Anastasiia Sedova
Behavioral Testing: Can Large Language Models Implicitly Resolve Ambiguous Entities?
Jul 25, 2024



Abstract:One of the major aspects contributing to the striking performance of large language models (LLMs) is the vast amount of factual knowledge accumulated during pre-training. Yet, many LLMs suffer from self-inconsistency, which raises doubts about their trustworthiness and reliability. In this paper, we focus on entity type ambiguity and analyze current state-of-the-art LLMs for their proficiency and consistency in applying their factual knowledge when prompted for entities under ambiguity. To do so, we propose an evaluation protocol that disentangles knowing from applying knowledge, and test state-of-the-art LLMs on 49 entities. Our experiments reveal that LLMs perform poorly with ambiguous prompts, achieving only 80% accuracy. Our results further demonstrate systematic discrepancies in LLM behavior and their failure to consistently apply information, indicating that the models can exhibit knowledge without being able to utilize it, significant biases for preferred readings, as well as self inconsistencies. Our study highlights the importance of handling entity ambiguity in future for more trustworthy LLMs
Analysing zero-shot temporal relation extraction on clinical notes using temporal consistency
Jun 17, 2024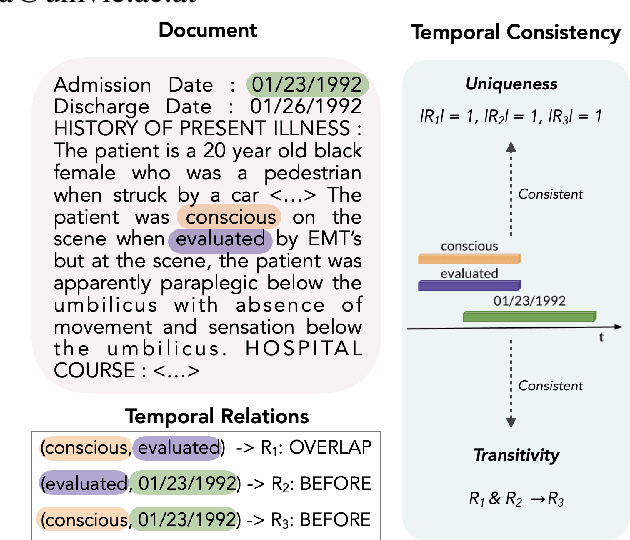
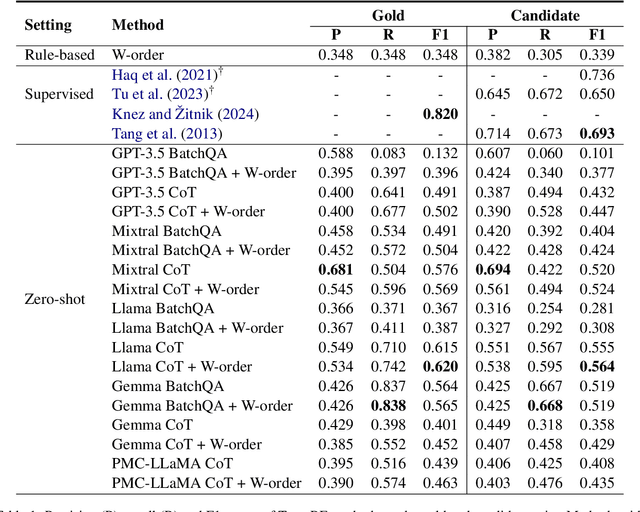
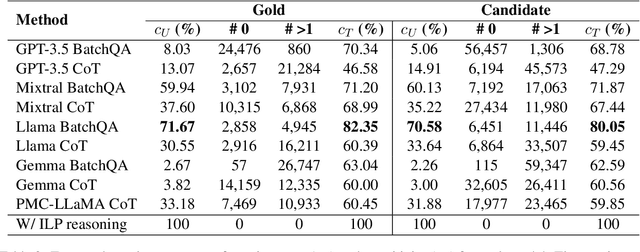
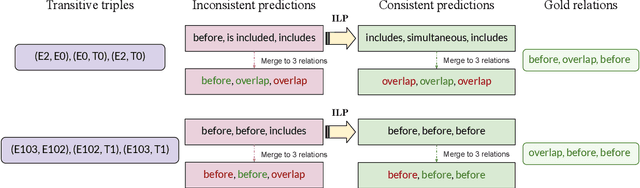
Abstract:This paper presents the first study for temporal relation extraction in a zero-shot setting focusing on biomedical text. We employ two types of prompts and five LLMs (GPT-3.5, Mixtral, Llama 2, Gemma, and PMC-LLaMA) to obtain responses about the temporal relations between two events. Our experiments demonstrate that LLMs struggle in the zero-shot setting performing worse than fine-tuned specialized models in terms of F1 score, showing that this is a challenging task for LLMs. We further contribute a novel comprehensive temporal analysis by calculating consistency scores for each LLM. Our findings reveal that LLMs face challenges in providing responses consistent to the temporal properties of uniqueness and transitivity. Moreover, we study the relation between the temporal consistency of an LLM and its accuracy and whether the latter can be improved by solving temporal inconsistencies. Our analysis shows that even when temporal consistency is achieved, the predictions can remain inaccurate.
Exploring prompts to elicit memorization in masked language model-based named entity recognition
May 05, 2024Abstract:Training data memorization in language models impacts model capability (generalization) and safety (privacy risk). This paper focuses on analyzing prompts' impact on detecting the memorization of 6 masked language model-based named entity recognition models. Specifically, we employ a diverse set of 400 automatically generated prompts, and a pairwise dataset where each pair consists of one person's name from the training set and another name out of the set. A prompt completed with a person's name serves as input for getting the model's confidence in predicting this name. Finally, the prompt performance of detecting model memorization is quantified by the percentage of name pairs for which the model has higher confidence for the name from the training set. We show that the performance of different prompts varies by as much as 16 percentage points on the same model, and prompt engineering further increases the gap. Moreover, our experiments demonstrate that prompt performance is model-dependent but does generalize across different name sets. A comprehensive analysis indicates how prompt performance is influenced by prompt properties, contained tokens, and the model's self-attention weights on the prompt.
Learning with Noisy Labels by Adaptive Gradient-Based Outlier Removal
Jun 28, 2023Abstract:An accurate and substantial dataset is essential for training a reliable and well-performing model. However, even manually annotated datasets contain label errors, not to mention automatically labeled ones. Previous methods for label denoising have primarily focused on detecting outliers and their permanent removal - a process that is likely to over- or underfilter the dataset. In this work, we propose AGRA: a new method for learning with noisy labels by using Adaptive GRAdient-based outlier removal. Instead of cleaning the dataset prior to model training, the dataset is dynamically adjusted during the training process. By comparing the aggregated gradient of a batch of samples and an individual example gradient, our method dynamically decides whether a corresponding example is helpful for the model at this point or is counter-productive and should be left out for the current update. Extensive evaluation on several datasets demonstrates AGRA's effectiveness, while a comprehensive results analysis supports our initial hypothesis: permanent hard outlier removal is not always what model benefits the most from.
ACTC: Active Threshold Calibration for Cold-Start Knowledge Graph Completion
May 10, 2023Abstract:Self-supervised knowledge-graph completion (KGC) relies on estimating a scoring model over (entity, relation, entity)-tuples, for example, by embedding an initial knowledge graph. Prediction quality can be improved by calibrating the scoring model, typically by adjusting the prediction thresholds using manually annotated examples. In this paper, we attempt for the first time cold-start calibration for KGC, where no annotated examples exist initially for calibration, and only a limited number of tuples can be selected for annotation. Our new method ACTC finds good per-relation thresholds efficiently based on a limited set of annotated tuples. Additionally to a few annotated tuples, ACTC also leverages unlabeled tuples by estimating their correctness with Logistic Regression or Gaussian Process classifiers. We also experiment with different methods for selecting candidate tuples for annotation: density-based and random selection. Experiments with five scoring models and an oracle annotator show an improvement of 7% points when using ACTC in the challenging setting with an annotation budget of only 10 tuples, and an average improvement of 4% points over different budgets.
ULF: Unsupervised Labeling Function Correction using Cross-Validation for Weak Supervision
Apr 14, 2022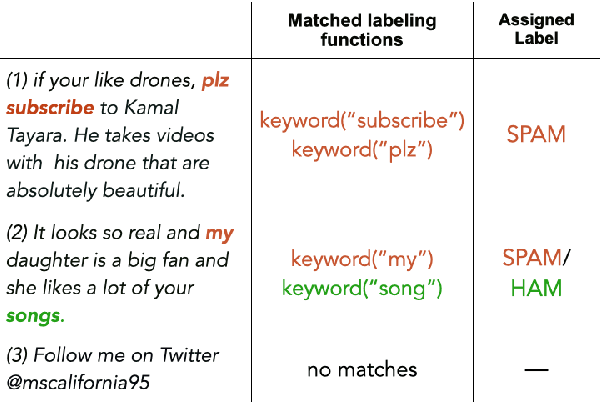
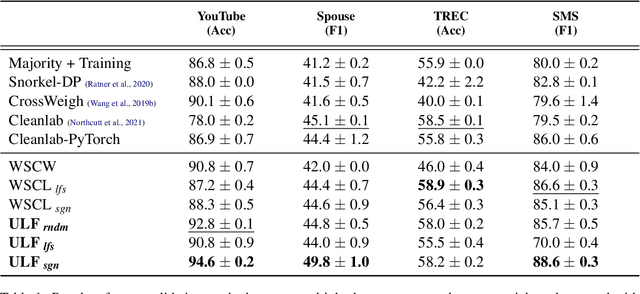
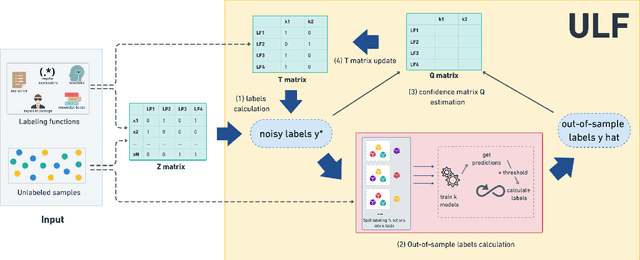

Abstract:A way to overcome expensive and time-consuming manual data labeling is weak supervision - automatic annotation of data samples via a predefined set of labeling functions (LFs), rule-based mechanisms that generate potentially erroneous labels. In this work, we investigate noise reduction techniques for weak supervision based on the principle of k-fold cross-validation. In particular, we extend two frameworks for detecting the erroneous samples in manually annotated data to the weakly supervised setting. Our methods profit from leveraging the information about matching LFs and detect noisy samples more accurately. We also introduce a new algorithm for denoising the weakly annotated data called ULF, that refines the allocation of LFs to classes by estimating the reliable LFs-to-classes joint matrix. Evaluation on several datasets shows that ULF successfully improves weakly supervised learning without using any manually labeled data.
Knodle: Modular Weakly Supervised Learning with PyTorch
May 10, 2021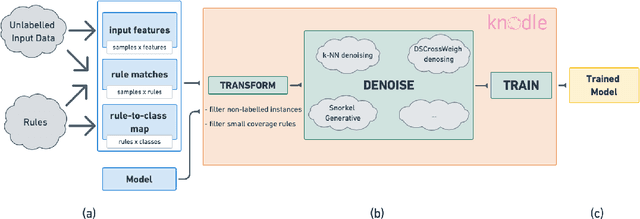
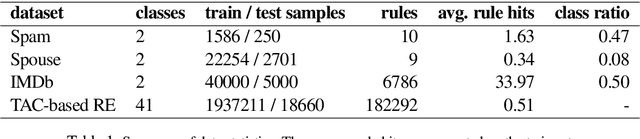
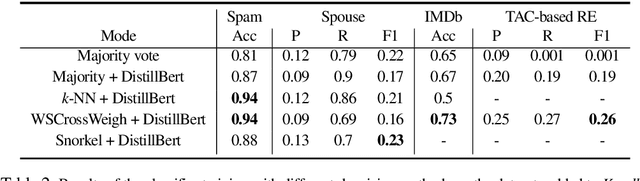
Abstract:Strategies for improving the training and prediction quality of weakly supervised machine learning models vary in how much they are tailored to a specific task or integrated with a specific model architecture. In this work, we propose a software framework Knodle that treats weak data annotations, deep learning models, and methods for improving weakly supervised training as separate, modular components. The standardized interfaces between these independent parts account for data- and model-agnostic weak supervision method development, but still allow the training process to access fine-grained information such as data set characteristics, matches of heuristic rules, as well as elements of the deep learning model ultimately used for prediction. Hence, our framework can encompass a wide range of training methods for improving weak supervision, ranging from methods that only look at correlations of rules and output classes (independently of the machine learning model trained with the resulting labels), to those that harness the interplay of neural networks and weakly labeled data. We illustrate the benchmarking potential of the framework with a performance comparison of several reference implementations on a selection of datasets that are already available in Knodle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge