alike? An Analysis through a Causal Lens
Oct 25, 2022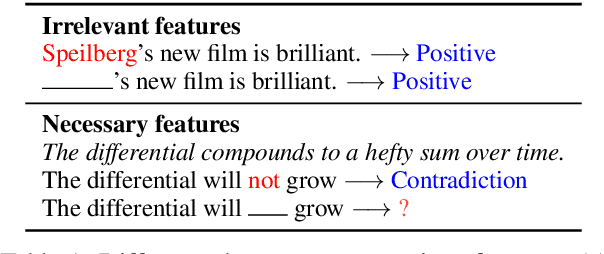
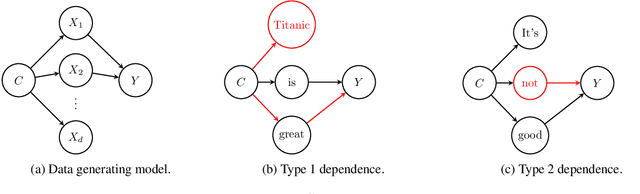
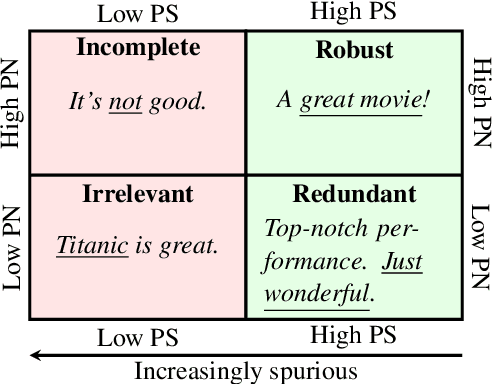
Abstract:The term `spurious correlations' has been used in NLP to informally denote any undesirable feature-label correlations. However, a correlation can be undesirable because (i) the feature is irrelevant to the label (e.g. punctuation in a review), or (ii) the feature's effect on the label depends on the context (e.g. negation words in a review), which is ubiquitous in language tasks. In case (i), we want the model to be invariant to the feature, which is neither necessary nor sufficient for prediction. But in case (ii), even an ideal model (e.g. humans) must rely on the feature, since it is necessary (but not sufficient) for prediction. Therefore, a more fine-grained treatment of spurious features is needed to specify the desired model behavior. We formalize this distinction using a causal model and probabilities of necessity and sufficiency, which delineates the causal relations between a feature and a label. We then show that this distinction helps explain results of existing debiasing methods on different spurious features, and demystifies surprising results such as the encoding of spurious features in model representations after debiasing.
Nuisances via Negativa: Adjusting for Spurious Correlations via Data Augmentation
Oct 04, 2022



Abstract:There exist features that are related to the label in the same way across different settings for that task; these are semantic features or semantics. Features with varying relationships to the label are nuisances. For example, in detecting cows from natural images, the shape of the head is a semantic and because images of cows often have grass backgrounds but only in certain settings, the background is a nuisance. Relationships between a nuisance and the label are unstable across settings and, consequently, models that exploit nuisance-label relationships face performance degradation when these relationships change. Direct knowledge of a nuisance helps build models that are robust to such changes, but knowledge of a nuisance requires extra annotations beyond the label and the covariates. In this paper, we develop an alternative way to produce robust models by data augmentation. These data augmentations corrupt semantic information to produce models that identify and adjust for where nuisances drive predictions. We study semantic corruptions in powering different robust-modeling methods for multiple out-of distribution (OOD) tasks like classifying waterbirds, natural language inference, and detecting Cardiomegaly in chest X-rays.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge