Stephanie Eckman
Bias in the Loop: How Humans Evaluate AI-Generated Suggestions
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Human-AI collaboration increasingly drives decision-making across industries, from medical diagnosis to content moderation. While AI systems promise efficiency gains by providing automated suggestions for human review, these workflows can trigger cognitive biases that degrade performance. We know little about the psychological factors that determine when these collaborations succeed or fail. We conducted a randomized experiment with 2,784 participants to examine how task design and individual characteristics shape human responses to AI-generated suggestions. Using a controlled annotation task, we manipulated three factors: AI suggestion quality in the first three instances, task burden through required corrections, and performance-based financial incentives. We collected demographics, attitudes toward AI, and behavioral data to assess four performance metrics: accuracy, correction activity, overcorrection, and undercorrection. Two patterns emerged that challenge conventional assumptions about human-AI collaboration. First, requiring corrections for flagged AI errors reduced engagement and increased the tendency to accept incorrect suggestions, demonstrating how cognitive shortcuts influence collaborative outcomes. Second, individual attitudes toward AI emerged as the strongest predictor of performance, surpassing demographic factors. Participants skeptical of AI detected errors more reliably and achieved higher accuracy, while those favorable toward automation exhibited dangerous overreliance on algorithmic suggestions. The findings reveal that successful human-AI collaboration depends not only on algorithmic performance but also on who reviews AI outputs and how review processes are structured. Effective human-AI collaborations require consideration of human psychology: selecting diverse evaluator samples, measuring attitudes, and designing workflows that counteract cognitive biases.
Correcting Annotator Bias in Training Data: Population-Aligned Instance Replication (PAIR)
Jan 12, 2025Abstract:Models trained on crowdsourced labels may not reflect broader population views when annotator pools are not representative. Since collecting representative labels is challenging, we propose Population-Aligned Instance Replication (PAIR), a method to address this bias through statistical adjustment. Using a simulation study of hate speech and offensive language detection, we create two types of annotators with different labeling tendencies and generate datasets with varying proportions of the types. Models trained on unbalanced annotator pools show poor calibration compared to those trained on representative data. However, PAIR, which duplicates labels from underrepresented annotator groups to match population proportions, significantly reduces bias without requiring new data collection. These results suggest statistical techniques from survey research can help align model training with target populations even when representative annotator pools are unavailable. We conclude with three practical recommendations for improving training data quality.
Mitigating Selection Bias with Node Pruning and Auxiliary Options
Sep 27, 2024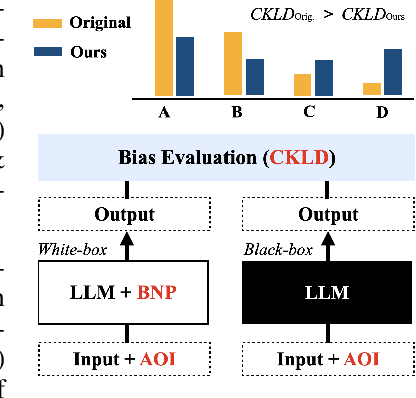
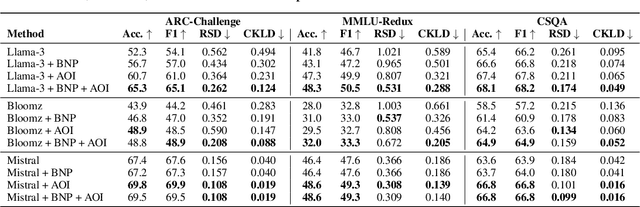
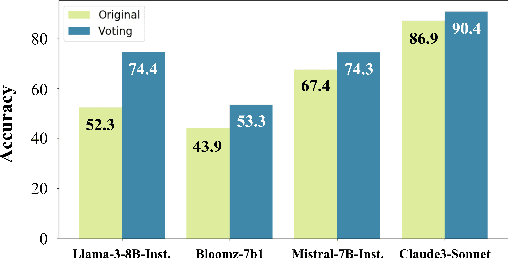
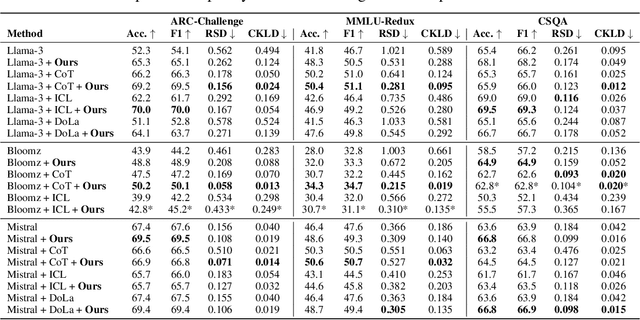
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often show unwarranted preference for certain choice options when responding to multiple-choice questions, posing significant reliability concerns in LLM-automated systems. To mitigate this selection bias problem, previous solutions utilized debiasing methods to adjust the model's input and/or output. Our work, in contrast, investigates the model's internal representation of the selection bias. Specifically, we introduce a novel debiasing approach, Bias Node Pruning (BNP), which eliminates the linear layer parameters that contribute to the bias. Furthermore, we present Auxiliary Option Injection (AOI), a simple yet effective input modification technique for debiasing, which is compatible even with black-box LLMs. To provide a more systematic evaluation of selection bias, we review existing metrics and introduce Choice Kullback-Leibler Divergence (CKLD), which addresses the insensitivity of the commonly used metrics to label imbalance. Experiments show that our methods are robust and adaptable across various datasets when applied to three LLMs.
Annotation Sensitivity: Training Data Collection Methods Affect Model Performance
Nov 23, 2023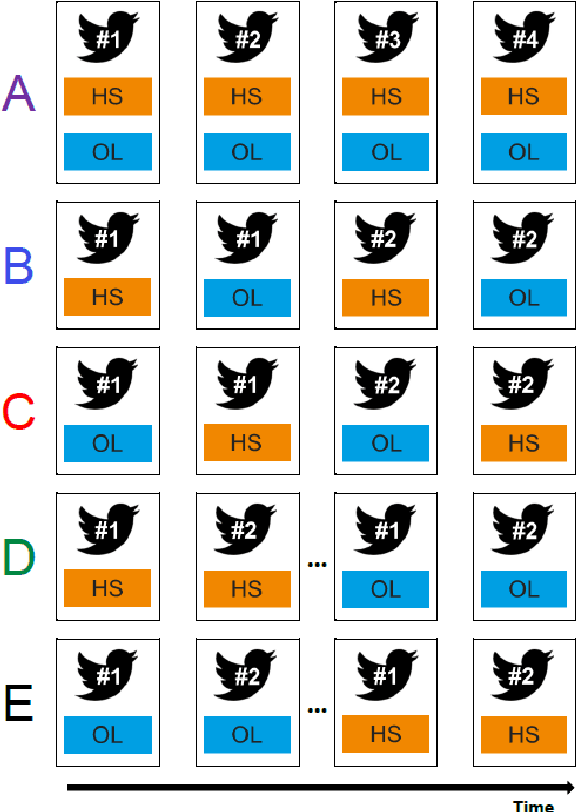
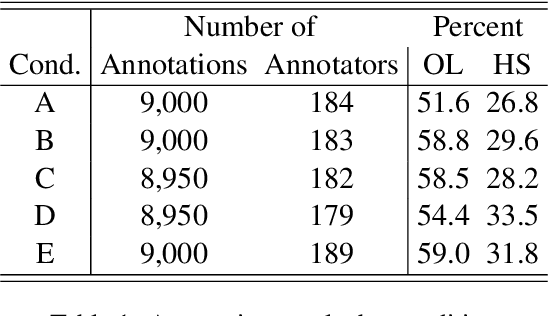
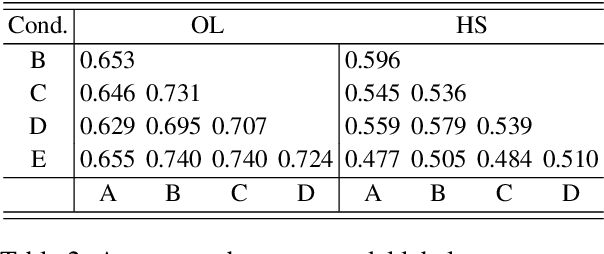
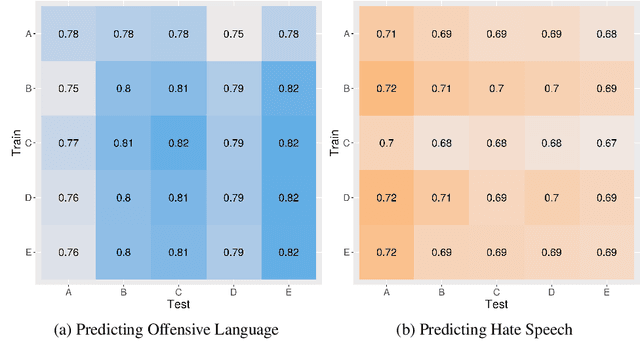
Abstract:When training data are collected from human annotators, the design of the annotation instrument, the instructions given to annotators, the characteristics of the annotators, and their interactions can impact training data. This study demonstrates that design choices made when creating an annotation instrument also impact the models trained on the resulting annotations. We introduce the term annotation sensitivity to refer to the impact of annotation data collection methods on the annotations themselves and on downstream model performance and predictions. We collect annotations of hate speech and offensive language in five experimental conditions of an annotation instrument, randomly assigning annotators to conditions. We then fine-tune BERT models on each of the five resulting datasets and evaluate model performance on a holdout portion of each condition. We find considerable differences between the conditions for 1) the share of hate speech/offensive language annotations, 2) model performance, 3) model predictions, and 4) model learning curves. Our results emphasize the crucial role played by the annotation instrument which has received little attention in the machine learning literature. We call for additional research into how and why the instrument impacts the annotations to inform the development of best practices in instrument design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge