Niklas Kühl
University of Bayreuth, Germany, IBM Consulting, Germany
PromptPilot: Improving Human-AI Collaboration Through LLM-Enhanced Prompt Engineering
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Effective prompt engineering is critical to realizing the promised productivity gains of large language models (LLMs) in knowledge-intensive tasks. Yet, many users struggle to craft prompts that yield high-quality outputs, limiting the practical benefits of LLMs. Existing approaches, such as prompt handbooks or automated optimization pipelines, either require substantial effort, expert knowledge, or lack interactive guidance. To address this gap, we design and evaluate PromptPilot, an interactive prompting assistant grounded in four empirically derived design objectives for LLM-enhanced prompt engineering. We conducted a randomized controlled experiment with 80 participants completing three realistic, work-related writing tasks. Participants supported by PromptPilot achieved significantly higher performance (median: 78.3 vs. 61.7; p = .045, d = 0.56), and reported enhanced efficiency, ease-of-use, and autonomy during interaction. These findings empirically validate the effectiveness of our proposed design objectives, establishing LLM-enhanced prompt engineering as a viable technique for improving human-AI collaboration.
Data Quality Challenges in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Organizations increasingly adopt Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to enhance Large Language Models with enterprise-specific knowledge. However, current data quality (DQ) frameworks have been primarily developed for static datasets, and only inadequately address the dynamic, multi-stage nature of RAG systems. This study aims to develop DQ dimensions for this new type of AI-based systems. We conduct 16 semi-structured interviews with practitioners of leading IT service companies. Through a qualitative content analysis, we inductively derive 15 distinct DQ dimensions across the four processing stages of RAG systems: data extraction, data transformation, prompt & search, and generation. Our findings reveal that (1) new dimensions have to be added to traditional DQ frameworks to also cover RAG contexts; (2) these new dimensions are concentrated in early RAG steps, suggesting the need for front-loaded quality management strategies, and (3) DQ issues transform and propagate through the RAG pipeline, necessitating a dynamic, step-aware approach to quality management.
Honey, I Shrunk the Language Model: Impact of Knowledge Distillation Methods on Performance and Explainability
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) has increasingly influenced modern society, recently in particular through significant advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs). However, high computational and storage demands of LLMs still limit their deployment in resource-constrained environments. Knowledge distillation addresses this challenge by training a small student model from a larger teacher model. Previous research has introduced several distillation methods for both generating training data and for training the student model. Despite their relevance, the effects of state-of-the-art distillation methods on model performance and explainability have not been thoroughly investigated and compared. In this work, we enlarge the set of available methods by applying critique-revision prompting to distillation for data generation and by synthesizing existing methods for training. For these methods, we provide a systematic comparison based on the widely used Commonsense Question-Answering (CQA) dataset. While we measure performance via student model accuracy, we employ a human-grounded study to evaluate explainability. We contribute new distillation methods and their comparison in terms of both performance and explainability. This should further advance the distillation of small language models and, thus, contribute to broader applicability and faster diffusion of LLM technology.
Beware of "Explanations" of AI
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Understanding the decisions made and actions taken by increasingly complex AI system remains a key challenge. This has led to an expanding field of research in explainable artificial intelligence (XAI), highlighting the potential of explanations to enhance trust, support adoption, and meet regulatory standards. However, the question of what constitutes a "good" explanation is dependent on the goals, stakeholders, and context. At a high level, psychological insights such as the concept of mental model alignment can offer guidance, but success in practice is challenging due to social and technical factors. As a result of this ill-defined nature of the problem, explanations can be of poor quality (e.g. unfaithful, irrelevant, or incoherent), potentially leading to substantial risks. Instead of fostering trust and safety, poorly designed explanations can actually cause harm, including wrong decisions, privacy violations, manipulation, and even reduced AI adoption. Therefore, we caution stakeholders to beware of explanations of AI: while they can be vital, they are not automatically a remedy for transparency or responsible AI adoption, and their misuse or limitations can exacerbate harm. Attention to these caveats can help guide future research to improve the quality and impact of AI explanations.
Towards Human-Understandable Multi-Dimensional Concept Discovery
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Concept-based eXplainable AI (C-XAI) aims to overcome the limitations of traditional saliency maps by converting pixels into human-understandable concepts that are consistent across an entire dataset. A crucial aspect of C-XAI is completeness, which measures how well a set of concepts explains a model's decisions. Among C-XAI methods, Multi-Dimensional Concept Discovery (MCD) effectively improves completeness by breaking down the CNN latent space into distinct and interpretable concept subspaces. However, MCD's explanations can be difficult for humans to understand, raising concerns about their practical utility. To address this, we propose Human-Understandable Multi-dimensional Concept Discovery (HU-MCD). HU-MCD uses the Segment Anything Model for concept identification and implements a CNN-specific input masking technique to reduce noise introduced by traditional masking methods. These changes to MCD, paired with the completeness relation, enable HU-MCD to enhance concept understandability while maintaining explanation faithfulness. Our experiments, including human subject studies, show that HU-MCD provides more precise and reliable explanations than existing C-XAI methods. The code is available at https://github.com/grobruegge/hu-mcd.
Human Preferences in Large Language Model Latent Space: A Technical Analysis on the Reliability of Synthetic Data in Voting Outcome Prediction
Feb 22, 2025
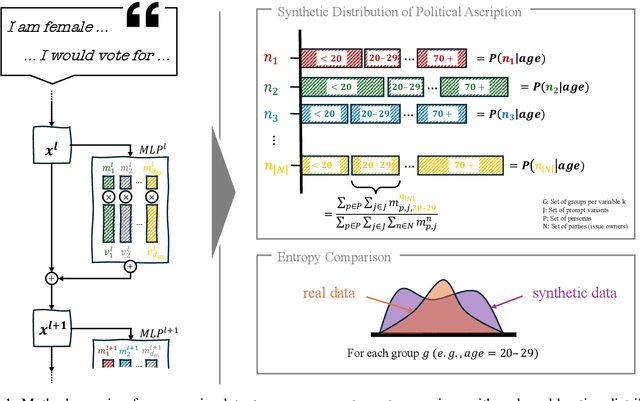
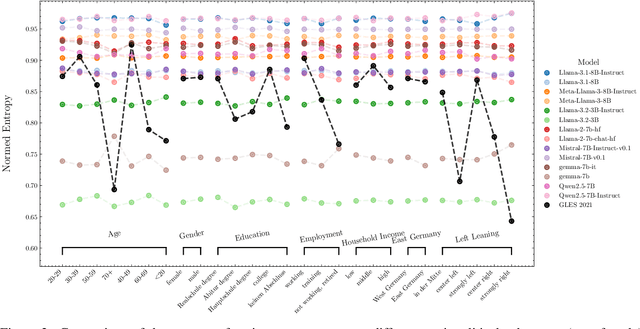
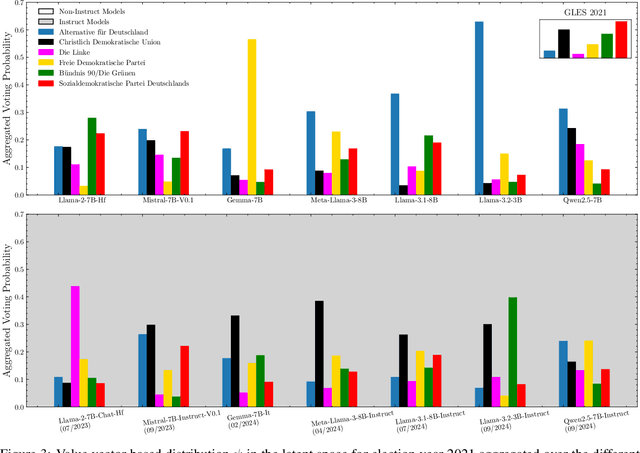
Abstract:Generative AI (GenAI) is increasingly used in survey contexts to simulate human preferences. While many research endeavors evaluate the quality of synthetic GenAI data by comparing model-generated responses to gold-standard survey results, fundamental questions about the validity and reliability of using LLMs as substitutes for human respondents remain. Our study provides a technical analysis of how demographic attributes and prompt variations influence latent opinion mappings in large language models (LLMs) and evaluates their suitability for survey-based predictions. Using 14 different models, we find that LLM-generated data fails to replicate the variance observed in real-world human responses, particularly across demographic subgroups. In the political space, persona-to-party mappings exhibit limited differentiation, resulting in synthetic data that lacks the nuanced distribution of opinions found in survey data. Moreover, we show that prompt sensitivity can significantly alter outputs for some models, further undermining the stability and predictiveness of LLM-based simulations. As a key contribution, we adapt a probe-based methodology that reveals how LLMs encode political affiliations in their latent space, exposing the systematic distortions introduced by these models. Our findings highlight critical limitations in AI-generated survey data, urging caution in its use for public opinion research, social science experimentation, and computational behavioral modeling.
Towards a Problem-Oriented Domain Adaptation Framework for Machine Learning
Jan 08, 2025Abstract:Domain adaptation is a sub-field of machine learning that involves transferring knowledge from a source domain to perform the same task in the target domain. It is a typical challenge in machine learning that arises, e.g., when data is obtained from various sources or when using a data basis that changes over time. Recent advances in the field offer promising methods, but it is still challenging for researchers and practitioners to determine if domain adaptation is suitable for a given problem -- and, subsequently, to select the appropriate approach. This article employs design science research to develop a problem-oriented framework for domain adaptation, which is matured in three evaluation episodes. We describe a framework that distinguishes between five domain adaptation scenarios, provides recommendations for addressing each scenario, and offers guidelines for determining if a problem falls into one of these scenarios. During the multiple evaluation episodes, the framework is tested on artificial and real-world datasets and an experimental study involving 100 participants. The evaluation demonstrates that the framework has the explanatory power to capture any domain adaptation problem effectively. In summary, we provide clear guidance for researchers and practitioners who want to employ domain adaptation but lack in-depth knowledge of the possibilities.
Utilizing Data Fingerprints for Privacy-Preserving Algorithm Selection in Time Series Classification: Performance and Uncertainty Estimation on Unseen Datasets
Sep 13, 2024



Abstract:The selection of algorithms is a crucial step in designing AI services for real-world time series classification use cases. Traditional methods such as neural architecture search, automated machine learning, combined algorithm selection, and hyperparameter optimizations are effective but require considerable computational resources and necessitate access to all data points to run their optimizations. In this work, we introduce a novel data fingerprint that describes any time series classification dataset in a privacy-preserving manner and provides insight into the algorithm selection problem without requiring training on the (unseen) dataset. By decomposing the multi-target regression problem, only our data fingerprints are used to estimate algorithm performance and uncertainty in a scalable and adaptable manner. Our approach is evaluated on the 112 University of California riverside benchmark datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in predicting the performance of 35 state-of-the-art algorithms and providing valuable insights for effective algorithm selection in time series classification service systems, improving a naive baseline by 7.32% on average in estimating the mean performance and 15.81% in estimating the uncertainty.
A Multivocal Literature Review on Privacy and Fairness in Federated Learning
Aug 16, 2024
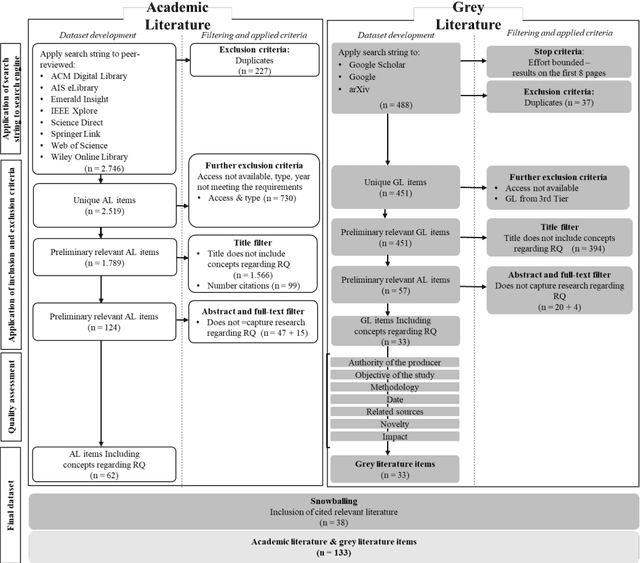
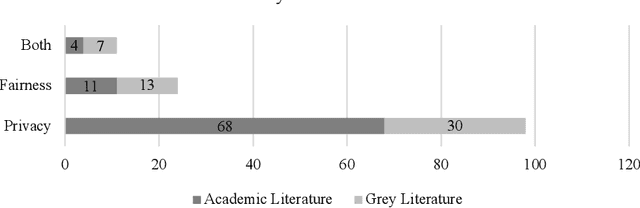
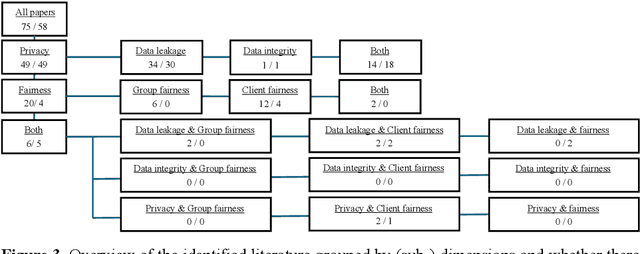
Abstract:Federated Learning presents a way to revolutionize AI applications by eliminating the necessity for data sharing. Yet, research has shown that information can still be extracted during training, making additional privacy-preserving measures such as differential privacy imperative. To implement real-world federated learning applications, fairness, ranging from a fair distribution of performance to non-discriminative behaviour, must be considered. Particularly in high-risk applications (e.g. healthcare), avoiding the repetition of past discriminatory errors is paramount. As recent research has demonstrated an inherent tension between privacy and fairness, we conduct a multivocal literature review to examine the current methods to integrate privacy and fairness in federated learning. Our analyses illustrate that the relationship between privacy and fairness has been neglected, posing a critical risk for real-world applications. We highlight the need to explore the relationship between privacy, fairness, and performance, advocating for the creation of integrated federated learning frameworks.
A Survey of AI Reliance
Jul 22, 2024



Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) systems have become an indispensable component of modern technology. However, research on human behavioral responses is lagging behind, i.e., the research into human reliance on AI advice (AI reliance). Current shortcomings in the literature include the unclear influences on AI reliance, lack of external validity, conflicting approaches to measuring reliance, and disregard for a change in reliance over time. Promising avenues for future research include reliance on generative AI output and reliance in multi-user situations. In conclusion, we present a morphological box that serves as a guide for research on AI reliance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge