Xiang Pan
LOP: Learning Optimal Pruning for Efficient On-Demand MLLMs Scaling
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Structural pruning techniques are essential for deploying multimodal large language models (MLLMs) across various hardware platforms, from edge devices to cloud servers. However, current pruning methods typically determine optimal strategies through iterative search processes, resulting in substantial computational overhead for on-demand MLLMs adaptation. To address this challenge, we propose LOP, an efficient neural pruning framework that learns optimal pruning strategies from the target pruning constraint, eliminating the need for computationally expensive search-based methods. LOP approach trains autoregressive neural networks (NNs) to directly predict layer-wise pruning strategies adaptive to the target pruning constraint, eliminating the time-consuming iterative searches. Experimental results across multiple tasks show that LOP outperforms state-of-the-art pruning methods in various metrics while achieving up to three orders of magnitude speedup.
Beyond Interpretability: The Gains of Feature Monosemanticity on Model Robustness
Oct 27, 2024Abstract:Deep learning models often suffer from a lack of interpretability due to polysemanticity, where individual neurons are activated by multiple unrelated semantics, resulting in unclear attributions of model behavior. Recent advances in monosemanticity, where neurons correspond to consistent and distinct semantics, have significantly improved interpretability but are commonly believed to compromise accuracy. In this work, we challenge the prevailing belief of the accuracy-interpretability tradeoff, showing that monosemantic features not only enhance interpretability but also bring concrete gains in model performance. Across multiple robust learning scenarios-including input and label noise, few-shot learning, and out-of-domain generalization-our results show that models leveraging monosemantic features significantly outperform those relying on polysemantic features. Furthermore, we provide empirical and theoretical understandings on the robustness gains of feature monosemanticity. Our preliminary analysis suggests that monosemanticity, by promoting better separation of feature representations, leads to more robust decision boundaries. This diverse evidence highlights the generality of monosemanticity in improving model robustness. As a first step in this new direction, we embark on exploring the learning benefits of monosemanticity beyond interpretability, supporting the long-standing hypothesis of linking interpretability and robustness. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/PKU-ML/Beyond_Interpretability}.
Sketchy Moment Matching: Toward Fast and Provable Data Selection for Finetuning
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:We revisit data selection in a modern context of finetuning from a fundamental perspective. Extending the classical wisdom of variance minimization in low dimensions to high-dimensional finetuning, our generalization analysis unveils the importance of additionally reducing bias induced by low-rank approximation. Inspired by the variance-bias tradeoff in high dimensions from the theory, we introduce Sketchy Moment Matching (SkMM), a scalable data selection scheme with two stages. (i) First, the bias is controlled using gradient sketching that explores the finetuning parameter space for an informative low-dimensional subspace $\mathcal{S}$; (ii) then the variance is reduced over $\mathcal{S}$ via moment matching between the original and selected datasets. Theoretically, we show that gradient sketching is fast and provably accurate: selecting $n$ samples by reducing variance over $\mathcal{S}$ preserves the fast-rate generalization $O(\dim(\mathcal{S})/n)$, independent of the parameter dimension. Empirically, we concretize the variance-bias balance via synthetic experiments and demonstrate the effectiveness of SkMM for finetuning in real vision tasks.
AIS 2024 Challenge on Video Quality Assessment of User-Generated Content: Methods and Results
Apr 24, 2024



Abstract:This paper reviews the AIS 2024 Video Quality Assessment (VQA) Challenge, focused on User-Generated Content (UGC). The aim of this challenge is to gather deep learning-based methods capable of estimating the perceptual quality of UGC videos. The user-generated videos from the YouTube UGC Dataset include diverse content (sports, games, lyrics, anime, etc.), quality and resolutions. The proposed methods must process 30 FHD frames under 1 second. In the challenge, a total of 102 participants registered, and 15 submitted code and models. The performance of the top-5 submissions is reviewed and provided here as a survey of diverse deep models for efficient video quality assessment of user-generated content.
NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Short-form UGC Video Quality Assessment: Methods and Results
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Shortform UGC Video Quality Assessment (S-UGC VQA), where various excellent solutions are submitted and evaluated on the collected dataset KVQ from popular short-form video platform, i.e., Kuaishou/Kwai Platform. The KVQ database is divided into three parts, including 2926 videos for training, 420 videos for validation, and 854 videos for testing. The purpose is to build new benchmarks and advance the development of S-UGC VQA. The competition had 200 participants and 13 teams submitted valid solutions for the final testing phase. The proposed solutions achieved state-of-the-art performances for S-UGC VQA. The project can be found at https://github.com/lixinustc/KVQChallenge-CVPR-NTIRE2024.
Bridging Domains with Approximately Shared Features
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:Multi-source domain adaptation aims to reduce performance degradation when applying machine learning models to unseen domains. A fundamental challenge is devising the optimal strategy for feature selection. Existing literature is somewhat paradoxical: some advocate for learning invariant features from source domains, while others favor more diverse features. To address the challenge, we propose a statistical framework that distinguishes the utilities of features based on the variance of their correlation to label $y$ across domains. Under our framework, we design and analyze a learning procedure consisting of learning approximately shared feature representation from source tasks and fine-tuning it on the target task. Our theoretical analysis necessitates the importance of learning approximately shared features instead of only the strictly invariant features and yields an improved population risk compared to previous results on both source and target tasks, thus partly resolving the paradox mentioned above. Inspired by our theory, we proposed a more practical way to isolate the content (invariant+approximately shared) from environmental features and further consolidate our theoretical findings.
Transferable Learned Image Compression-Resistant Adversarial Perturbations
Jan 06, 2024Abstract:Adversarial attacks can readily disrupt the image classification system, revealing the vulnerability of DNN-based recognition tasks. While existing adversarial perturbations are primarily applied to uncompressed images or compressed images by the traditional image compression method, i.e., JPEG, limited studies have investigated the robustness of models for image classification in the context of DNN-based image compression. With the rapid evolution of advanced image compression, DNN-based learned image compression has emerged as the promising approach for transmitting images in many security-critical applications, such as cloud-based face recognition and autonomous driving, due to its superior performance over traditional compression. Therefore, there is a pressing need to fully investigate the robustness of a classification system post-processed by learned image compression. To bridge this research gap, we explore the adversarial attack on a new pipeline that targets image classification models that utilize learned image compressors as pre-processing modules. Furthermore, to enhance the transferability of perturbations across various quality levels and architectures of learned image compression models, we introduce a saliency score-based sampling method to enable the fast generation of transferable perturbation. Extensive experiments with popular attack methods demonstrate the enhanced transferability of our proposed method when attacking images that have been post-processed with different learned image compression models.
Corner-to-Center Long-range Context Model for Efficient Learned Image Compression
Nov 29, 2023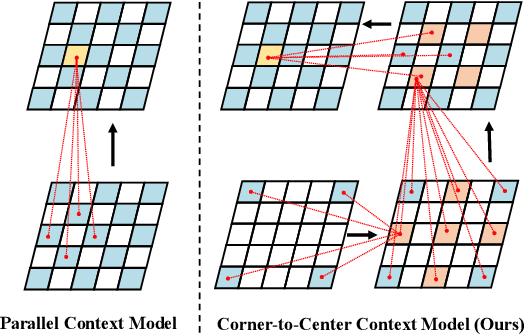
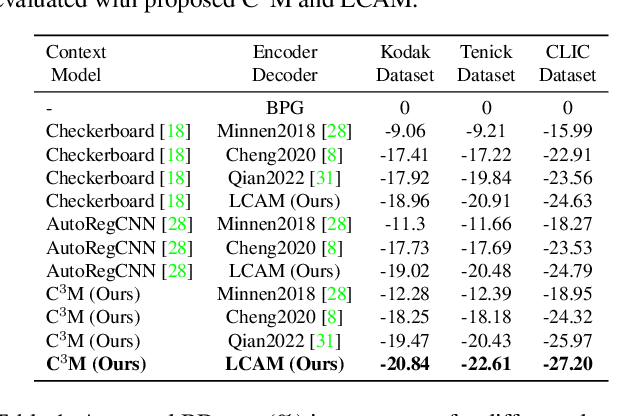
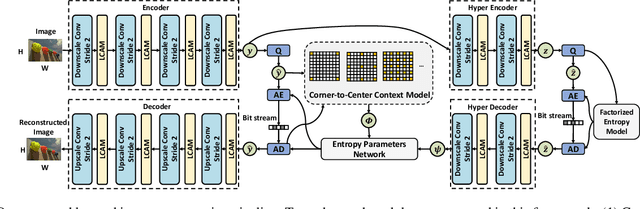

Abstract:In the framework of learned image compression, the context model plays a pivotal role in capturing the dependencies among latent representations. To reduce the decoding time resulting from the serial autoregressive context model, the parallel context model has been proposed as an alternative that necessitates only two passes during the decoding phase, thus facilitating efficient image compression in real-world scenarios. However, performance degradation occurs due to its incomplete casual context. To tackle this issue, we conduct an in-depth analysis of the performance degradation observed in existing parallel context models, focusing on two aspects: the Quantity and Quality of information utilized for context prediction and decoding. Based on such analysis, we propose the \textbf{Corner-to-Center transformer-based Context Model (C$^3$M)} designed to enhance context and latent predictions and improve rate-distortion performance. Specifically, we leverage the logarithmic-based prediction order to predict more context features from corner to center progressively. In addition, to enlarge the receptive field in the analysis and synthesis transformation, we use the Long-range Crossing Attention Module (LCAM) in the encoder/decoder to capture the long-range semantic information by assigning the different window shapes in different channels. Extensive experimental evaluations show that the proposed method is effective and outperforms the state-of-the-art parallel methods. Finally, according to the subjective analysis, we suggest that improving the detailed representation in transformer-based image compression is a promising direction to be explored.
PostRainBench: A comprehensive benchmark and a new model for precipitation forecasting
Oct 05, 2023



Abstract:Accurate precipitation forecasting is a vital challenge of both scientific and societal importance. Data-driven approaches have emerged as a widely used solution for addressing this challenge. However, solely relying on data-driven approaches has limitations in modeling the underlying physics, making accurate predictions difficult. Coupling AI-based post-processing techniques with traditional Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) methods offers a more effective solution for improving forecasting accuracy. Despite previous post-processing efforts, accurately predicting heavy rainfall remains challenging due to the imbalanced precipitation data across locations and complex relationships between multiple meteorological variables. To address these limitations, we introduce the PostRainBench, a comprehensive multi-variable NWP post-processing benchmark consisting of three datasets for NWP post-processing-based precipitation forecasting. We propose CAMT, a simple yet effective Channel Attention Enhanced Multi-task Learning framework with a specially designed weighted loss function. Its flexible design allows for easy plug-and-play integration with various backbones. Extensive experimental results on the proposed benchmark show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 6.3%, 4.7%, and 26.8% in rain CSI on the three datasets respectively. Most notably, our model is the first deep learning-based method to outperform traditional Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) approaches in extreme precipitation conditions. It shows improvements of 15.6%, 17.4%, and 31.8% over NWP predictions in heavy rain CSI on respective datasets. These results highlight the potential impact of our model in reducing the severe consequences of extreme weather events.
Reconstruction Distortion of Learned Image Compression with Imperceptible Perturbations
Jun 01, 2023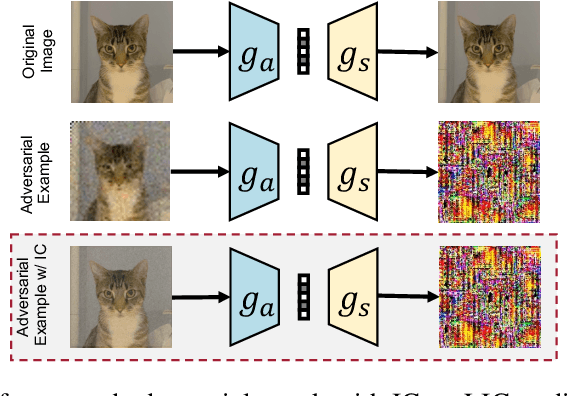
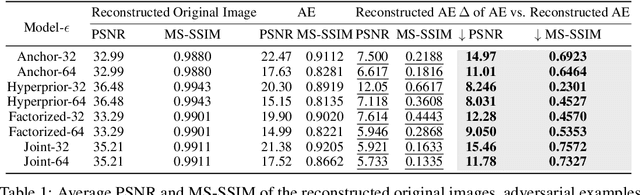

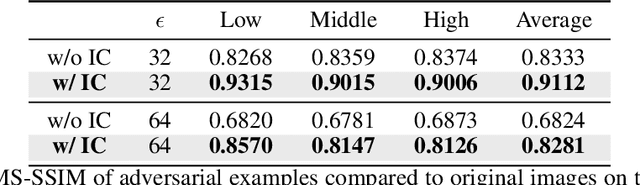
Abstract:Learned Image Compression (LIC) has recently become the trending technique for image transmission due to its notable performance. Despite its popularity, the robustness of LIC with respect to the quality of image reconstruction remains under-explored. In this paper, we introduce an imperceptible attack approach designed to effectively degrade the reconstruction quality of LIC, resulting in the reconstructed image being severely disrupted by noise where any object in the reconstructed images is virtually impossible. More specifically, we generate adversarial examples by introducing a Frobenius norm-based loss function to maximize the discrepancy between original images and reconstructed adversarial examples. Further, leveraging the insensitivity of high-frequency components to human vision, we introduce Imperceptibility Constraint (IC) to ensure that the perturbations remain inconspicuous. Experiments conducted on the Kodak dataset using various LIC models demonstrate effectiveness. In addition, we provide several findings and suggestions for designing future defenses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge