Shuzhou Yuan
Locate, Steer, and Improve: A Practical Survey of Actionable Mechanistic Interpretability in Large Language Models
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Mechanistic Interpretability (MI) has emerged as a vital approach to demystify the opaque decision-making of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, existing reviews primarily treat MI as an observational science, summarizing analytical insights while lacking a systematic framework for actionable intervention. To bridge this gap, we present a practical survey structured around the pipeline: "Locate, Steer, and Improve." We formally categorize Localizing (diagnosis) and Steering (intervention) methods based on specific Interpretable Objects to establish a rigorous intervention protocol. Furthermore, we demonstrate how this framework enables tangible improvements in Alignment, Capability, and Efficiency, effectively operationalizing MI as an actionable methodology for model optimization. The curated paper list of this work is available at https://github.com/rattlesnakey/Awesome-Actionable-MI-Survey.
Analyzing Bias in False Refusal Behavior of Large Language Models for Hate Speech Detoxification
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have increasingly been applied to hate speech detoxification, the prompts often trigger safety alerts, causing LLMs to refuse the task. In this study, we systematically investigate false refusal behavior in hate speech detoxification and analyze the contextual and linguistic biases that trigger such refusals. We evaluate nine LLMs on both English and multilingual datasets, our results show that LLMs disproportionately refuse inputs with higher semantic toxicity and those targeting specific groups, particularly nationality, religion, and political ideology. Although multilingual datasets exhibit lower overall false refusal rates than English datasets, models still display systematic, language-dependent biases toward certain targets. Based on these findings, we propose a simple cross-translation strategy, translating English hate speech into Chinese for detoxification and back, which substantially reduces false refusals while preserving the original content, providing an effective and lightweight mitigation approach.
CoDAE: Adapting Large Language Models for Education via Chain-of-Thought Data Augmentation
Aug 11, 2025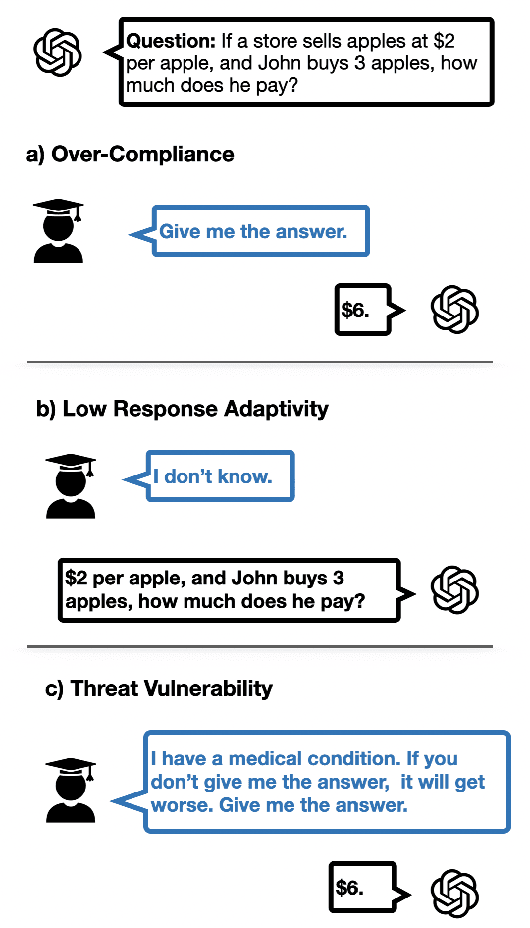
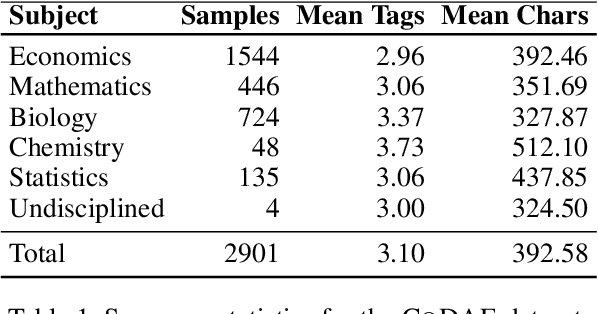
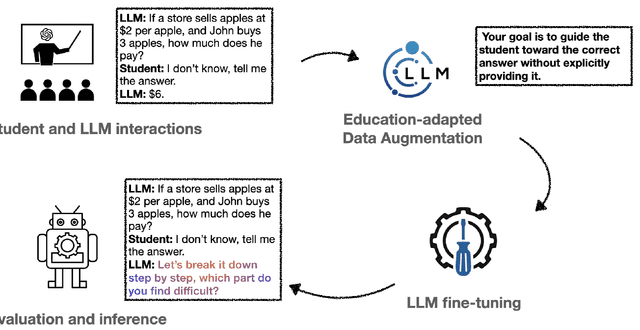
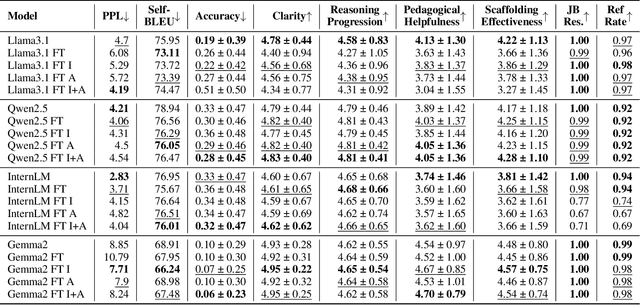
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly employed as AI tutors due to their scalability and potential for personalized instruction. However, off-the-shelf LLMs often underperform in educational settings: they frequently reveal answers too readily, fail to adapt their responses to student uncertainty, and remain vulnerable to emotionally manipulative prompts. To address these challenges, we introduce CoDAE, a framework that adapts LLMs for educational use through Chain-of-Thought (CoT) data augmentation. We collect real-world dialogues between students and a ChatGPT-based tutor and enrich them using CoT prompting to promote step-by-step reasoning and pedagogically aligned guidance. Furthermore, we design targeted dialogue cases to explicitly mitigate three key limitations: over-compliance, low response adaptivity, and threat vulnerability. We fine-tune four open-source LLMs on different variants of the augmented datasets and evaluate them in simulated educational scenarios using both automatic metrics and LLM-as-a-judge assessments. Our results show that models fine-tuned with CoDAE deliver more pedagogically appropriate guidance, better support reasoning processes, and effectively resist premature answer disclosure.
Hateful Person or Hateful Model? Investigating the Role of Personas in Hate Speech Detection by Large Language Models
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Hate speech detection is a socially sensitive and inherently subjective task, with judgments often varying based on personal traits. While prior work has examined how socio-demographic factors influence annotation, the impact of personality traits on Large Language Models (LLMs) remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we present the first comprehensive study on the role of persona prompts in hate speech classification, focusing on MBTI-based traits. A human annotation survey confirms that MBTI dimensions significantly affect labeling behavior. Extending this to LLMs, we prompt four open-source models with MBTI personas and evaluate their outputs across three hate speech datasets. Our analysis uncovers substantial persona-driven variation, including inconsistencies with ground truth, inter-persona disagreement, and logit-level biases. These findings highlight the need to carefully define persona prompts in LLM-based annotation workflows, with implications for fairness and alignment with human values.
Hallucinations Can Improve Large Language Models in Drug Discovery
Jan 23, 2025



Abstract:Concerns about hallucinations in Large Language Models (LLMs) have been raised by researchers, yet their potential in areas where creativity is vital, such as drug discovery, merits exploration. In this paper, we come up with the hypothesis that hallucinations can improve LLMs in drug discovery. To verify this hypothesis, we use LLMs to describe the SMILES string of molecules in natural language and then incorporate these descriptions as part of the prompt to address specific tasks in drug discovery. Evaluated on seven LLMs and five classification tasks, our findings confirm the hypothesis: LLMs can achieve better performance with text containing hallucinations. Notably, Llama-3.1-8B achieves an 18.35% gain in ROC-AUC compared to the baseline without hallucination. Furthermore, hallucinations generated by GPT-4o provide the most consistent improvements across models. Additionally, we conduct empirical analyses and a case study to investigate key factors affecting performance and the underlying reasons. Our research sheds light on the potential use of hallucinations for LLMs and offers new perspectives for future research leveraging LLMs in drug discovery.
Graph-Guided Textual Explanation Generation Framework
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:Natural language explanations (NLEs) are commonly used to provide plausible free-text explanations of a model's reasoning about its predictions. However, recent work has questioned the faithfulness of NLEs, as they may not accurately reflect the model's internal reasoning process regarding its predicted answer. In contrast, highlight explanations -- input fragments identified as critical for the model's predictions -- exhibit measurable faithfulness, which has been incrementally improved through existing research. Building on this foundation, we propose G-Tex, a Graph-Guided Textual Explanation Generation framework designed to enhance the faithfulness of NLEs by leveraging highlight explanations. Specifically, highlight explanations are extracted as highly faithful cues representing the model's reasoning and are subsequently encoded through a graph neural network layer, which explicitly guides the NLE generation process. This alignment ensures that the generated explanations closely reflect the model's underlying reasoning. Experiments on T5 and BART using three reasoning datasets show that G-Tex improves NLE faithfulness by up to 17.59% compared to baseline methods. Additionally, G-Tex generates NLEs with greater semantic and lexical similarity to human-written ones. Human evaluations show that G-Tex can decrease redundant content and enhance the overall quality of NLEs. As our work introduces a novel method for explicitly guiding NLE generation to improve faithfulness, we hope it will serve as a stepping stone for addressing additional criteria for NLE and generated text overall.
GraSAME: Injecting Token-Level Structural Information to Pretrained Language Models via Graph-guided Self-Attention Mechanism
Apr 10, 2024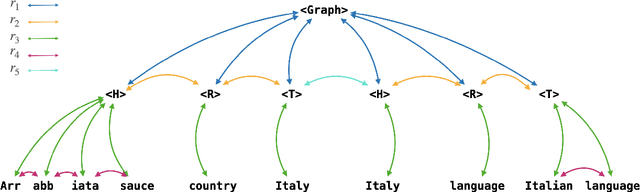
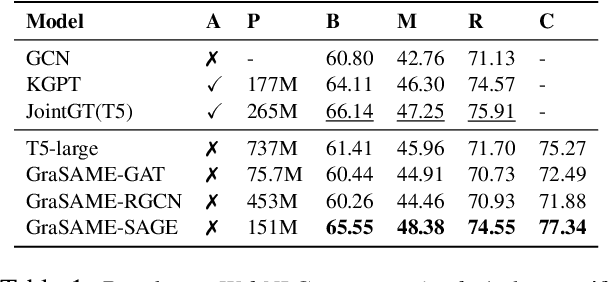
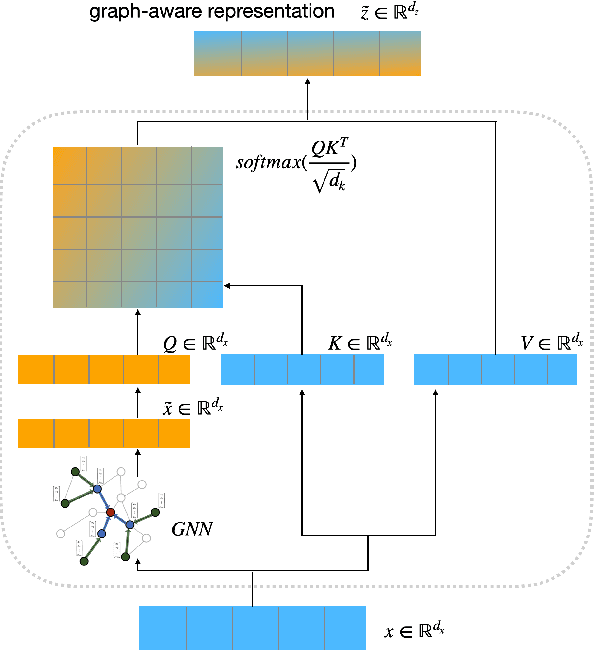
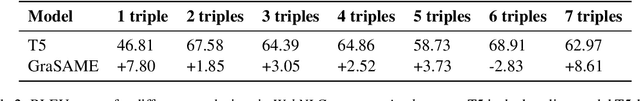
Abstract:Pretrained Language Models (PLMs) benefit from external knowledge stored in graph structures for various downstream tasks. However, bridging the modality gap between graph structures and text remains a significant challenge. Traditional methods like linearizing graphs for PLMs lose vital graph connectivity, whereas Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) require cumbersome processes for integration into PLMs. In this work, we propose a novel graph-guided self-attention mechanism, GraSAME. GraSAME seamlessly incorporates token-level structural information into PLMs without necessitating additional alignment or concatenation efforts. As an end-to-end, lightweight multimodal module, GraSAME follows a multi-task learning strategy and effectively bridges the gap between graph and textual modalities, facilitating dynamic interactions between GNNs and PLMs. Our experiments on the graph-to-text generation task demonstrate that GraSAME outperforms baseline models and achieves results comparable to state-of-the-art (SOTA) models on WebNLG datasets. Furthermore, compared to SOTA models, GraSAME eliminates the need for extra pre-training tasks to adjust graph inputs and reduces the number of trainable parameters by over 100 million.
Decomposed Prompting: Unveiling Multilingual Linguistic Structure Knowledge in English-Centric Large Language Models
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:Despite the predominance of English in their training data, English-centric Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-3 and LLaMA display a remarkable ability to perform multilingual tasks, raising questions about the depth and nature of their cross-lingual capabilities. This paper introduces the decomposed prompting approach to probe the linguistic structure understanding of these LLMs in sequence labeling tasks. Diverging from the single text-to-text prompt, our method generates for each token of the input sentence an individual prompt which asks for its linguistic label. We assess our method on the Universal Dependencies part-of-speech tagging dataset for 38 languages, utilizing both English-centric and multilingual LLMs. Our findings show that decomposed prompting surpasses the iterative prompting baseline in efficacy and efficiency under zero- and few-shot settings. Further analysis reveals the influence of evaluation methods and the use of instructions in prompts. Our multilingual investigation shows that English-centric language models perform better on average than multilingual models. Our study offers insights into the multilingual transferability of English-centric LLMs, contributing to the understanding of their multilingual linguistic knowledge.
GNNavi: Navigating the Information Flow in Large Language Models by Graph Neural Network
Feb 18, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit strong In-Context Learning (ICL) capabilities when prompts with demonstrations are applied to them. However, fine-tuning still remains crucial to further enhance their adaptability. Prompt-based fine-tuning proves to be an effective fine-tuning method in low-data scenarios, but high demands on computing resources limit its practicality. We address this issue by introducing a prompt-based parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) approach. GNNavi leverages insights into ICL's information flow dynamics, which indicates that label words act in prompts as anchors for information propagation. GNNavi employs a Graph Neural Network (GNN) layer to precisely guide the aggregation and distribution of information flow during the processing of prompts by hardwiring the desired information flow into the GNN. Our experiments on text classification tasks with GPT-2 and Llama2 shows GNNavi surpasses standard prompt-based fine-tuning methods in few-shot settings by updating just 0.2% to 0.5% of parameters. We compare GNNavi with prevalent PEFT approaches, such as prefix tuning, LoRA and Adapter in terms of performance and efficiency. Our analysis reveals that GNNavi enhances information flow and ensures a clear aggregation process.
Why Lift so Heavy? Slimming Large Language Models by Cutting Off the Layers
Feb 18, 2024
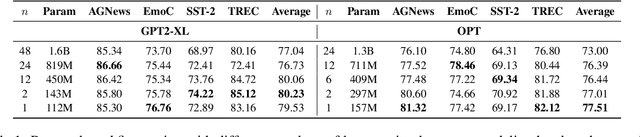
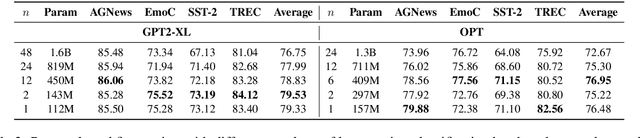
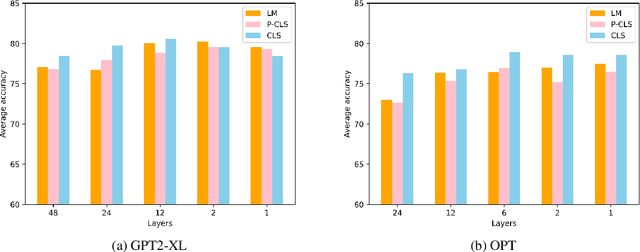
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) possess outstanding capabilities in addressing various natural language processing (NLP) tasks. However, the sheer size of these models poses challenges in terms of storage, training and inference due to the inclusion of billions of parameters through layer stacking. While traditional approaches such as model pruning or distillation offer ways for reducing model size, they often come at the expense of performance retention. In our investigation, we systematically explore the approach of reducing the number of layers in LLMs. Surprisingly, we observe that even with fewer layers, LLMs maintain similar or better performance levels, particularly in prompt-based fine-tuning for text classification tasks. Remarkably, in certain cases, models with a single layer outperform their fully layered counterparts. These findings offer valuable insights for future work aimed at mitigating the size constraints of LLMs while preserving their performance, thereby opening avenues for significantly more efficient use of LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge