Nina Rimsky
Refusal in Language Models Is Mediated by a Single Direction
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Conversational large language models are fine-tuned for both instruction-following and safety, resulting in models that obey benign requests but refuse harmful ones. While this refusal behavior is widespread across chat models, its underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. In this work, we show that refusal is mediated by a one-dimensional subspace, across 13 popular open-source chat models up to 72B parameters in size. Specifically, for each model, we find a single direction such that erasing this direction from the model's residual stream activations prevents it from refusing harmful instructions, while adding this direction elicits refusal on even harmless instructions. Leveraging this insight, we propose a novel white-box jailbreak method that surgically disables refusal with minimal effect on other capabilities. Finally, we mechanistically analyze how adversarial suffixes suppress propagation of the refusal-mediating direction. Our findings underscore the brittleness of current safety fine-tuning methods. More broadly, our work showcases how an understanding of model internals can be leveraged to develop practical methods for controlling model behavior.
Understanding Jailbreak Success: A Study of Latent Space Dynamics in Large Language Models
Jun 13, 2024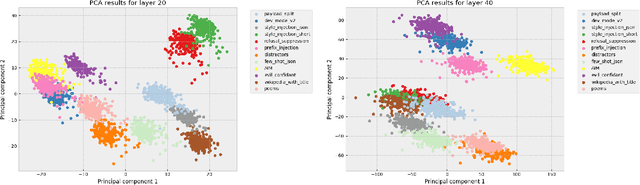
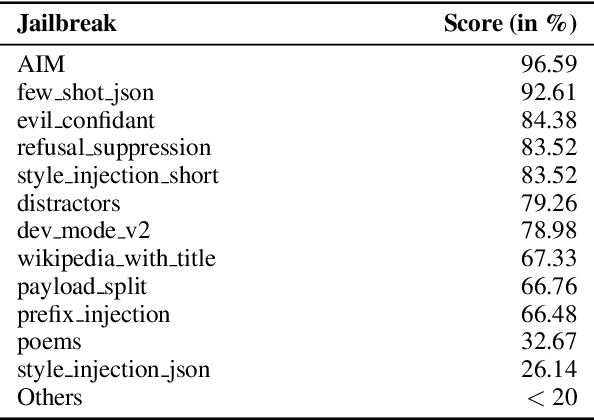
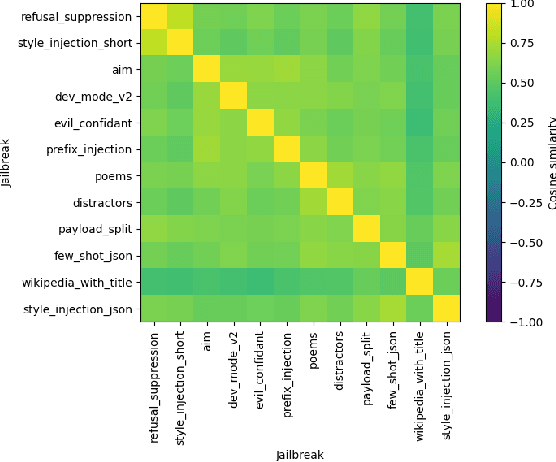
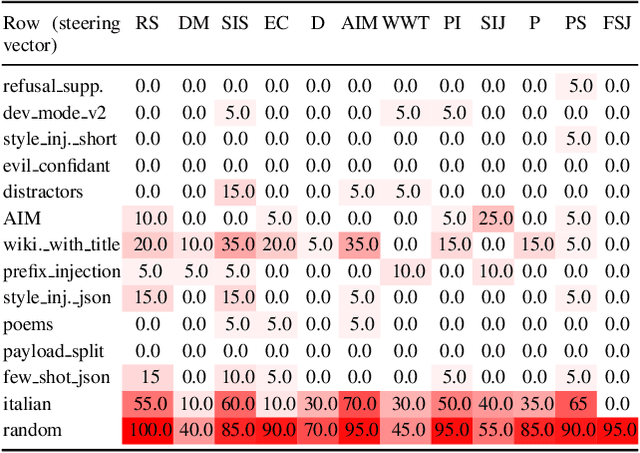
Abstract:Conversational Large Language Models are trained to refuse to answer harmful questions. However, emergent jailbreaking techniques can still elicit unsafe outputs, presenting an ongoing challenge for model alignment. To better understand how different jailbreak types circumvent safeguards, this paper analyses model activations on different jailbreak inputs. We find that it is possible to extract a jailbreak vector from a single class of jailbreaks that works to mitigate jailbreak effectiveness from other classes. This may indicate that different kinds of effective jailbreaks operate via similar internal mechanisms. We investigate a potential common mechanism of harmfulness feature suppression, and provide evidence for its existence by looking at the harmfulness vector component. These findings offer actionable insights for developing more robust jailbreak countermeasures and lay the groundwork for a deeper, mechanistic understanding of jailbreak dynamics in language models.
Investigating Bias Representations in Llama 2 Chat via Activation Steering
Feb 01, 2024Abstract:We address the challenge of societal bias in Large Language Models (LLMs), focusing on the Llama 2 7B Chat model. As LLMs are increasingly integrated into decision-making processes with substantial societal impact, it becomes imperative to ensure these models do not reinforce existing biases. Our approach employs activation steering to probe for and mitigate biases related to gender, race, and religion. This method manipulates model activations to direct responses towards or away from biased outputs, utilizing steering vectors derived from the StereoSet dataset and custom GPT4 generated gender bias prompts. Our findings reveal inherent gender bias in Llama 2 7B Chat, persisting even after Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). We also observe a predictable negative correlation between bias and the model's tendency to refuse responses. Significantly, our study uncovers that RLHF tends to increase the similarity in the model's representation of different forms of societal biases, which raises questions about the model's nuanced understanding of different forms of bias. This work also provides valuable insights into effective red-teaming strategies for LLMs using activation steering, particularly emphasizing the importance of integrating a refusal vector.
Steering Llama 2 via Contrastive Activation Addition
Dec 09, 2023
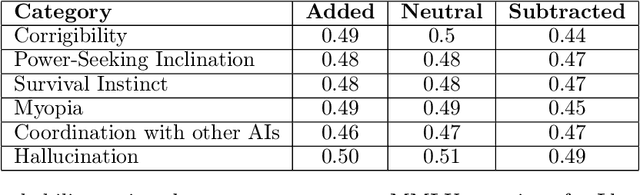

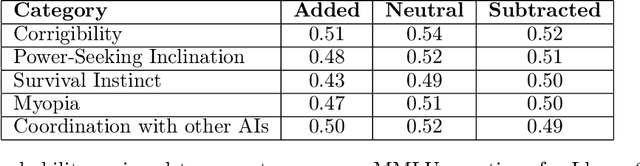
Abstract:We introduce Contrastive Activation Addition (CAA), an innovative method for steering language models by modifying activations during their forward passes. CAA computes ``steering vectors'' by averaging the difference in residual stream activations between pairs of positive and negative examples of a particular behavior such as factual versus hallucinatory responses. During inference, these steering vectors are added at all token positions after the user's prompt with either a positive or negative coefficient, allowing precise control over the degree of the targeted behavior. We evaluate CAA's effectiveness on Llama 2 Chat using both multiple-choice behavioral question datasets and open-ended generation tasks. We demonstrate that CAA significantly alters model behavior, outperforms traditional methods like finetuning and few-shot prompting, and minimally reduces capabilities. Moreover, by employing various activation space interpretation methods, we gain deeper insights into CAA's mechanisms. CAA both accurately steers model outputs and also sheds light on how high-level concepts are represented in Large Language Models (LLMs).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge