Frauke Kreuter
Moral Lenses, Political Coordinates: Towards Ideological Positioning of Morally Conditioned LLMs
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:While recent research has systematically documented political orientation in large language models (LLMs), existing evaluations rely primarily on direct probing or demographic persona engineering to surface ideological biases. In social psychology, however, political ideology is also understood as a downstream consequence of fundamental moral intuitions. In this work, we investigate the causal relationship between moral values and political positioning by treating moral orientation as a controllable condition. Rather than simply assigning a demographic persona, we condition models to endorse or reject specific moral values and evaluate the resulting shifts on their political orientations, using the Political Compass Test. By treating moral values as lenses, we observe how moral conditioning actively steers model trajectories across economic and social dimensions. Our findings show that such conditioning induces pronounced, value-specific shifts in models' political coordinates. We further notice that these effects are systematically modulated by role framing and model scale, and are robust across alternative assessment instruments instantiating the same moral value. This highlights that effective alignment requires anchoring political assessments within the context of broader social values including morality, paving the way for more socially grounded alignment techniques.
Bias Begins with Data: The FairGround Corpus for Robust and Reproducible Research on Algorithmic Fairness
Oct 25, 2025Abstract:As machine learning (ML) systems are increasingly adopted in high-stakes decision-making domains, ensuring fairness in their outputs has become a central challenge. At the core of fair ML research are the datasets used to investigate bias and develop mitigation strategies. Yet, much of the existing work relies on a narrow selection of datasets--often arbitrarily chosen, inconsistently processed, and lacking in diversity--undermining the generalizability and reproducibility of results. To address these limitations, we present FairGround: a unified framework, data corpus, and Python package aimed at advancing reproducible research and critical data studies in fair ML classification. FairGround currently comprises 44 tabular datasets, each annotated with rich fairness-relevant metadata. Our accompanying Python package standardizes dataset loading, preprocessing, transformation, and splitting, streamlining experimental workflows. By providing a diverse and well-documented dataset corpus along with robust tooling, FairGround enables the development of fairer, more reliable, and more reproducible ML models. All resources are publicly available to support open and collaborative research.
Bias in the Loop: How Humans Evaluate AI-Generated Suggestions
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Human-AI collaboration increasingly drives decision-making across industries, from medical diagnosis to content moderation. While AI systems promise efficiency gains by providing automated suggestions for human review, these workflows can trigger cognitive biases that degrade performance. We know little about the psychological factors that determine when these collaborations succeed or fail. We conducted a randomized experiment with 2,784 participants to examine how task design and individual characteristics shape human responses to AI-generated suggestions. Using a controlled annotation task, we manipulated three factors: AI suggestion quality in the first three instances, task burden through required corrections, and performance-based financial incentives. We collected demographics, attitudes toward AI, and behavioral data to assess four performance metrics: accuracy, correction activity, overcorrection, and undercorrection. Two patterns emerged that challenge conventional assumptions about human-AI collaboration. First, requiring corrections for flagged AI errors reduced engagement and increased the tendency to accept incorrect suggestions, demonstrating how cognitive shortcuts influence collaborative outcomes. Second, individual attitudes toward AI emerged as the strongest predictor of performance, surpassing demographic factors. Participants skeptical of AI detected errors more reliably and achieved higher accuracy, while those favorable toward automation exhibited dangerous overreliance on algorithmic suggestions. The findings reveal that successful human-AI collaboration depends not only on algorithmic performance but also on who reviews AI outputs and how review processes are structured. Effective human-AI collaborations require consideration of human psychology: selecting diverse evaluator samples, measuring attitudes, and designing workflows that counteract cognitive biases.
On the Impossibility of Separating Intelligence from Judgment: The Computational Intractability of Filtering for AI Alignment
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:With the increased deployment of large language models (LLMs), one concern is their potential misuse for generating harmful content. Our work studies the alignment challenge, with a focus on filters to prevent the generation of unsafe information. Two natural points of intervention are the filtering of the input prompt before it reaches the model, and filtering the output after generation. Our main results demonstrate computational challenges in filtering both prompts and outputs. First, we show that there exist LLMs for which there are no efficient prompt filters: adversarial prompts that elicit harmful behavior can be easily constructed, which are computationally indistinguishable from benign prompts for any efficient filter. Our second main result identifies a natural setting in which output filtering is computationally intractable. All of our separation results are under cryptographic hardness assumptions. In addition to these core findings, we also formalize and study relaxed mitigation approaches, demonstrating further computational barriers. We conclude that safety cannot be achieved by designing filters external to the LLM internals (architecture and weights); in particular, black-box access to the LLM will not suffice. Based on our technical results, we argue that an aligned AI system's intelligence cannot be separated from its judgment.
Human Preferences in Large Language Model Latent Space: A Technical Analysis on the Reliability of Synthetic Data in Voting Outcome Prediction
Feb 22, 2025
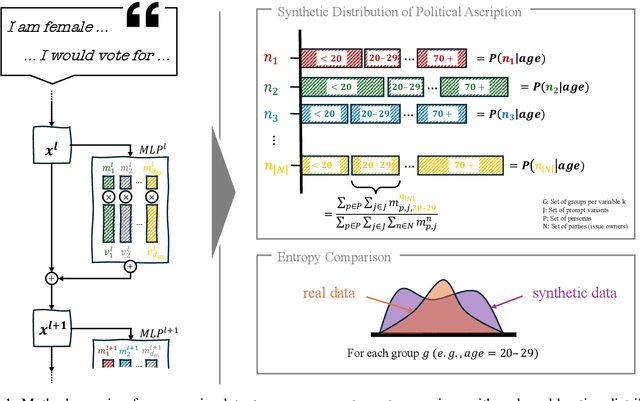
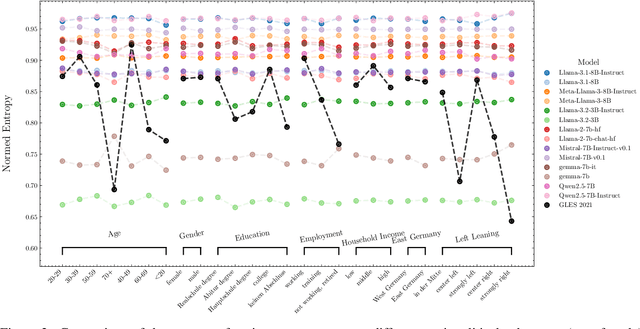
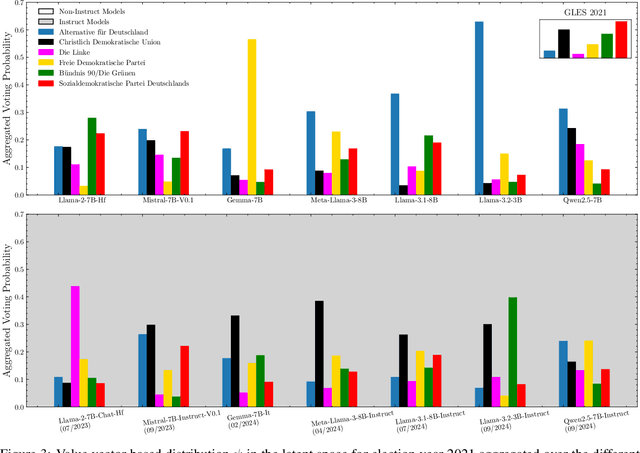
Abstract:Generative AI (GenAI) is increasingly used in survey contexts to simulate human preferences. While many research endeavors evaluate the quality of synthetic GenAI data by comparing model-generated responses to gold-standard survey results, fundamental questions about the validity and reliability of using LLMs as substitutes for human respondents remain. Our study provides a technical analysis of how demographic attributes and prompt variations influence latent opinion mappings in large language models (LLMs) and evaluates their suitability for survey-based predictions. Using 14 different models, we find that LLM-generated data fails to replicate the variance observed in real-world human responses, particularly across demographic subgroups. In the political space, persona-to-party mappings exhibit limited differentiation, resulting in synthetic data that lacks the nuanced distribution of opinions found in survey data. Moreover, we show that prompt sensitivity can significantly alter outputs for some models, further undermining the stability and predictiveness of LLM-based simulations. As a key contribution, we adapt a probe-based methodology that reveals how LLMs encode political affiliations in their latent space, exposing the systematic distortions introduced by these models. Our findings highlight critical limitations in AI-generated survey data, urging caution in its use for public opinion research, social science experimentation, and computational behavioral modeling.
Pragmatics in the Era of Large Language Models: A Survey on Datasets, Evaluation, Opportunities and Challenges
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Understanding pragmatics-the use of language in context-is crucial for developing NLP systems capable of interpreting nuanced language use. Despite recent advances in language technologies, including large language models, evaluating their ability to handle pragmatic phenomena such as implicatures and references remains challenging. To advance pragmatic abilities in models, it is essential to understand current evaluation trends and identify existing limitations. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of resources designed for evaluating pragmatic capabilities in NLP, categorizing datasets by the pragmatics phenomena they address. We analyze task designs, data collection methods, evaluation approaches, and their relevance to real-world applications. By examining these resources in the context of modern language models, we highlight emerging trends, challenges, and gaps in existing benchmarks. Our survey aims to clarify the landscape of pragmatic evaluation and guide the development of more comprehensive and targeted benchmarks, ultimately contributing to more nuanced and context-aware NLP models.
Correcting Annotator Bias in Training Data: Population-Aligned Instance Replication (PAIR)
Jan 12, 2025Abstract:Models trained on crowdsourced labels may not reflect broader population views when annotator pools are not representative. Since collecting representative labels is challenging, we propose Population-Aligned Instance Replication (PAIR), a method to address this bias through statistical adjustment. Using a simulation study of hate speech and offensive language detection, we create two types of annotators with different labeling tendencies and generate datasets with varying proportions of the types. Models trained on unbalanced annotator pools show poor calibration compared to those trained on representative data. However, PAIR, which duplicates labels from underrepresented annotator groups to match population proportions, significantly reduces bias without requiring new data collection. These results suggest statistical techniques from survey research can help align model training with target populations even when representative annotator pools are unavailable. We conclude with three practical recommendations for improving training data quality.
Algorithmic Fidelity of Large Language Models in Generating Synthetic German Public Opinions: A Case Study
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:In recent research, large language models (LLMs) have been increasingly used to investigate public opinions. This study investigates the algorithmic fidelity of LLMs, i.e., the ability to replicate the socio-cultural context and nuanced opinions of human participants. Using open-ended survey data from the German Longitudinal Election Studies (GLES), we prompt different LLMs to generate synthetic public opinions reflective of German subpopulations by incorporating demographic features into the persona prompts. Our results show that Llama performs better than other LLMs at representing subpopulations, particularly when there is lower opinion diversity within those groups. Our findings further reveal that the LLM performs better for supporters of left-leaning parties like The Greens and The Left compared to other parties, and matches the least with the right-party AfD. Additionally, the inclusion or exclusion of specific variables in the prompts can significantly impact the models' predictions. These findings underscore the importance of aligning LLMs to more effectively model diverse public opinions while minimizing political biases and enhancing robustness in representativeness.
Problem Solving Through Human-AI Preference-Based Cooperation
Aug 15, 2024


Abstract:While there is a widespread belief that artificial general intelligence (AGI) -- or even superhuman AI -- is imminent, complex problems in expert domains are far from being solved. We argue that such problems require human-AI cooperation and that the current state of the art in generative AI is unable to play the role of a reliable partner due to a multitude of shortcomings, including inability to keep track of a complex solution artifact (e.g., a software program), limited support for versatile human preference expression and lack of adapting to human preference in an interactive setting. To address these challenges, we propose HAI-Co2, a novel human-AI co-construction framework. We formalize HAI-Co2 and discuss the difficult open research problems that it faces. Finally, we present a case study of HAI-Co2 and demonstrate its efficacy compared to monolithic generative AI models.
The Missing Link: Allocation Performance in Causal Machine Learning
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:Automated decision-making (ADM) systems are being deployed across a diverse range of critical problem areas such as social welfare and healthcare. Recent work highlights the importance of causal ML models in ADM systems, but implementing them in complex social environments poses significant challenges. Research on how these challenges impact the performance in specific downstream decision-making tasks is limited. Addressing this gap, we make use of a comprehensive real-world dataset of jobseekers to illustrate how the performance of a single CATE model can vary significantly across different decision-making scenarios and highlight the differential influence of challenges such as distribution shifts on predictions and allocations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge