Diego Frassinelli
Controlling Reading Ease with Gaze-Guided Text Generation
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:The way our eyes move while reading can tell us about the cognitive effort required to process the text. In the present study, we use this fact to generate texts with controllable reading ease. Our method employs a model that predicts human gaze patterns to steer language model outputs towards eliciting certain reading behaviors. We evaluate the approach in an eye-tracking experiment with native and non-native speakers of English. The results demonstrate that the method is effective at making the generated texts easier or harder to read, measured both in terms of reading times and perceived difficulty of the texts. A statistical analysis reveals that the changes in reading behavior are mostly due to features that affect lexical processing. Possible applications of our approach include text simplification for information accessibility and generation of personalized educational material for language learning.
Do LLMs Give Psychometrically Plausible Responses in Educational Assessments?
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Knowing how test takers answer items in educational assessments is essential for test development, to evaluate item quality, and to improve test validity. However, this process usually requires extensive pilot studies with human participants. If large language models (LLMs) exhibit human-like response behavior to test items, this could open up the possibility of using them as pilot participants to accelerate test development. In this paper, we evaluate the human-likeness or psychometric plausibility of responses from 18 instruction-tuned LLMs with two publicly available datasets of multiple-choice test items across three subjects: reading, U.S. history, and economics. Our methodology builds on two theoretical frameworks from psychometrics which are commonly used in educational assessment, classical test theory and item response theory. The results show that while larger models are excessively confident, their response distributions can be more human-like when calibrated with temperature scaling. In addition, we find that LLMs tend to correlate better with humans in reading comprehension items compared to other subjects. However, the correlations are not very strong overall, indicating that LLMs should not be used for piloting educational assessments in a zero-shot setting.
Unveiling the Mystery of Visual Attributes of Concrete and Abstract Concepts: Variability, Nearest Neighbors, and Challenging Categories
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:The visual representation of a concept varies significantly depending on its meaning and the context where it occurs; this poses multiple challenges both for vision and multimodal models. Our study focuses on concreteness, a well-researched lexical-semantic variable, using it as a case study to examine the variability in visual representations. We rely on images associated with approximately 1,000 abstract and concrete concepts extracted from two different datasets: Bing and YFCC. Our goals are: (i) evaluate whether visual diversity in the depiction of concepts can reliably distinguish between concrete and abstract concepts; (ii) analyze the variability of visual features across multiple images of the same concept through a nearest neighbor analysis; and (iii) identify challenging factors contributing to this variability by categorizing and annotating images. Our findings indicate that for classifying images of abstract versus concrete concepts, a combination of basic visual features such as color and texture is more effective than features extracted by more complex models like Vision Transformer (ViT). However, ViTs show better performances in the nearest neighbor analysis, emphasizing the need for a careful selection of visual features when analyzing conceptual variables through modalities other than text.
Behavioral Testing: Can Large Language Models Implicitly Resolve Ambiguous Entities?
Jul 25, 2024



Abstract:One of the major aspects contributing to the striking performance of large language models (LLMs) is the vast amount of factual knowledge accumulated during pre-training. Yet, many LLMs suffer from self-inconsistency, which raises doubts about their trustworthiness and reliability. In this paper, we focus on entity type ambiguity and analyze current state-of-the-art LLMs for their proficiency and consistency in applying their factual knowledge when prompted for entities under ambiguity. To do so, we propose an evaluation protocol that disentangles knowing from applying knowledge, and test state-of-the-art LLMs on 49 entities. Our experiments reveal that LLMs perform poorly with ambiguous prompts, achieving only 80% accuracy. Our results further demonstrate systematic discrepancies in LLM behavior and their failure to consistently apply information, indicating that the models can exhibit knowledge without being able to utilize it, significant biases for preferred readings, as well as self inconsistencies. Our study highlights the importance of handling entity ambiguity in future for more trustworthy LLMs
Generalizable Sarcasm Detection Is Just Around The Corner, Of Course!
Apr 10, 2024



Abstract:We tested the robustness of sarcasm detection models by examining their behavior when fine-tuned on four sarcasm datasets containing varying characteristics of sarcasm: label source (authors vs. third-party), domain (social media/online vs. offline conversations/dialogues), style (aggressive vs. humorous mocking). We tested their prediction performance on the same dataset (intra-dataset) and across different datasets (cross-dataset). For intra-dataset predictions, models consistently performed better when fine-tuned with third-party labels rather than with author labels. For cross-dataset predictions, most models failed to generalize well to the other datasets, implying that one type of dataset cannot represent all sorts of sarcasm with different styles and domains. Compared to the existing datasets, models fine-tuned on the new dataset we release in this work showed the highest generalizability to other datasets. With a manual inspection of the datasets and post-hoc analysis, we attributed the difficulty in generalization to the fact that sarcasm actually comes in different domains and styles. We argue that future sarcasm research should take the broad scope of sarcasm into account.
Investigating the Nature of Disagreements on Mid-Scale Ratings: A Case Study on the Abstractness-Concreteness Continuum
Nov 08, 2023


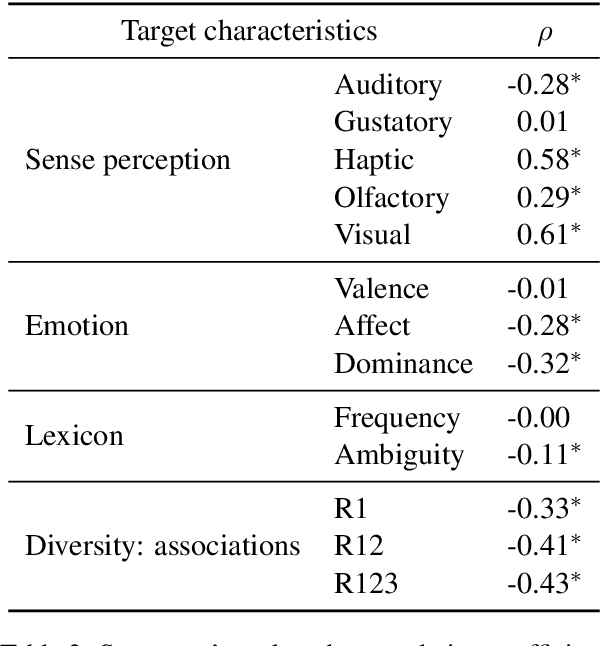
Abstract:Humans tend to strongly agree on ratings on a scale for extreme cases (e.g., a CAT is judged as very concrete), but judgements on mid-scale words exhibit more disagreement. Yet, collected rating norms are heavily exploited across disciplines. Our study focuses on concreteness ratings and (i) implements correlations and supervised classification to identify salient multi-modal characteristics of mid-scale words, and (ii) applies a hard clustering to identify patterns of systematic disagreement across raters. Our results suggest to either fine-tune or filter mid-scale target words before utilising them.
Interpreting Attention Models with Human Visual Attention in Machine Reading Comprehension
Oct 27, 2020



Abstract:While neural networks with attention mechanisms have achieved superior performance on many natural language processing tasks, it remains unclear to which extent learned attention resembles human visual attention. In this paper, we propose a new method that leverages eye-tracking data to investigate the relationship between human visual attention and neural attention in machine reading comprehension. To this end, we introduce a novel 23 participant eye tracking dataset - MQA-RC, in which participants read movie plots and answered pre-defined questions. We compare state of the art networks based on long short-term memory (LSTM), convolutional neural models (CNN) and XLNet Transformer architectures. We find that higher similarity to human attention and performance significantly correlates to the LSTM and CNN models. However, we show this relationship does not hold true for the XLNet models -- despite the fact that the XLNet performs best on this challenging task. Our results suggest that different architectures seem to learn rather different neural attention strategies and similarity of neural to human attention does not guarantee best performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge