Daniel Paleka
Consistency Checks for Language Model Forecasters
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Forecasting is a task that is difficult to evaluate: the ground truth can only be known in the future. Recent work showing LLM forecasters rapidly approaching human-level performance begs the question: how can we benchmark and evaluate these forecasters instantaneously? Following the consistency check framework, we measure the performance of forecasters in terms of the consistency of their predictions on different logically-related questions. We propose a new, general consistency metric based on arbitrage: for example, if a forecasting AI illogically predicts that both the Democratic and Republican parties have 60% probability of winning the 2024 US presidential election, an arbitrageur can trade against the forecaster's predictions and make a profit. We build an automated evaluation system that generates a set of base questions, instantiates consistency checks from these questions, elicits the predictions of the forecaster, and measures the consistency of the predictions. We then build a standard, proper-scoring-rule forecasting benchmark, and show that our (instantaneous) consistency metrics correlate with LLM forecasters' ground truth Brier scores (which are only known in the future). We also release a consistency benchmark that resolves in 2028, providing a long-term evaluation tool for forecasting.
Refusal in Language Models Is Mediated by a Single Direction
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Conversational large language models are fine-tuned for both instruction-following and safety, resulting in models that obey benign requests but refuse harmful ones. While this refusal behavior is widespread across chat models, its underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. In this work, we show that refusal is mediated by a one-dimensional subspace, across 13 popular open-source chat models up to 72B parameters in size. Specifically, for each model, we find a single direction such that erasing this direction from the model's residual stream activations prevents it from refusing harmful instructions, while adding this direction elicits refusal on even harmless instructions. Leveraging this insight, we propose a novel white-box jailbreak method that surgically disables refusal with minimal effect on other capabilities. Finally, we mechanistically analyze how adversarial suffixes suppress propagation of the refusal-mediating direction. Our findings underscore the brittleness of current safety fine-tuning methods. More broadly, our work showcases how an understanding of model internals can be leveraged to develop practical methods for controlling model behavior.
Dataset and Lessons Learned from the 2024 SaTML LLM Capture-the-Flag Competition
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Large language model systems face important security risks from maliciously crafted messages that aim to overwrite the system's original instructions or leak private data. To study this problem, we organized a capture-the-flag competition at IEEE SaTML 2024, where the flag is a secret string in the LLM system prompt. The competition was organized in two phases. In the first phase, teams developed defenses to prevent the model from leaking the secret. During the second phase, teams were challenged to extract the secrets hidden for defenses proposed by the other teams. This report summarizes the main insights from the competition. Notably, we found that all defenses were bypassed at least once, highlighting the difficulty of designing a successful defense and the necessity for additional research to protect LLM systems. To foster future research in this direction, we compiled a dataset with over 137k multi-turn attack chats and open-sourced the platform.
Foundational Challenges in Assuring Alignment and Safety of Large Language Models
Apr 15, 2024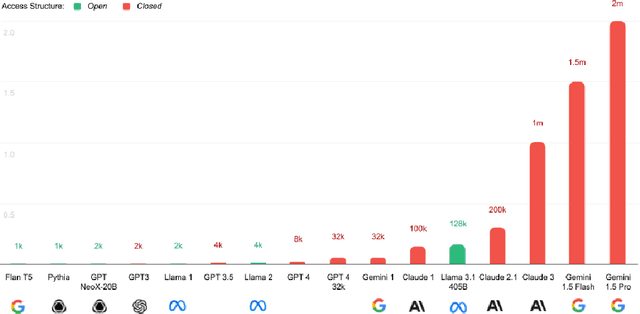


Abstract:This work identifies 18 foundational challenges in assuring the alignment and safety of large language models (LLMs). These challenges are organized into three different categories: scientific understanding of LLMs, development and deployment methods, and sociotechnical challenges. Based on the identified challenges, we pose $200+$ concrete research questions.
ARB: Advanced Reasoning Benchmark for Large Language Models
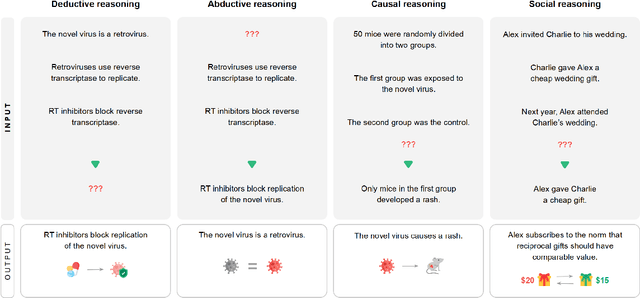
Jul 28, 2023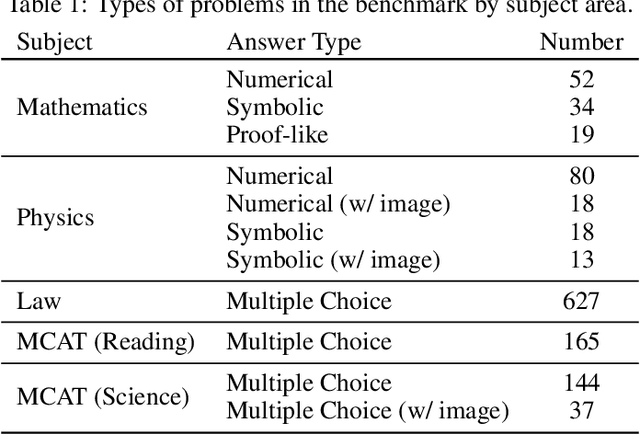
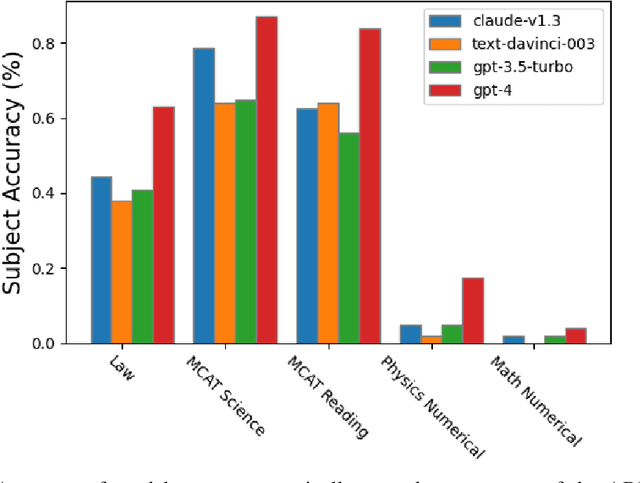

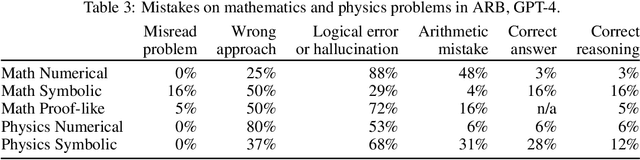
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on various quantitative reasoning and knowledge benchmarks. However, many of these benchmarks are losing utility as LLMs get increasingly high scores, despite not yet reaching expert performance in these domains. We introduce ARB, a novel benchmark composed of advanced reasoning problems in multiple fields. ARB presents a more challenging test than prior benchmarks, featuring problems in mathematics, physics, biology, chemistry, and law. As a subset of ARB, we introduce a challenging set of math and physics problems which require advanced symbolic reasoning and domain knowledge. We evaluate recent models such as GPT-4 and Claude on ARB and demonstrate that current models score well below 50% on more demanding tasks. In order to improve both automatic and assisted evaluation capabilities, we introduce a rubric-based evaluation approach, allowing GPT-4 to score its own intermediate reasoning steps. Further, we conduct a human evaluation of the symbolic subset of ARB, finding promising agreement between annotators and GPT-4 rubric evaluation scores.
Evaluating Superhuman Models with Consistency Checks
Jun 19, 2023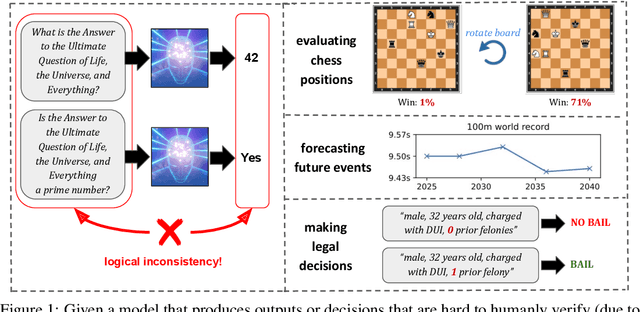
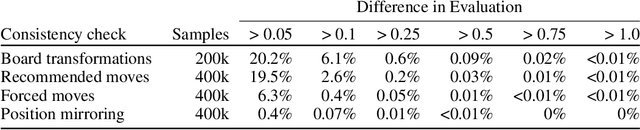
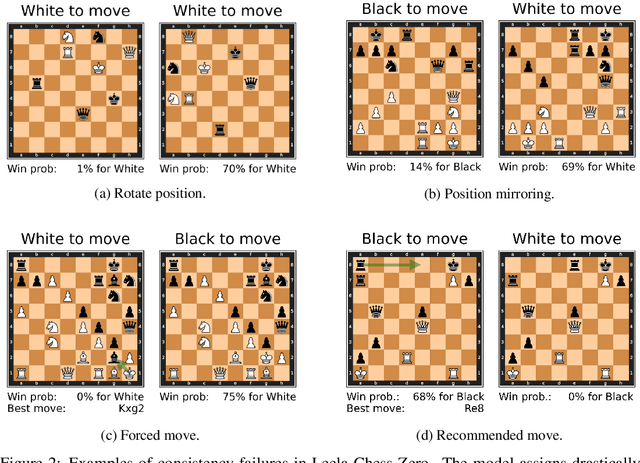
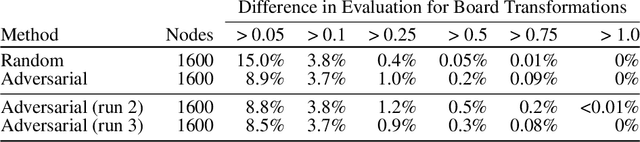
Abstract:If machine learning models were to achieve superhuman abilities at various reasoning or decision-making tasks, how would we go about evaluating such models, given that humans would necessarily be poor proxies for ground truth? In this paper, we propose a framework for evaluating superhuman models via consistency checks. Our premise is that while the correctness of superhuman decisions may be impossible to evaluate, we can still surface mistakes if the model's decisions fail to satisfy certain logical, human-interpretable rules. We instantiate our framework on three tasks where correctness of decisions is hard to evaluate due to either superhuman model abilities, or to otherwise missing ground truth: evaluating chess positions, forecasting future events, and making legal judgments. We show that regardless of a model's (possibly superhuman) performance on these tasks, we can discover logical inconsistencies in decision making. For example: a chess engine assigning opposing valuations to semantically identical boards; GPT-4 forecasting that sports records will evolve non-monotonically over time; or an AI judge assigning bail to a defendant only after we add a felony to their criminal record.
Poisoning Web-Scale Training Datasets is Practical
Feb 20, 2023Abstract:Deep learning models are often trained on distributed, webscale datasets crawled from the internet. In this paper, we introduce two new dataset poisoning attacks that intentionally introduce malicious examples to a model's performance. Our attacks are immediately practical and could, today, poison 10 popular datasets. Our first attack, split-view poisoning, exploits the mutable nature of internet content to ensure a dataset annotator's initial view of the dataset differs from the view downloaded by subsequent clients. By exploiting specific invalid trust assumptions, we show how we could have poisoned 0.01% of the LAION-400M or COYO-700M datasets for just $60 USD. Our second attack, frontrunning poisoning, targets web-scale datasets that periodically snapshot crowd-sourced content -- such as Wikipedia -- where an attacker only needs a time-limited window to inject malicious examples. In light of both attacks, we notify the maintainers of each affected dataset and recommended several low-overhead defenses.
Red-Teaming the Stable Diffusion Safety Filter
Oct 11, 2022



Abstract:Stable Diffusion is a recent open-source image generation model comparable to proprietary models such as DALLE, Imagen, or Parti. Stable Diffusion comes with a safety filter that aims to prevent generating explicit images. Unfortunately, the filter is obfuscated and poorly documented. This makes it hard for users to prevent misuse in their applications, and to understand the filter's limitations and improve it. We first show that it is easy to generate disturbing content that bypasses the safety filter. We then reverse-engineer the filter and find that while it aims to prevent sexual content, it ignores violence, gore, and other similarly disturbing content. Based on our analysis, we argue safety measures in future model releases should strive to be fully open and properly documented to stimulate security contributions from the community.
A law of adversarial risk, interpolation, and label noise
Jul 08, 2022
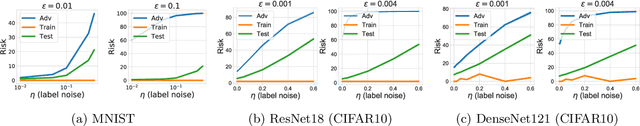
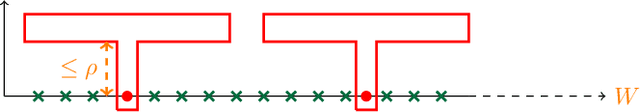
Abstract:In supervised learning, it has been shown that label noise in the data can be interpolated without penalties on test accuracy under many circumstances. We show that interpolating label noise induces adversarial vulnerability, and prove the first theorem showing the dependence of label noise and adversarial risk in terms of the data distribution. Our results are almost sharp without accounting for the inductive bias of the learning algorithm. We also show that inductive bias makes the effect of label noise much stronger.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge