Robert Litschko
Decoupling the Effect of Chain-of-Thought Reasoning: A Human Label Variation Perspective
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Reasoning-tuned LLMs utilizing long Chain-of-Thought (CoT) excel at single-answer tasks, yet their ability to model Human Label Variation--which requires capturing probabilistic ambiguity rather than resolving it--remains underexplored. We investigate this through systematic disentanglement experiments on distribution-based tasks, employing Cross-CoT experiments to isolate the effect of reasoning text from intrinsic model priors. We observe a distinct "decoupled mechanism": while CoT improves distributional alignment, final accuracy is dictated by CoT content (99% variance contribution), whereas distributional ranking is governed by model priors (over 80%). Step-wise analysis further shows that while CoT's influence on accuracy grows monotonically during the reasoning process, distributional structure is largely determined by LLM's intrinsic priors. These findings suggest that long CoT serves as a decisive LLM decision-maker for the top option but fails to function as a granular distribution calibrator for ambiguous tasks.
Evaluating Large Language Models for Cross-Lingual Retrieval
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Multi-stage information retrieval (IR) has become a widely-adopted paradigm in search. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have been extensively evaluated as second-stage reranking models for monolingual IR, a systematic large-scale comparison is still lacking for cross-lingual IR (CLIR). Moreover, while prior work shows that LLM-based rerankers improve CLIR performance, their evaluation setup relies on lexical retrieval with machine translation (MT) for the first stage. This is not only prohibitively expensive but also prone to error propagation across stages. Our evaluation on passage-level and document-level CLIR reveals that further gains can be achieved with multilingual bi-encoders as first-stage retrievers and that the benefits of translation diminishes with stronger reranking models. We further show that pairwise rerankers based on instruction-tuned LLMs perform competitively with listwise rerankers. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to study the interaction between retrievers and rerankers in two-stage CLIR with LLMs. Our findings reveal that, without MT, current state-of-the-art rerankers fall severely short when directly applied in CLIR.
Cross-Dialect Information Retrieval: Information Access in Low-Resource and High-Variance Languages
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:A large amount of local and culture-specific knowledge (e.g., people, traditions, food) can only be found in documents written in dialects. While there has been extensive research conducted on cross-lingual information retrieval (CLIR), the field of cross-dialect retrieval (CDIR) has received limited attention. Dialect retrieval poses unique challenges due to the limited availability of resources to train retrieval models and the high variability in non-standardized languages. We study these challenges on the example of German dialects and introduce the first German dialect retrieval dataset, dubbed WikiDIR, which consists of seven German dialects extracted from Wikipedia. Using WikiDIR, we demonstrate the weakness of lexical methods in dealing with high lexical variation in dialects. We further show that commonly used zero-shot cross-lingual transfer approach with multilingual encoders do not transfer well to extremely low-resource setups, motivating the need for resource-lean and dialect-specific retrieval models. We finally demonstrate that (document) translation is an effective way to reduce the dialect gap in CDIR.
Behavioral Testing: Can Large Language Models Implicitly Resolve Ambiguous Entities?
Jul 25, 2024



Abstract:One of the major aspects contributing to the striking performance of large language models (LLMs) is the vast amount of factual knowledge accumulated during pre-training. Yet, many LLMs suffer from self-inconsistency, which raises doubts about their trustworthiness and reliability. In this paper, we focus on entity type ambiguity and analyze current state-of-the-art LLMs for their proficiency and consistency in applying their factual knowledge when prompted for entities under ambiguity. To do so, we propose an evaluation protocol that disentangles knowing from applying knowledge, and test state-of-the-art LLMs on 49 entities. Our experiments reveal that LLMs perform poorly with ambiguous prompts, achieving only 80% accuracy. Our results further demonstrate systematic discrepancies in LLM behavior and their failure to consistently apply information, indicating that the models can exhibit knowledge without being able to utilize it, significant biases for preferred readings, as well as self inconsistencies. Our study highlights the importance of handling entity ambiguity in future for more trustworthy LLMs
An Empirical Comparison of Generative Approaches for Product Attribute-Value Identification
Jul 01, 2024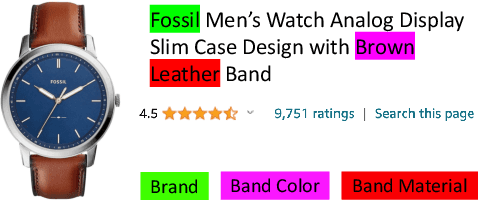
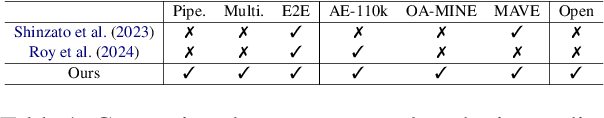
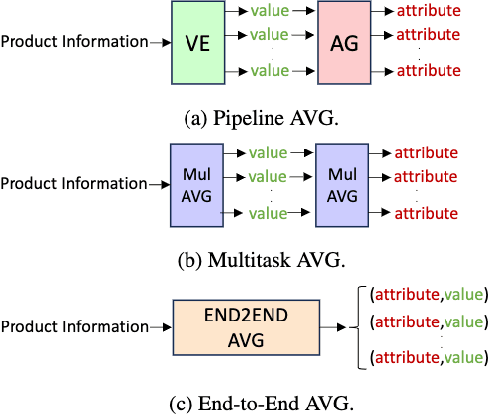
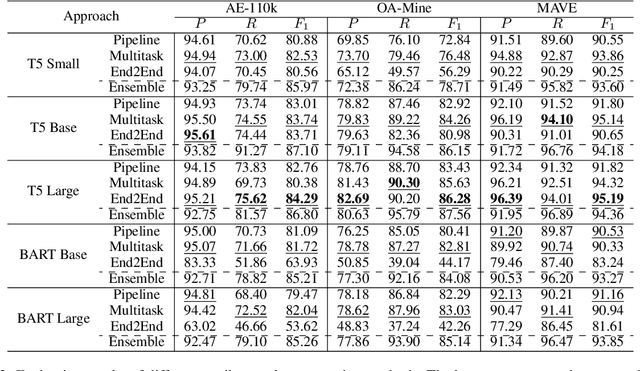
Abstract:Product attributes are crucial for e-commerce platforms, supporting applications like search, recommendation, and question answering. The task of Product Attribute and Value Identification (PAVI) involves identifying both attributes and their values from product information. In this paper, we formulate PAVI as a generation task and provide, to the best of our knowledge, the most comprehensive evaluation of PAVI so far. We compare three different attribute-value generation (AVG) strategies based on fine-tuning encoder-decoder models on three datasets. Experiments show that end-to-end AVG approach, which is computationally efficient, outperforms other strategies. However, there are differences depending on model sizes and the underlying language model. The code to reproduce all experiments is available at: https://github.com/kassemsabeh/pavi-avg
"Seeing the Big through the Small": Can LLMs Approximate Human Judgment Distributions on NLI from a Few Explanations?
Jun 25, 2024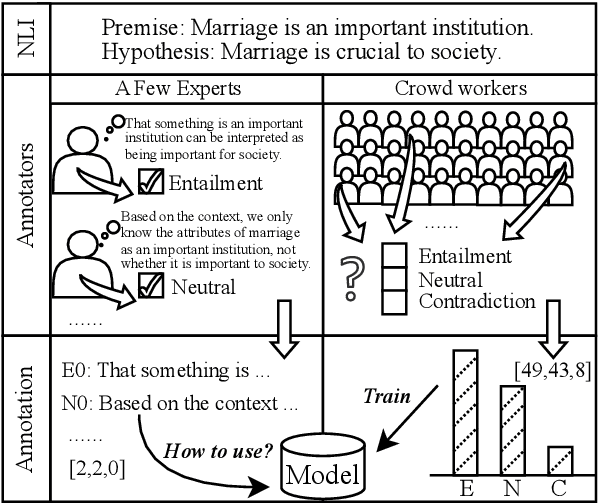
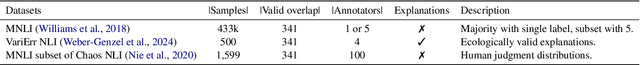
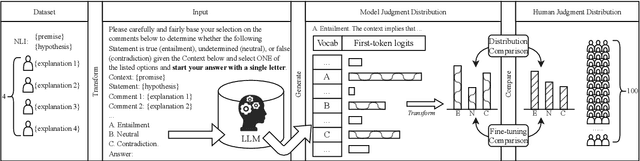
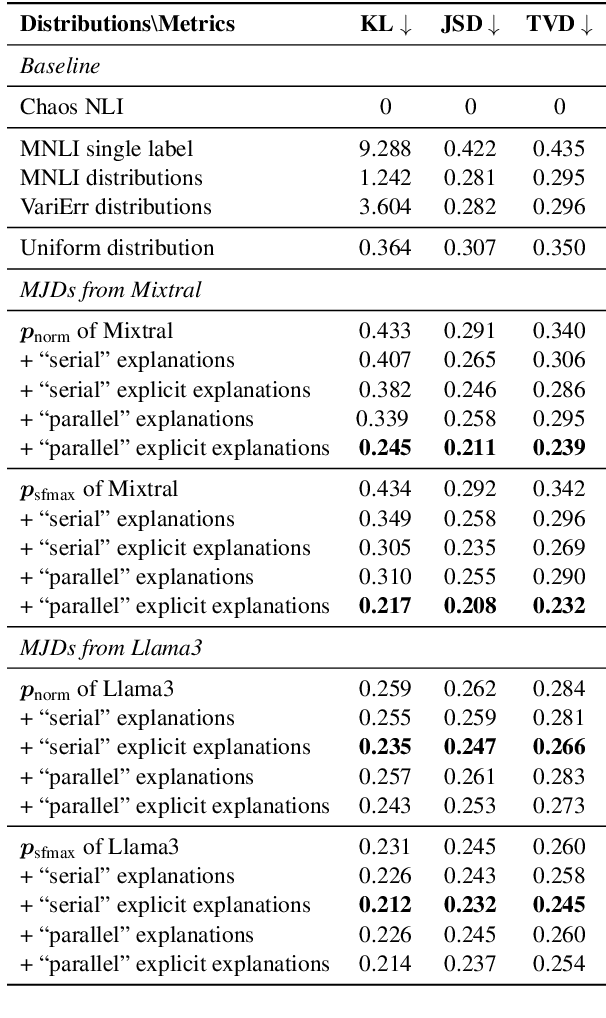
Abstract:Human label variation (HLV) is a valuable source of information that arises when multiple human annotators provide different labels for valid reasons. In Natural Language Inference (NLI) earlier approaches to capturing HLV involve either collecting annotations from many crowd workers to represent human judgment distribution (HJD) or use expert linguists to provide detailed explanations for their chosen labels. While the former method provides denser HJD information, obtaining it is resource-intensive. In contrast, the latter offers richer textual information but it is challenging to scale up to many human judges. Besides, large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used as evaluators (``LLM judges'') but with mixed results, and few works aim to study HJDs. This study proposes to exploit LLMs to approximate HJDs using a small number of expert labels and explanations. Our experiments show that a few explanations significantly improve LLMs' ability to approximate HJDs with and without explicit labels, thereby providing a solution to scale up annotations for HJD. However, fine-tuning smaller soft-label aware models with the LLM-generated model judgment distributions (MJDs) presents partially inconsistent results: while similar in distance, their resulting fine-tuned models and visualized distributions differ substantially. We show the importance of complementing instance-level distance measures with a global-level shape metric and visualization to more effectively evaluate MJDs against human judgment distributions.
MaiNLP at SemEval-2024 Task 1: Analyzing Source Language Selection in Cross-Lingual Textual Relatedness
Apr 03, 2024
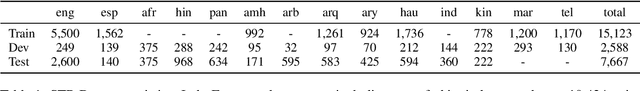
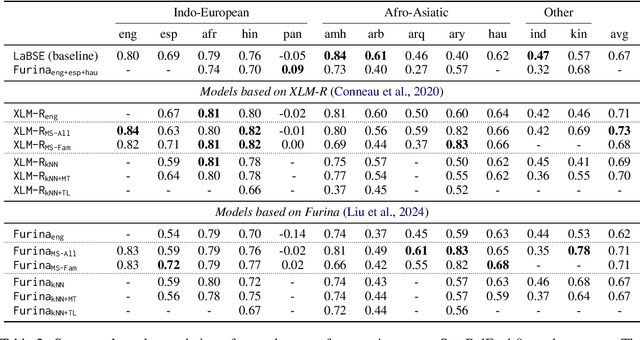
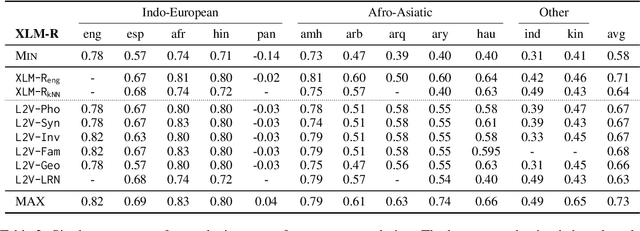
Abstract:This paper presents our system developed for the SemEval-2024 Task 1: Semantic Textual Relatedness (STR), on Track C: Cross-lingual. The task aims to detect semantic relatedness of two sentences in a given target language without access to direct supervision (i.e. zero-shot cross-lingual transfer). To this end, we focus on different source language selection strategies on two different pre-trained languages models: XLM-R and Furina. We experiment with 1) single-source transfer and select source languages based on typological similarity, 2) augmenting English training data with the two nearest-neighbor source languages, and 3) multi-source transfer where we compare selecting on all training languages against languages from the same family. We further study machine translation-based data augmentation and the impact of script differences. Our submission achieved the first place in the C8 (Kinyarwanda) test set.
Vicinal Risk Minimization for Few-Shot Cross-lingual Transfer in Abusive Language Detection
Nov 03, 2023Abstract:Cross-lingual transfer learning from high-resource to medium and low-resource languages has shown encouraging results. However, the scarcity of resources in target languages remains a challenge. In this work, we resort to data augmentation and continual pre-training for domain adaptation to improve cross-lingual abusive language detection. For data augmentation, we analyze two existing techniques based on vicinal risk minimization and propose MIXAG, a novel data augmentation method which interpolates pairs of instances based on the angle of their representations. Our experiments involve seven languages typologically distinct from English and three different domains. The results reveal that the data augmentation strategies can enhance few-shot cross-lingual abusive language detection. Specifically, we observe that consistently in all target languages, MIXAG improves significantly in multidomain and multilingual environments. Finally, we show through an error analysis how the domain adaptation can favour the class of abusive texts (reducing false negatives), but at the same time, declines the precision of the abusive language detection model.
Establishing Trustworthiness: Rethinking Tasks and Model Evaluation
Oct 23, 2023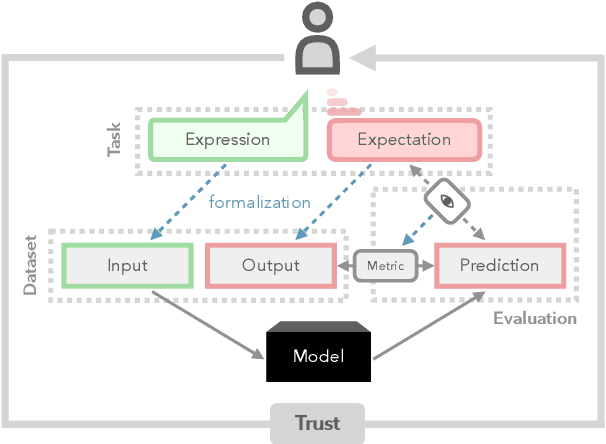
Abstract:Language understanding is a multi-faceted cognitive capability, which the Natural Language Processing (NLP) community has striven to model computationally for decades. Traditionally, facets of linguistic intelligence have been compartmentalized into tasks with specialized model architectures and corresponding evaluation protocols. With the advent of large language models (LLMs) the community has witnessed a dramatic shift towards general purpose, task-agnostic approaches powered by generative models. As a consequence, the traditional compartmentalized notion of language tasks is breaking down, followed by an increasing challenge for evaluation and analysis. At the same time, LLMs are being deployed in more real-world scenarios, including previously unforeseen zero-shot setups, increasing the need for trustworthy and reliable systems. Therefore, we argue that it is time to rethink what constitutes tasks and model evaluation in NLP, and pursue a more holistic view on language, placing trustworthiness at the center. Towards this goal, we review existing compartmentalized approaches for understanding the origins of a model's functional capacity, and provide recommendations for more multi-faceted evaluation protocols.
Donkii: Can Annotation Error Detection Methods Find Errors in Instruction-Tuning Datasets?
Sep 04, 2023



Abstract:Instruction-tuning has become an integral part of training pipelines for Large Language Models (LLMs) and has been shown to yield strong performance gains. In an orthogonal line of research, Annotation Error Detection (AED) has emerged as a tool for detecting quality issues of gold-standard labels. But so far, the application of AED methods is limited to discriminative settings. It is an open question how well AED methods generalize to generative settings which are becoming widespread via generative LLMs. In this work, we present a first and new benchmark for AED on instruction-tuning data: Donkii. It encompasses three instruction-tuning datasets enriched with annotations by experts and semi-automatic methods. We find that all three datasets contain clear-cut errors that sometimes directly propagate into instruction-tuned LLMs. We propose four AED baselines for the generative setting and evaluate them comprehensively on the newly introduced dataset. Our results demonstrate that choosing the right AED method and model size is indeed crucial, thereby deriving practical recommendations. To gain insights, we provide a first case-study to examine how the quality of the instruction-tuning datasets influences downstream performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge